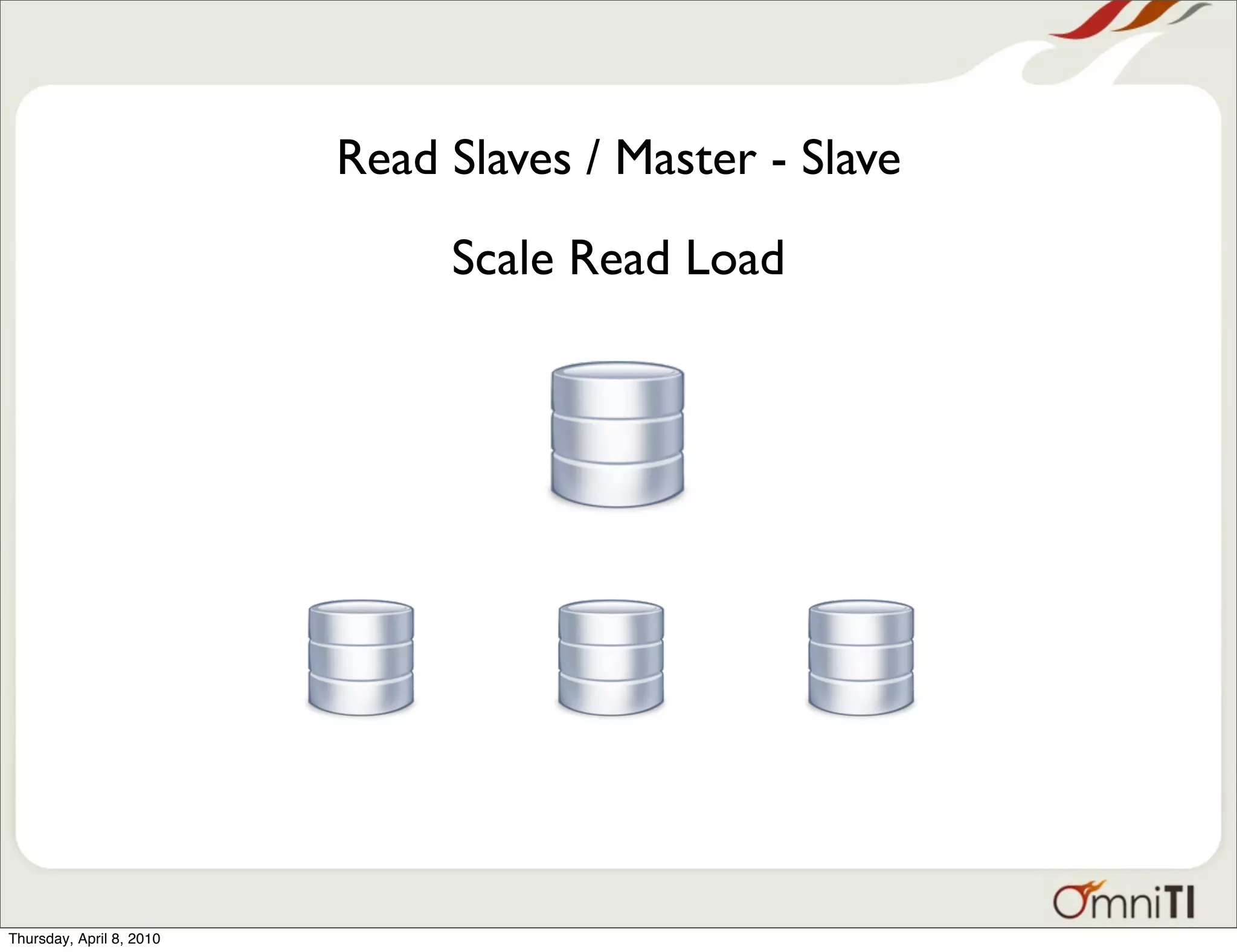
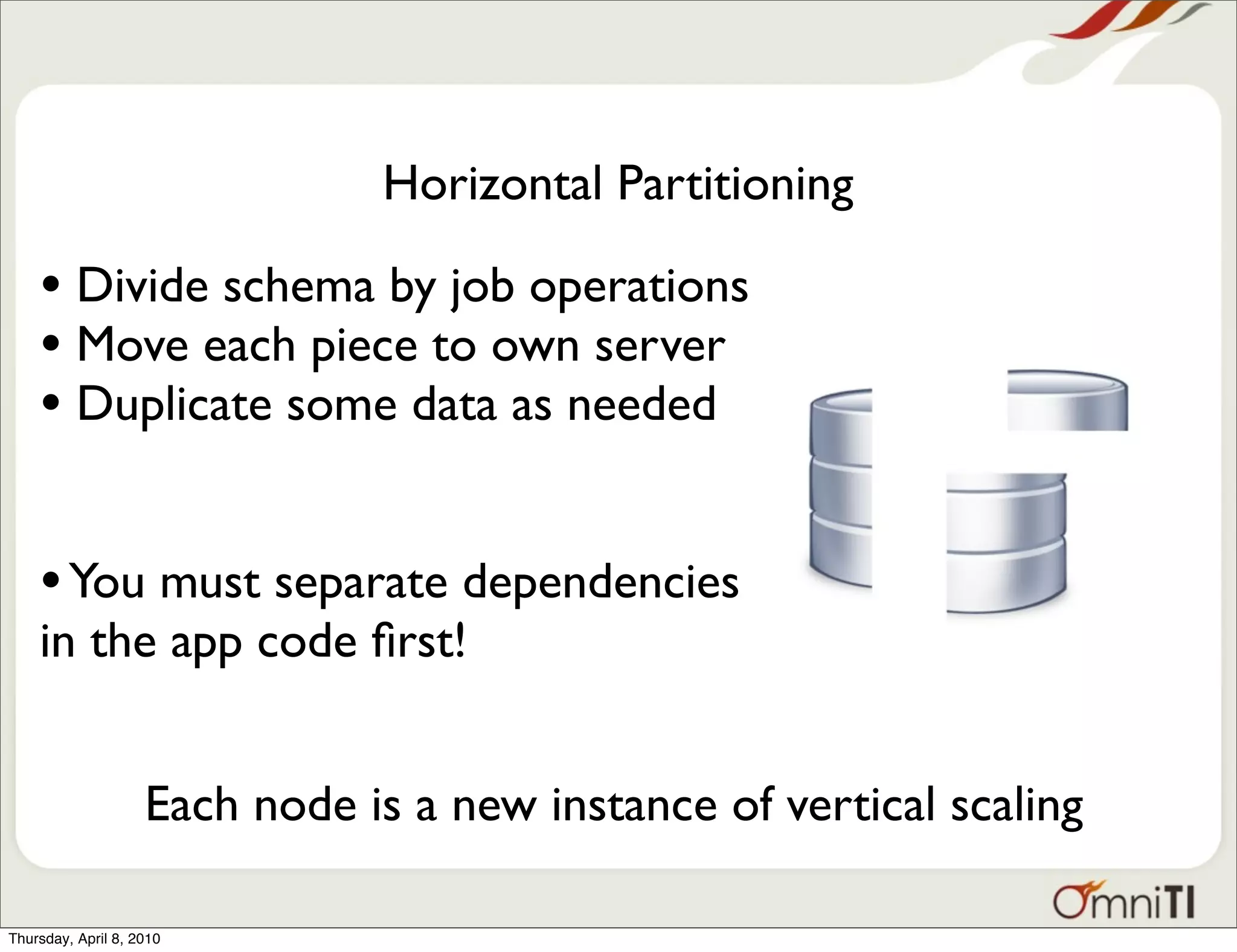
The document discusses various database scalability patterns, including vertical and horizontal scaling, read slaves, and multi-master configurations. It emphasizes the complexities and challenges of scaling, particularly focusing on write operations and the need for application changes. The significance of vertical scalability in both horizontally scaled systems and the costs associated with adding new nodes are also highlighted.