This document discusses PostgreSQL backups and disaster recovery. It covers the need for different types of backups like logical and physical backups. It discusses how to store backups and automate the backup process. The document also covers how to validate backups are working properly and tools that can be used. It emphasizes that both logical and physical backups are important to have for different recovery scenarios. Automation is recommended to manage the complex backup processes.







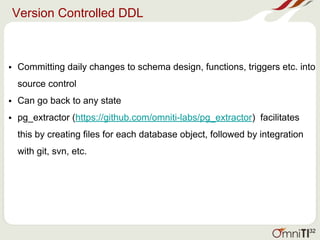
![Logical Backups Contd.
def take_dump():
try:
with open(config_file, 'r') as f:
for db in f:
if db.strip():
db = db.replace("n", "")
dump_command = pg_dump_path + " -U postgres -v -Fc -f " +
dump_file_path + db.split()[-1] + "_" + start_time + ".sql" + " " + db + " 2>>
" + dump_file_path + db.split()[-1] + "_" + start_time + ".log"
os.system(dump_command)
print('backup of ' + db.split()[-1] + ' completed successfully')
except:
print('ERROR: bash command did not execute properly')
8](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/backups-150407140109-conversion-gate01/85/Think_your_Postgres_backups_and_recovery_are_safe_lets_talk-pptx-8-320.jpg)

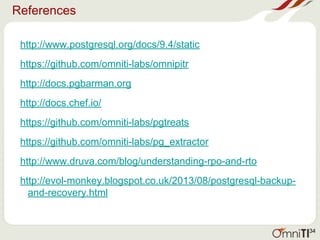
![Physical Backups Contd.
ZFS snapshots:
ZFS restore from snapshot
ZFS rollback to snapshot after failed upgrade or maintenance task
…
read_params "$@"
echo "read params done"
sanity_check
echo "sanity check done"
if [[ -z ${OFFLINE} ]]
then
postgres_start_backup
zfs_snap
postgres_stop_backup
else
zfs_snap
fi
backup
zfs_clear_snaps
rm ${LOCKFILE}
10](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/backups-150407140109-conversion-gate01/85/Think_your_Postgres_backups_and_recovery_are_safe_lets_talk-pptx-10-320.jpg)


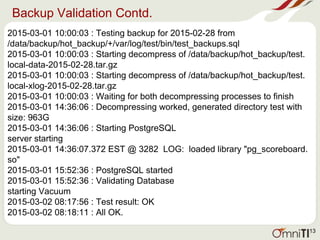







![S3 Backups Contd.
Sample Bucket Policy:
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Id": "S3-Account-Permissions",
"Statement": [
{
"Sid": "1",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Principal": {
"AWS": "arn:aws:iam::928763567489:user/omniti_testing"
},
"Action": "s3:*",
"Resource": [
"arn:aws:s3:::omniti_testing",
"arn:aws:s3:::omniti_testing/*"
]
}
]
}
21](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/backups-150407140109-conversion-gate01/85/Think_your_Postgres_backups_and_recovery_are_safe_lets_talk-pptx-21-320.jpg)
![S3 Backups Contd.
Sample User Policy:
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": "s3:*",
"Resource": [
"arn:aws:s3:::omniti_testing",
"arn:aws:s3:::omniti_testing/*"
]
}
]
}
22](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/backups-150407140109-conversion-gate01/85/Think_your_Postgres_backups_and_recovery_are_safe_lets_talk-pptx-22-320.jpg)
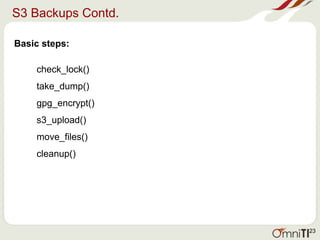
![S3 Backups Contd.
Sample check script placed on local machine:
latest_backup=$(/opt/python26/bin/s3cmd ls s3://omniti_client/ | awk {'print $1'} | sort -n | tail
-1)
today=$(/usr/gnu/bin/date --date=today "+%Y-%m-%d")
yesterday=$(/usr/gnu/bin/date --date=yesterday "+%Y-%m-%d")
if [ $yesterday -ne $latest_backup -a $today -ne $latest_backup ]
then
echo "Offsite Backups Missing for client" | mailx -s "Offsite Backup Missing for Client "
dba@omniti.com
24](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/backups-150407140109-conversion-gate01/85/Think_your_Postgres_backups_and_recovery_are_safe_lets_talk-pptx-24-320.jpg)