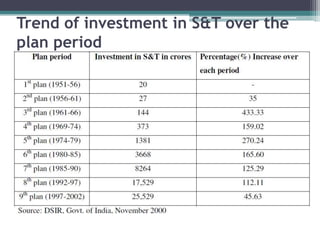
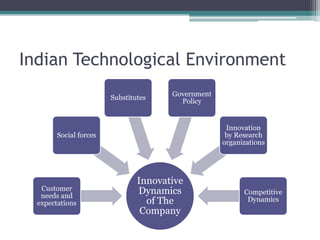
The document summarizes trends in investment and the technological environment in India over successive five-year plans. It notes that early plans focused on agriculture and education, while later plans emphasized industry, infrastructure, and research. It describes how India moved from technical collaborations under license raj to developing more homegrown innovations. Major investments in defense, space, and renewable technologies are shaping India's future technological prospects.