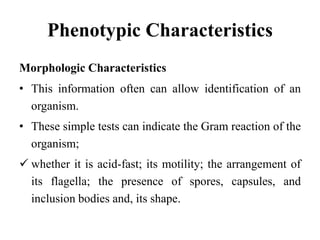
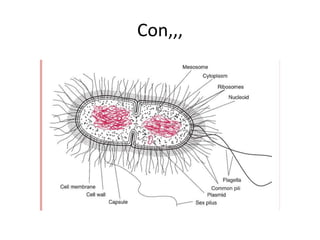
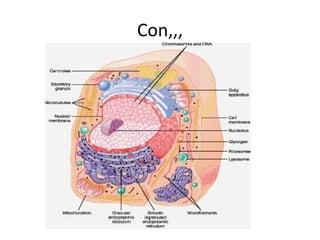
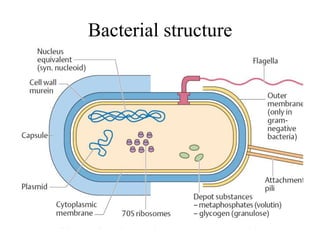
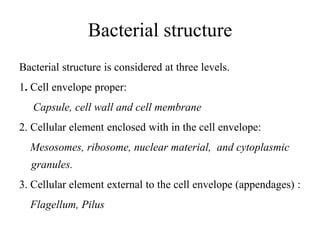
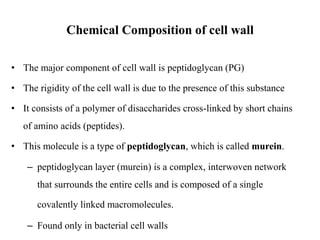
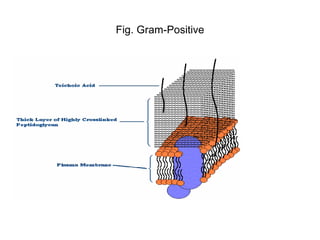
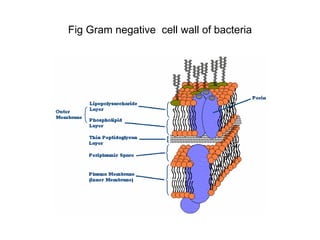
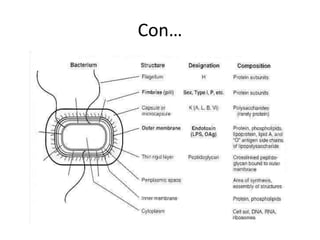
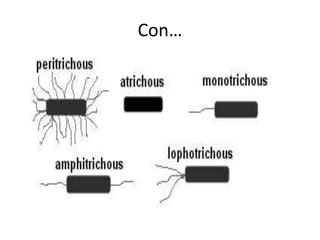
Bacteria are classified based on taxonomy, nomenclature, and observational techniques. Morphology, staining properties, motility, growth characteristics, biochemical activities, and genetics are used to classify and identify bacteria. Bacterial cells have a cell envelope consisting of a capsule, cell wall, and cell membrane. The cell envelope encloses cellular elements like ribosomes, nucleoid, and mesosomes. Some bacteria also have extracellular appendages like flagella and pili.