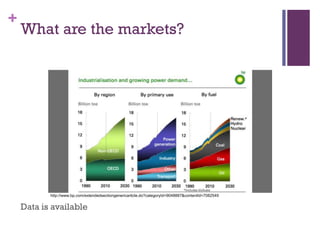
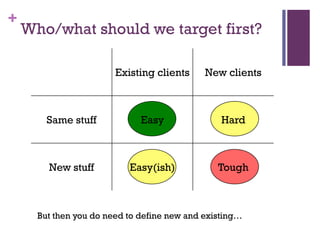
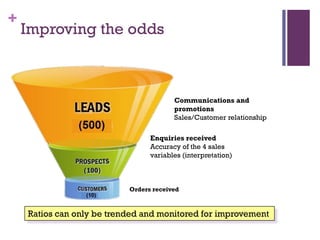
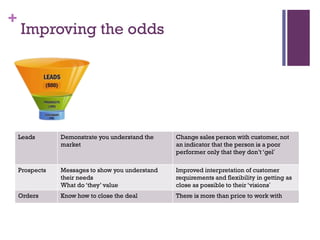
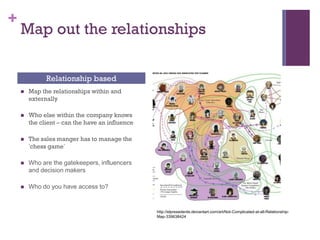
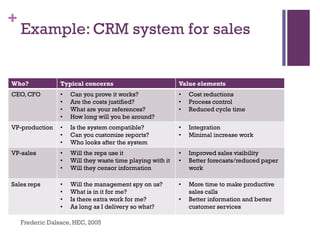
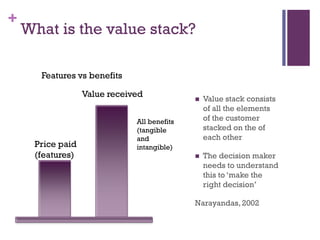
Dr. Shaun West has sold a variety of products and services in the B2B energy sector, including EPC projects, consultancy services, transactional services, and long-term service agreements. Some examples provided are a $16 million EPC project and $800 million long-term service agreement. The document discusses objectives of understanding the B2B energy market, customer needs, and determining what and when products could be sold. It emphasizes that not all customers have the same needs, so a variety of products and services may need to be offered.