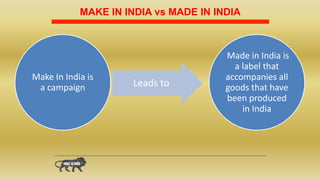
Make in India is a government campaign launched in 2014 to encourage companies to manufacture in India. It aims to create jobs and boost the manufacturing sector in 25 industries. The campaign has led to increased foreign direct investment in India, with India receiving more FDI than China in the first half of 2015. India's competitiveness has also improved, with its global competitiveness ranking increasing 16 places. However, the majority of India's workforce is employed in the large unorganized sector, which faces issues like a lack of technology, skills development, and infrastructure that Make in India would need to address to maximize its benefits.