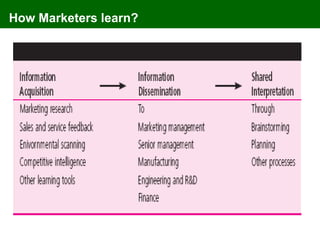
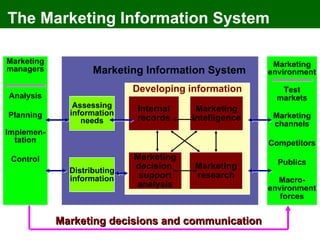
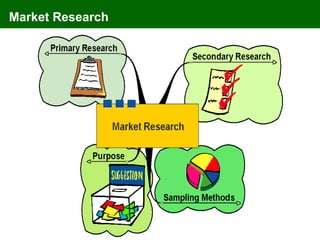
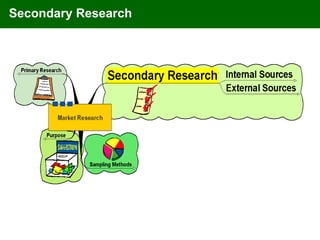
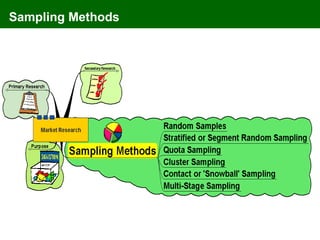
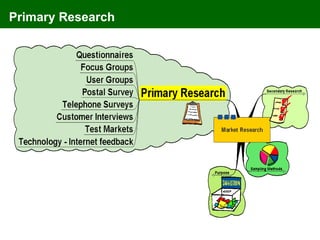
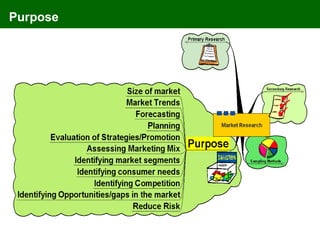
The document discusses marketing information systems and market research. It provides details on marketing intelligence systems, which gather everyday information about market developments. It also describes database marketing, secondary research sources, sampling methods for primary research, and the purposes and advantages/disadvantages of conducting market research.