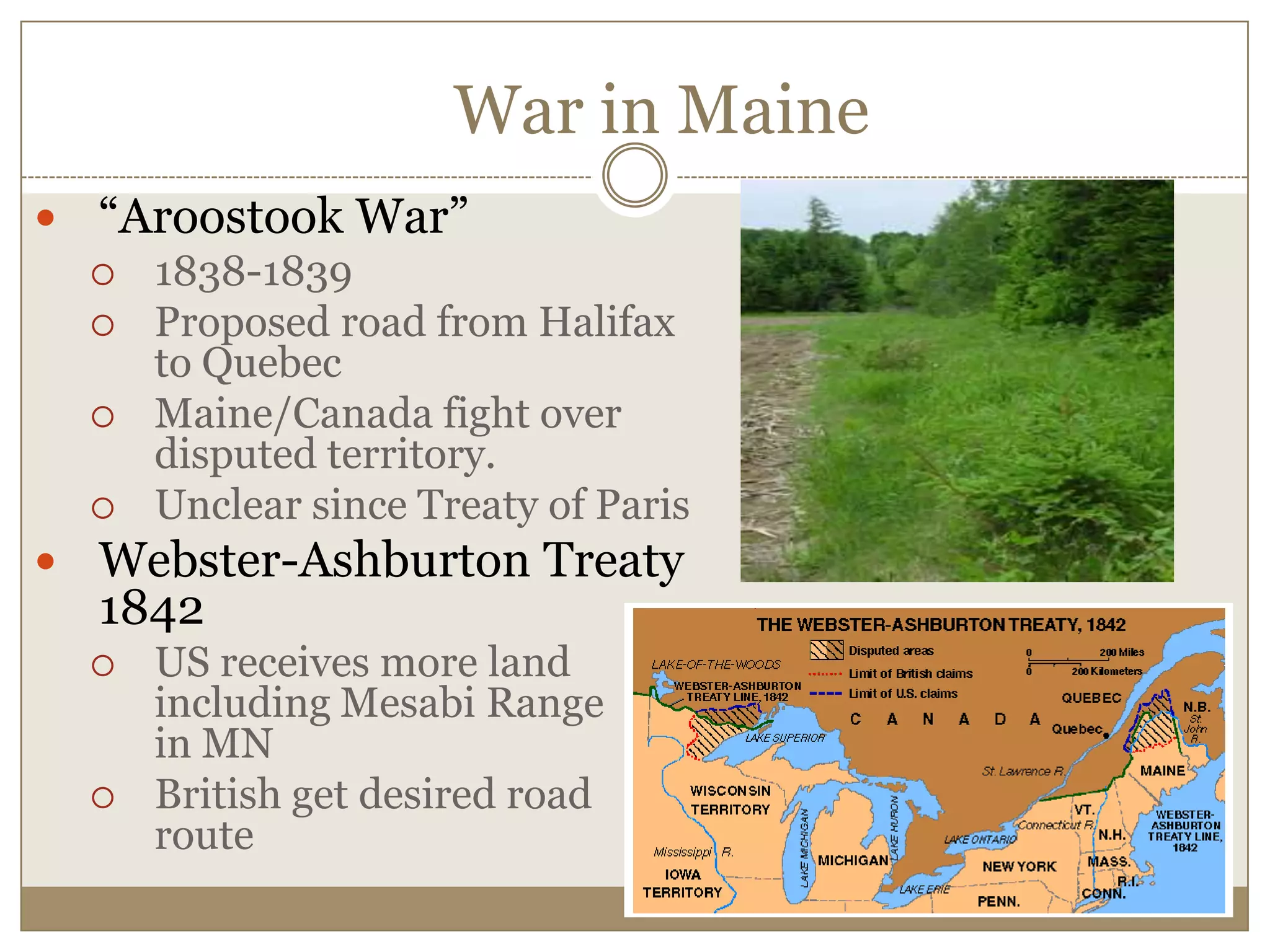
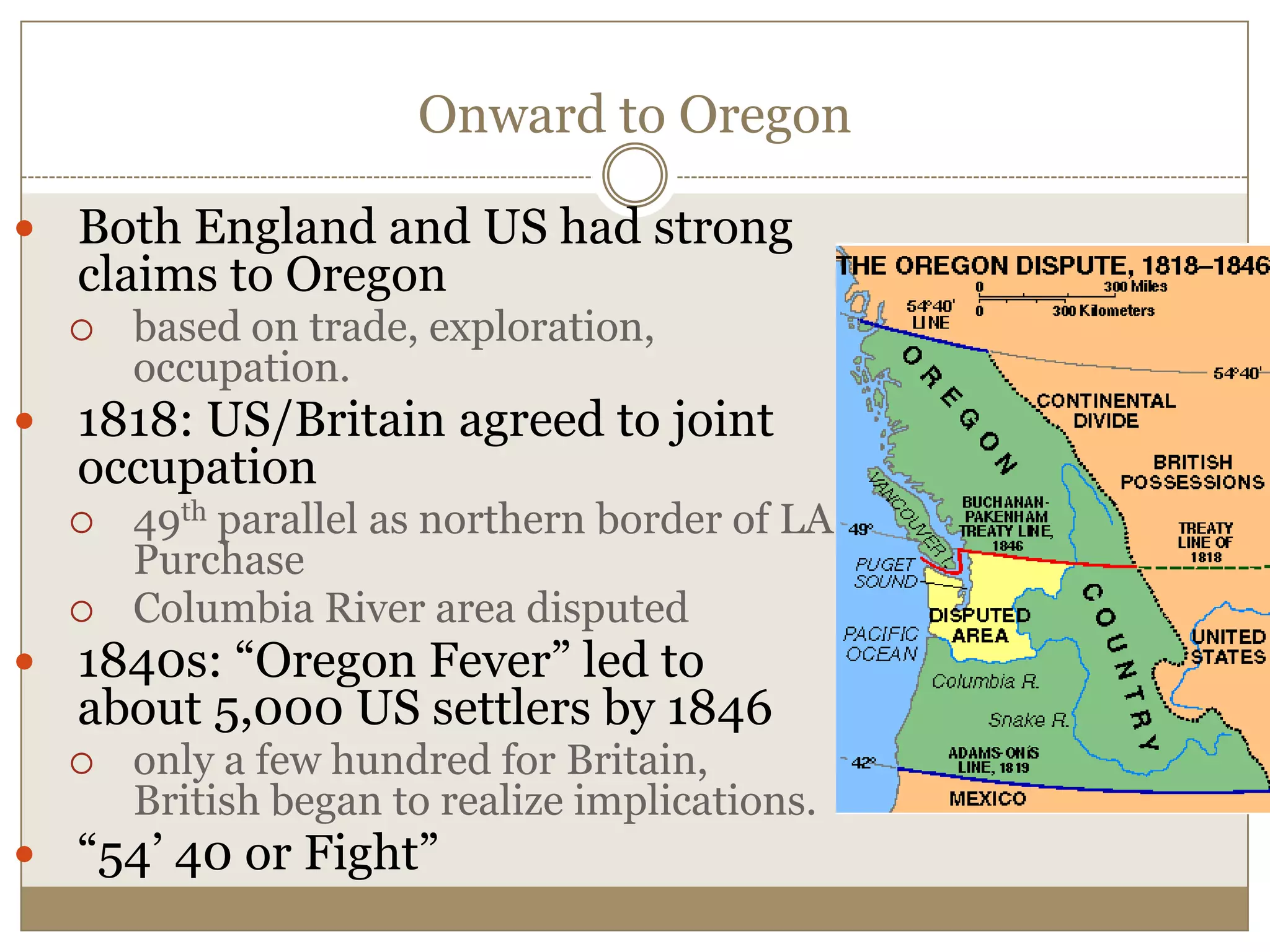
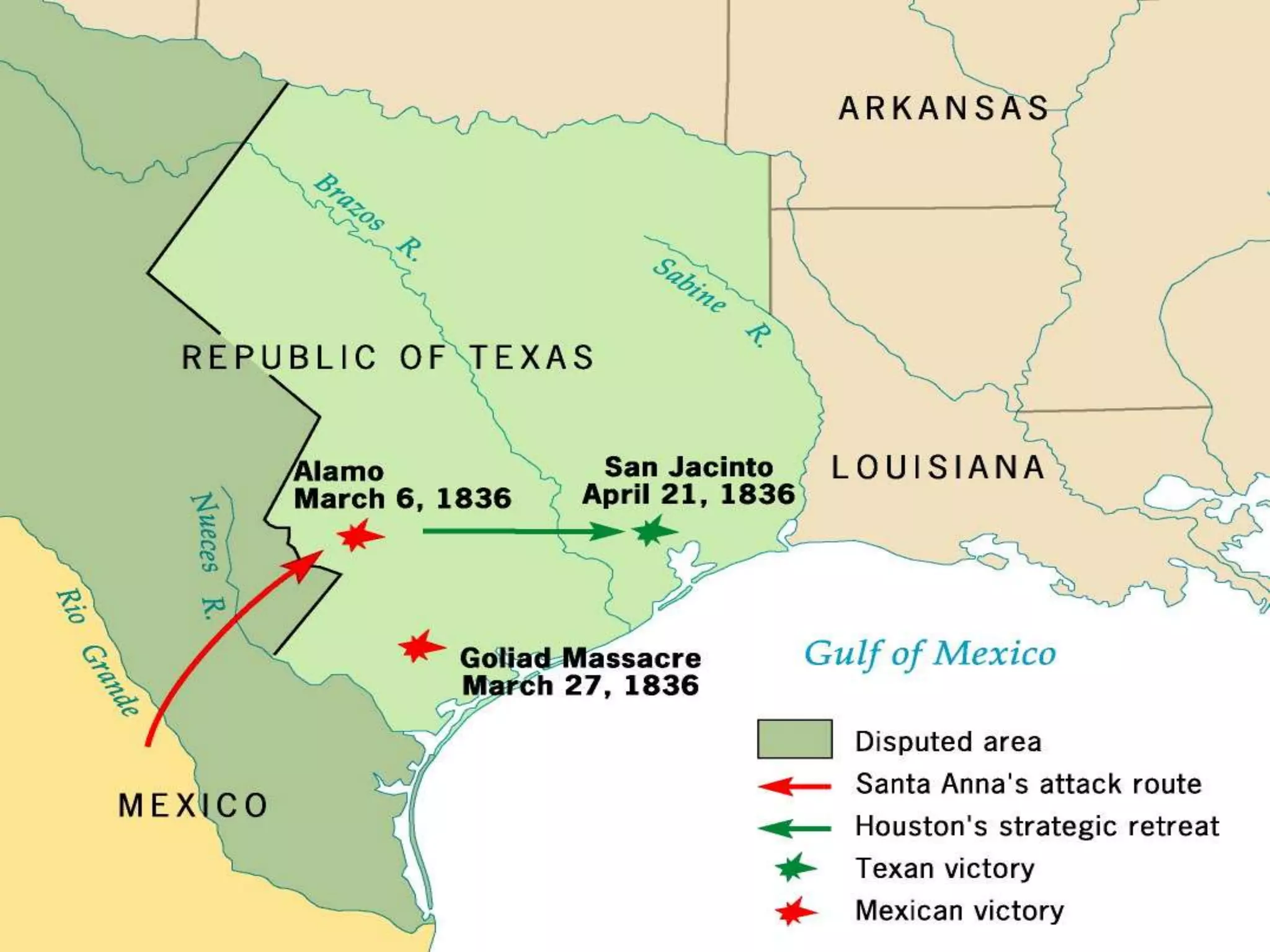
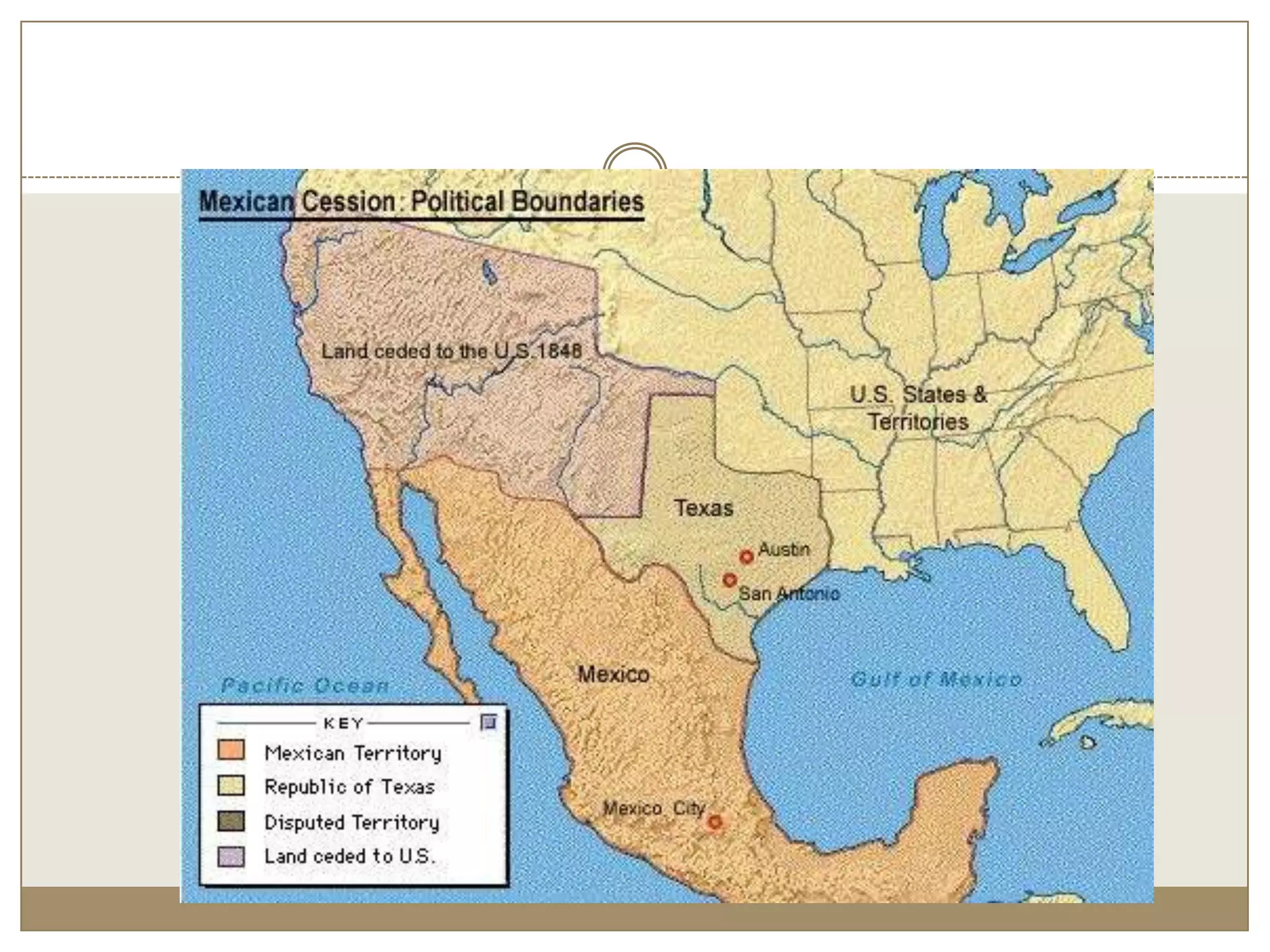
1) The document discusses the expansion of the United States in the 1840s under the ideology of Manifest Destiny, which held that American settlers were destined to expand across North America.
2) It outlines the election of James K. Polk in 1844 and his agenda to annex Texas and acquire Oregon and California from Britain and Mexico.
3) Polk provoked a war with Mexico by moving troops into disputed territory along the Rio Grande river, leading to clashes where American blood was shed on American soil, allowing Polk to ask Congress to declare war to seize California and the Southwest from Mexico.
4) The war was very successful militarily for the US, resulting in the acquisition of over 500,000 square miles