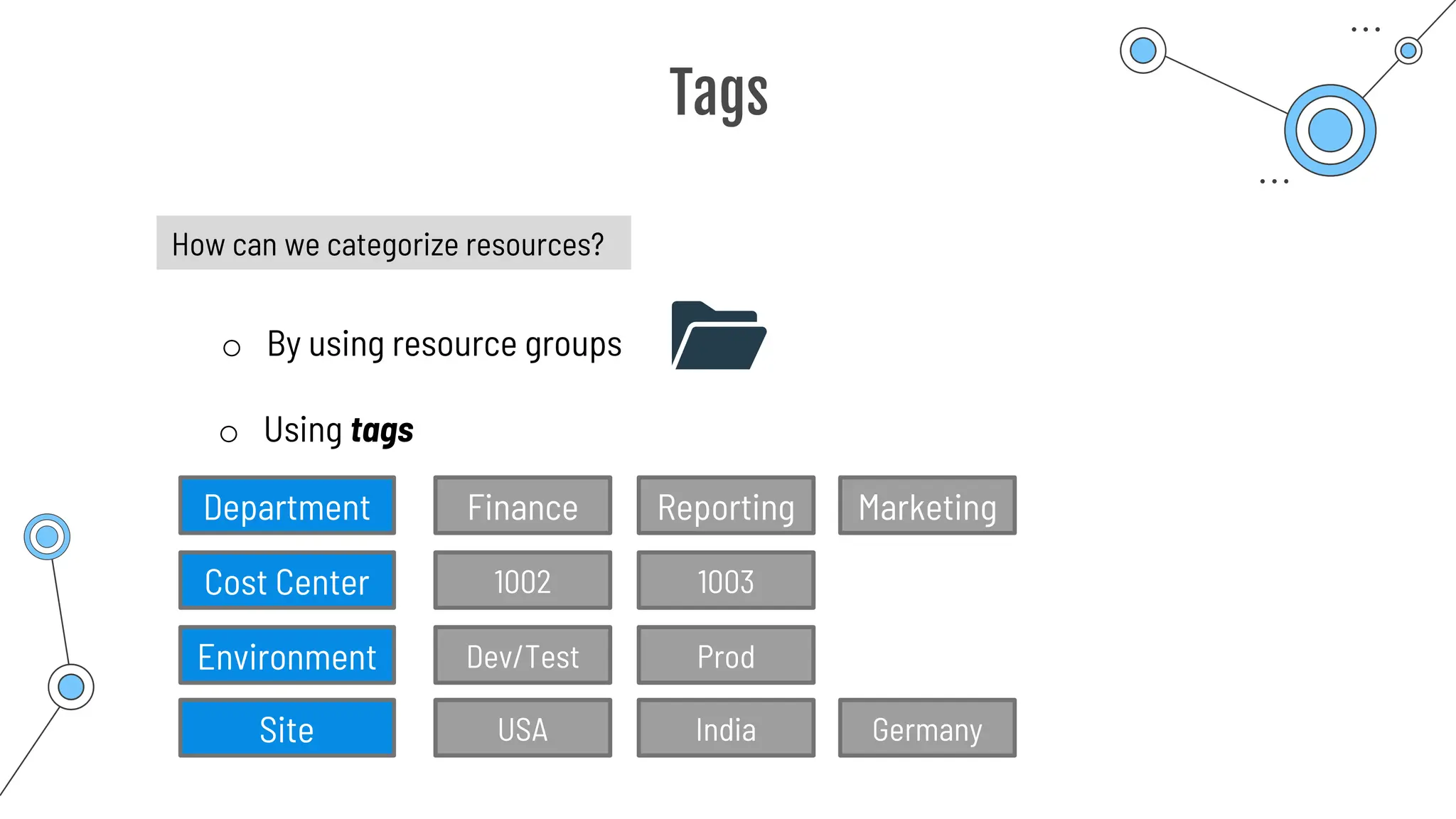
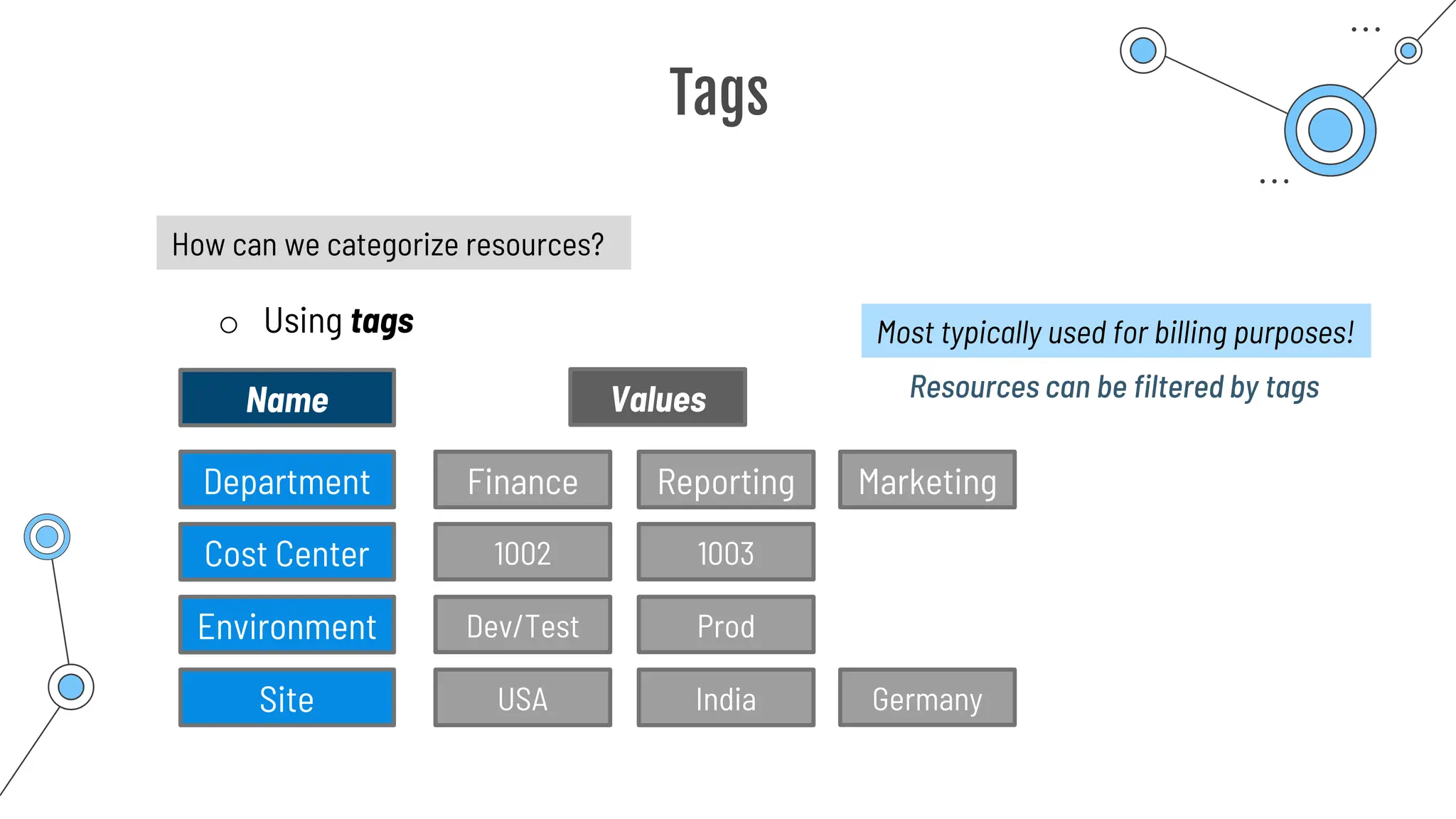
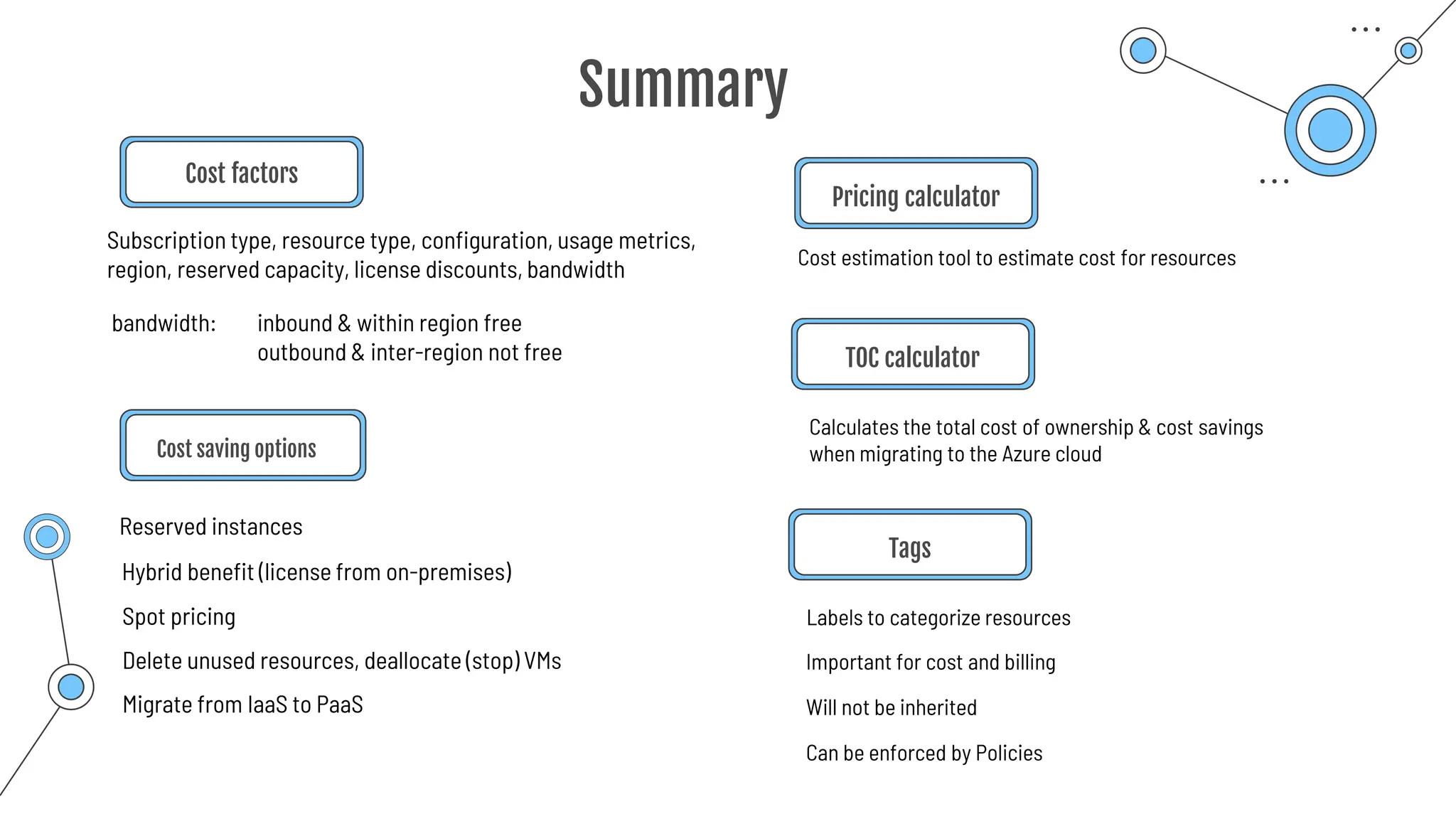
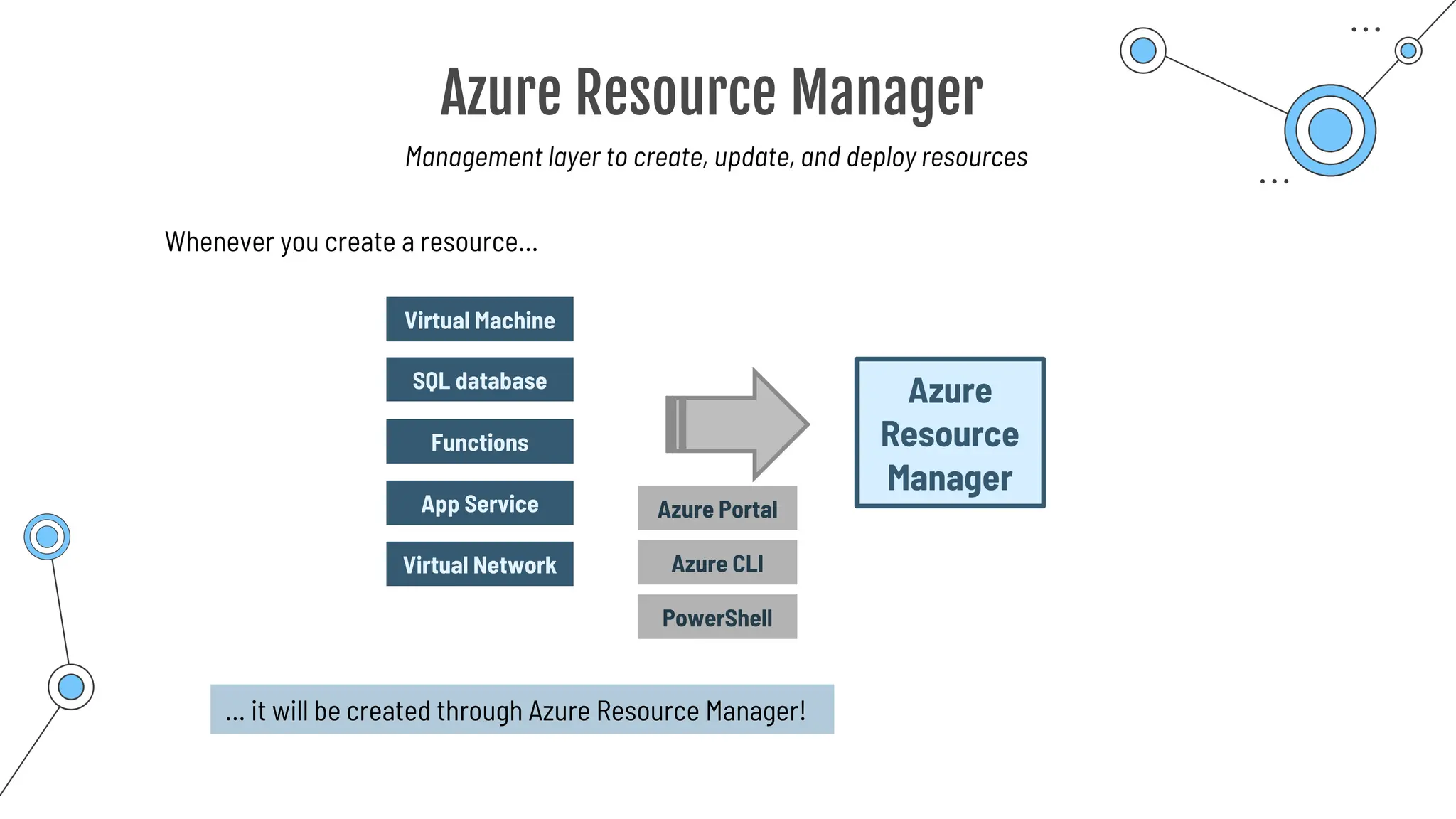
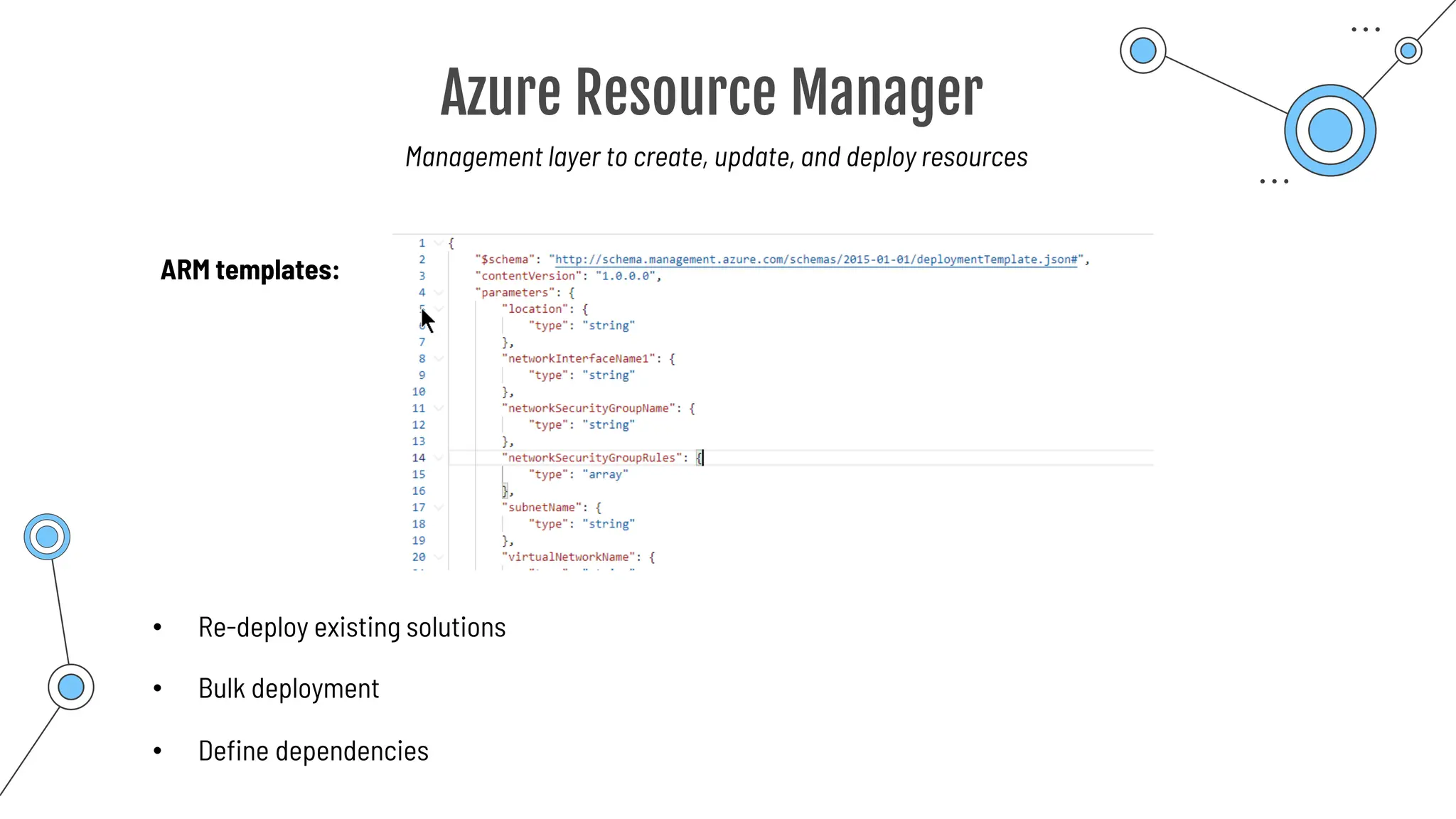
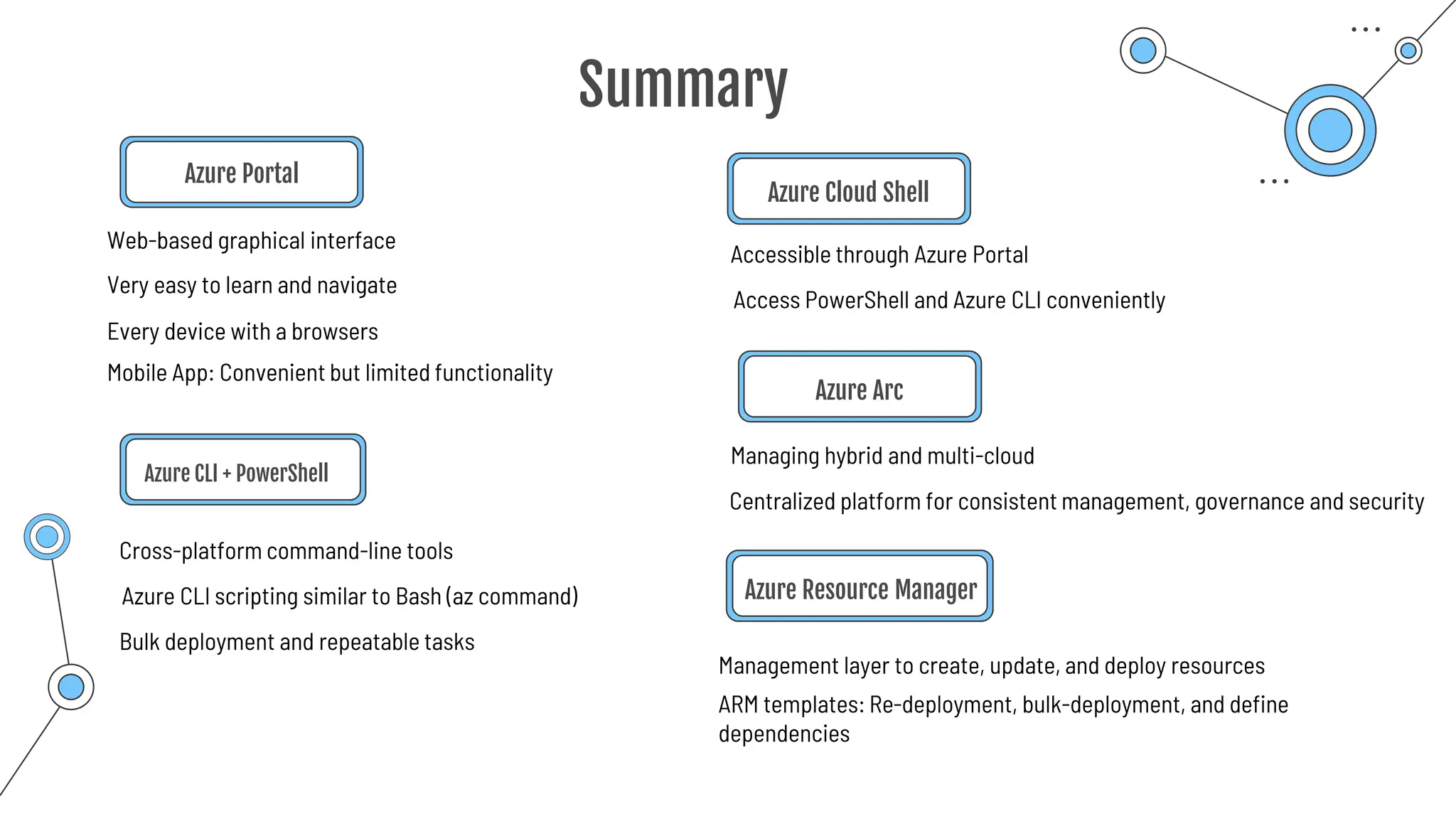
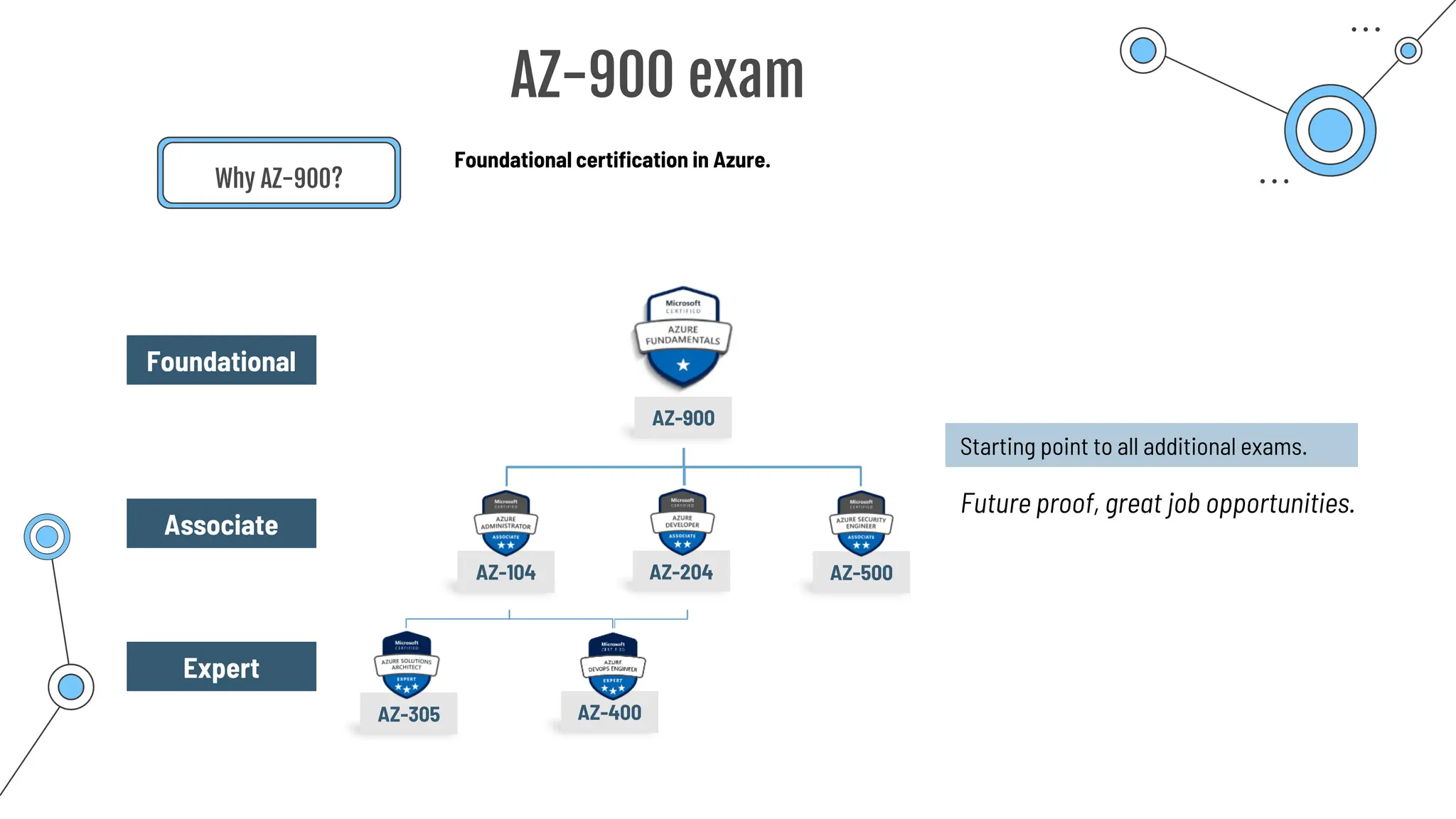
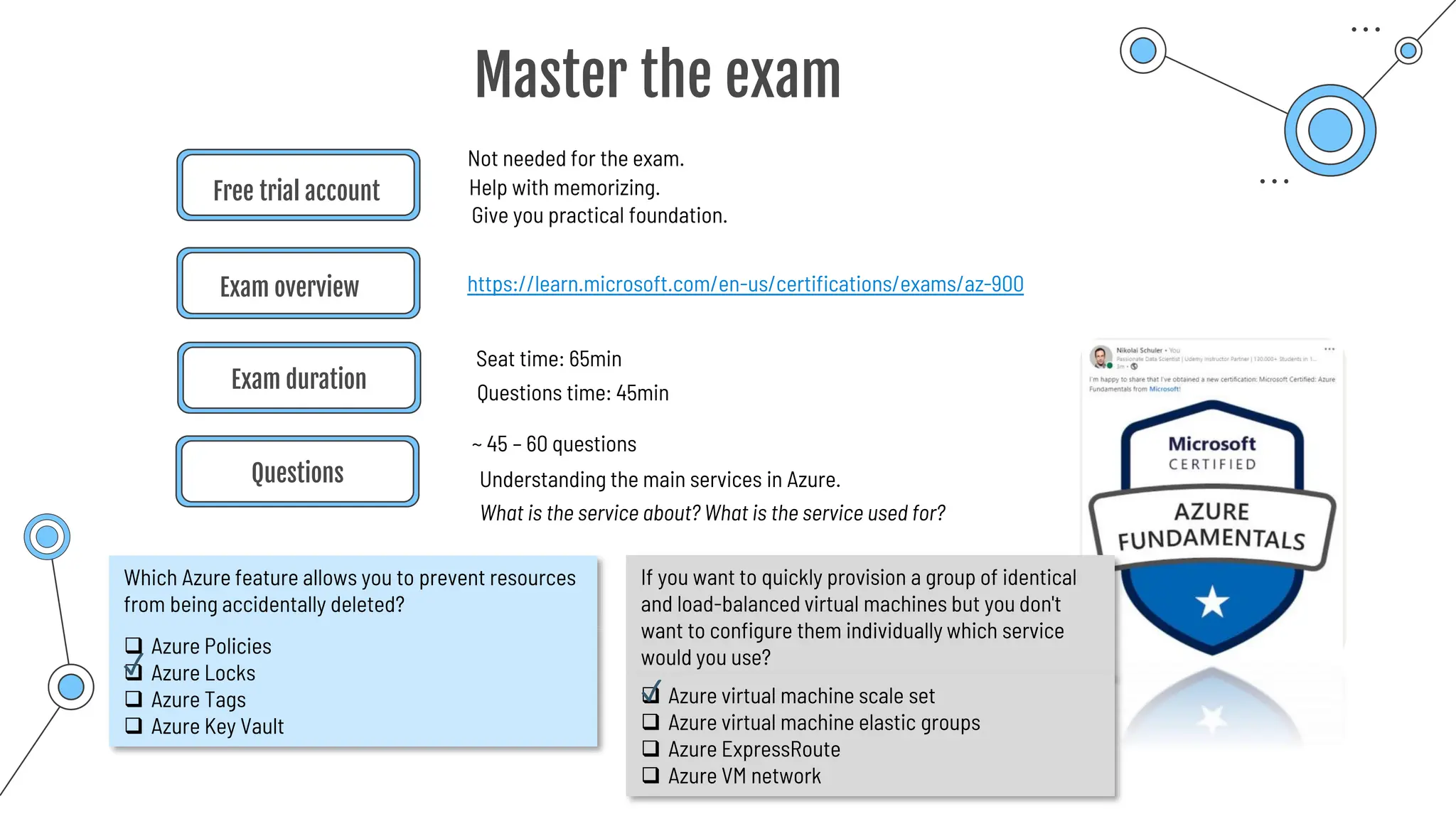
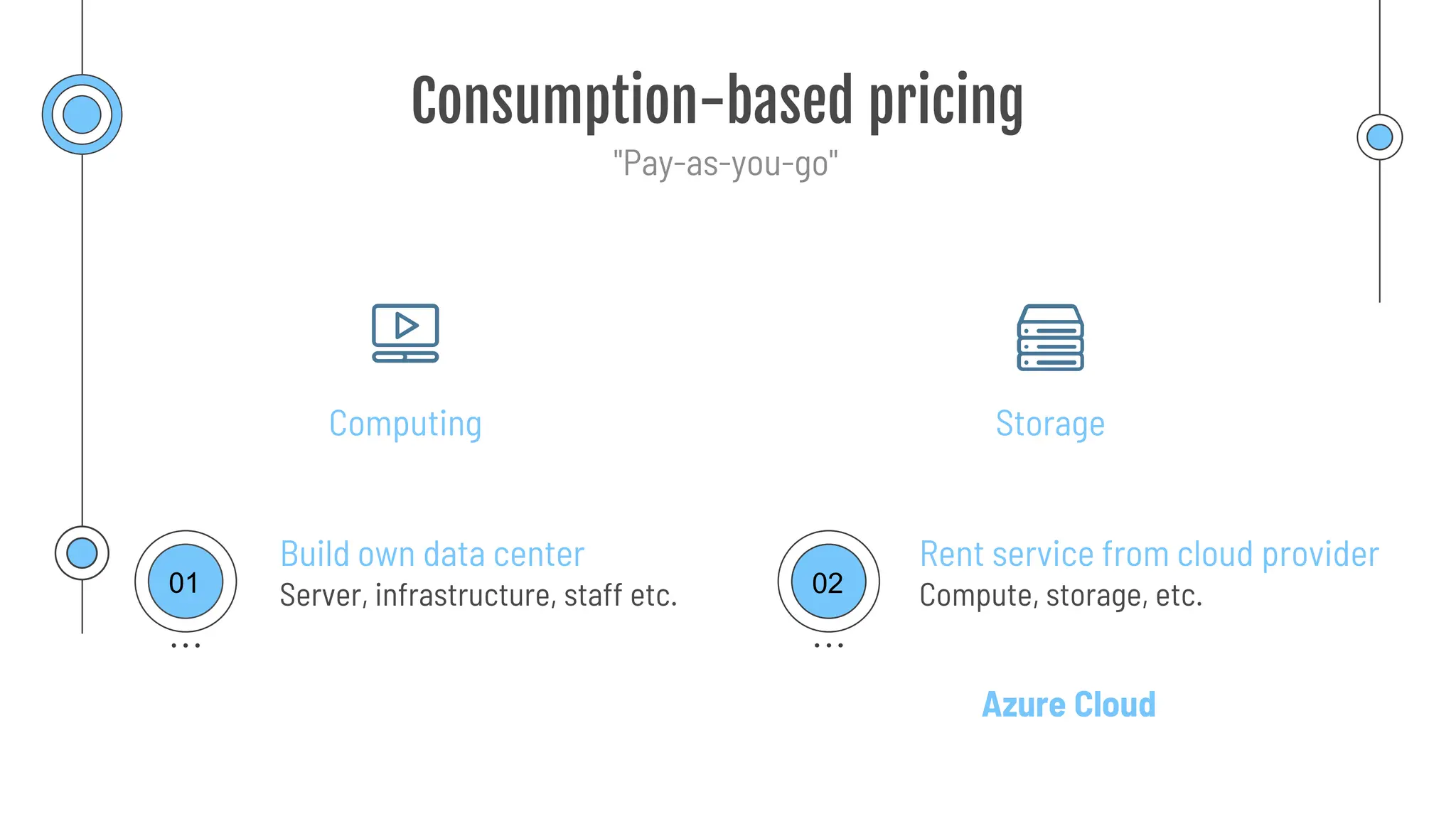
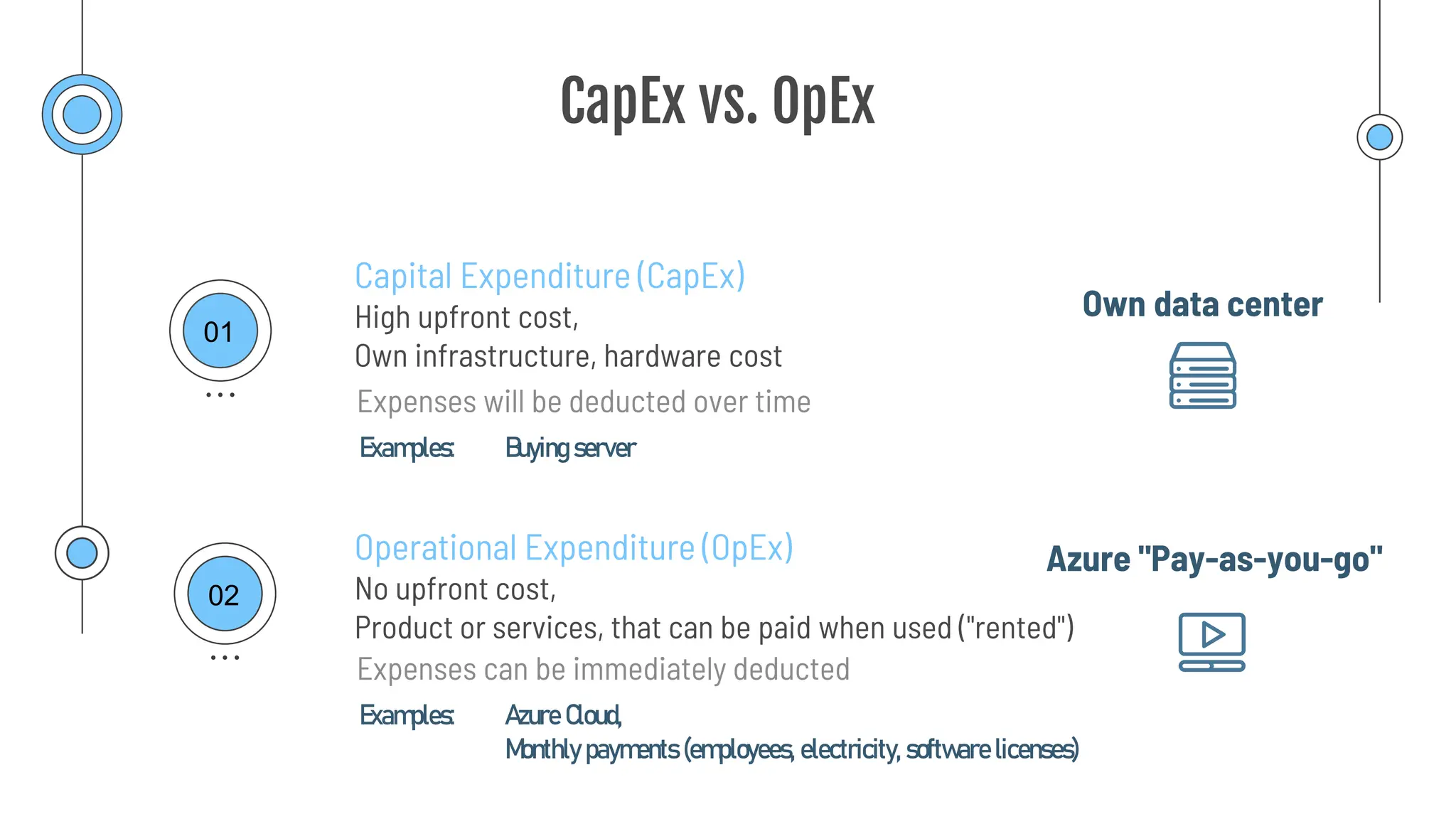
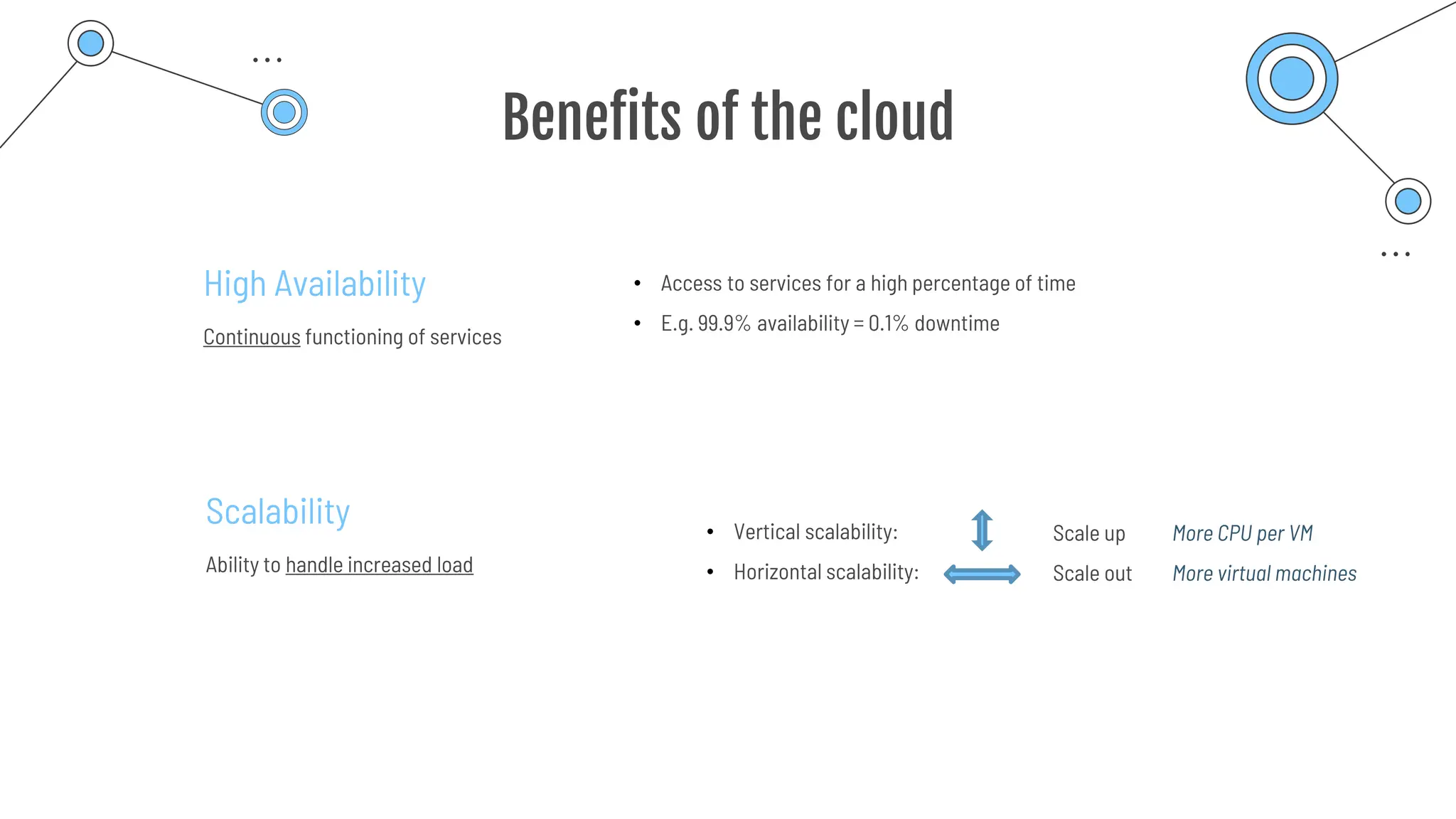
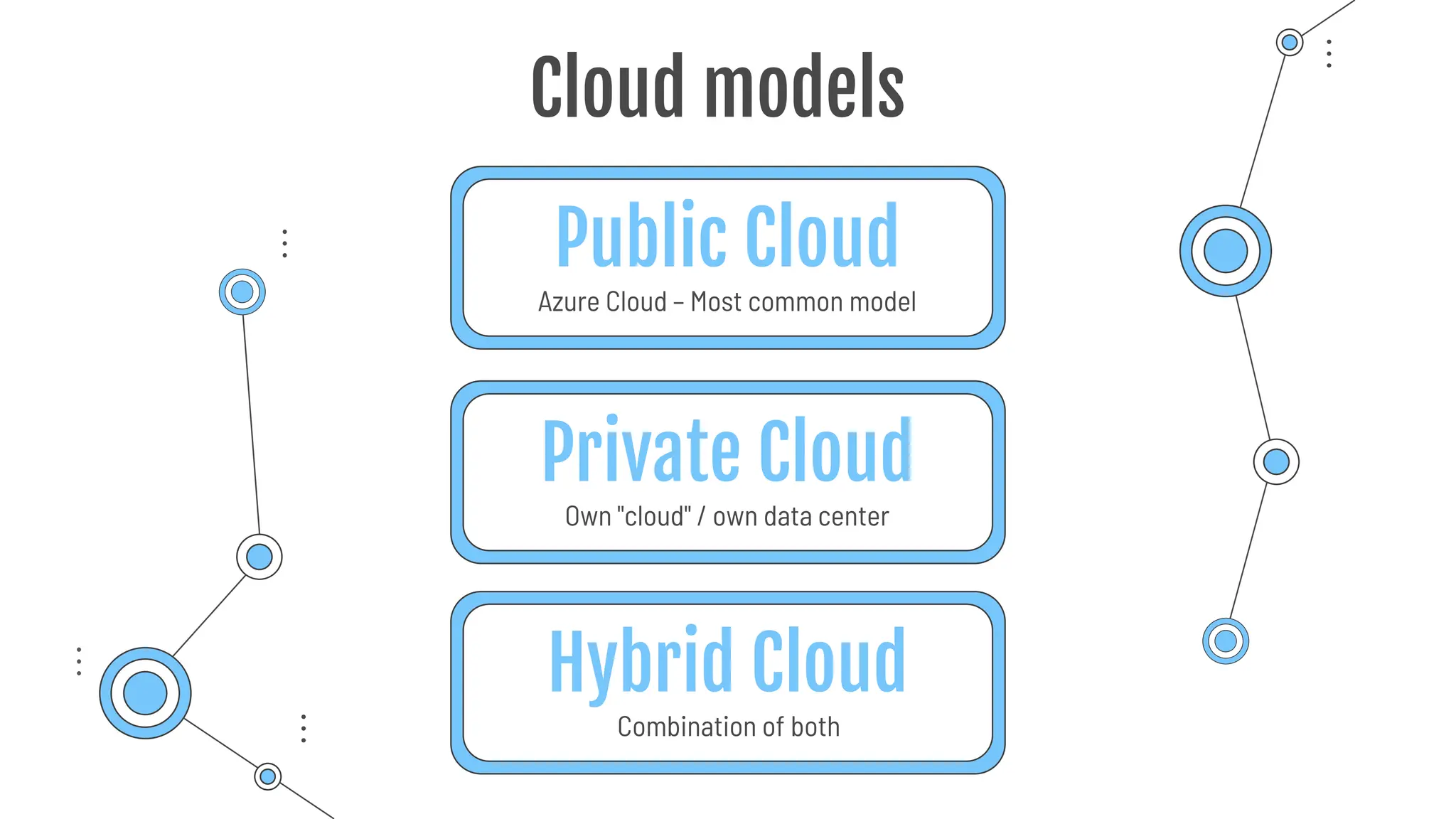
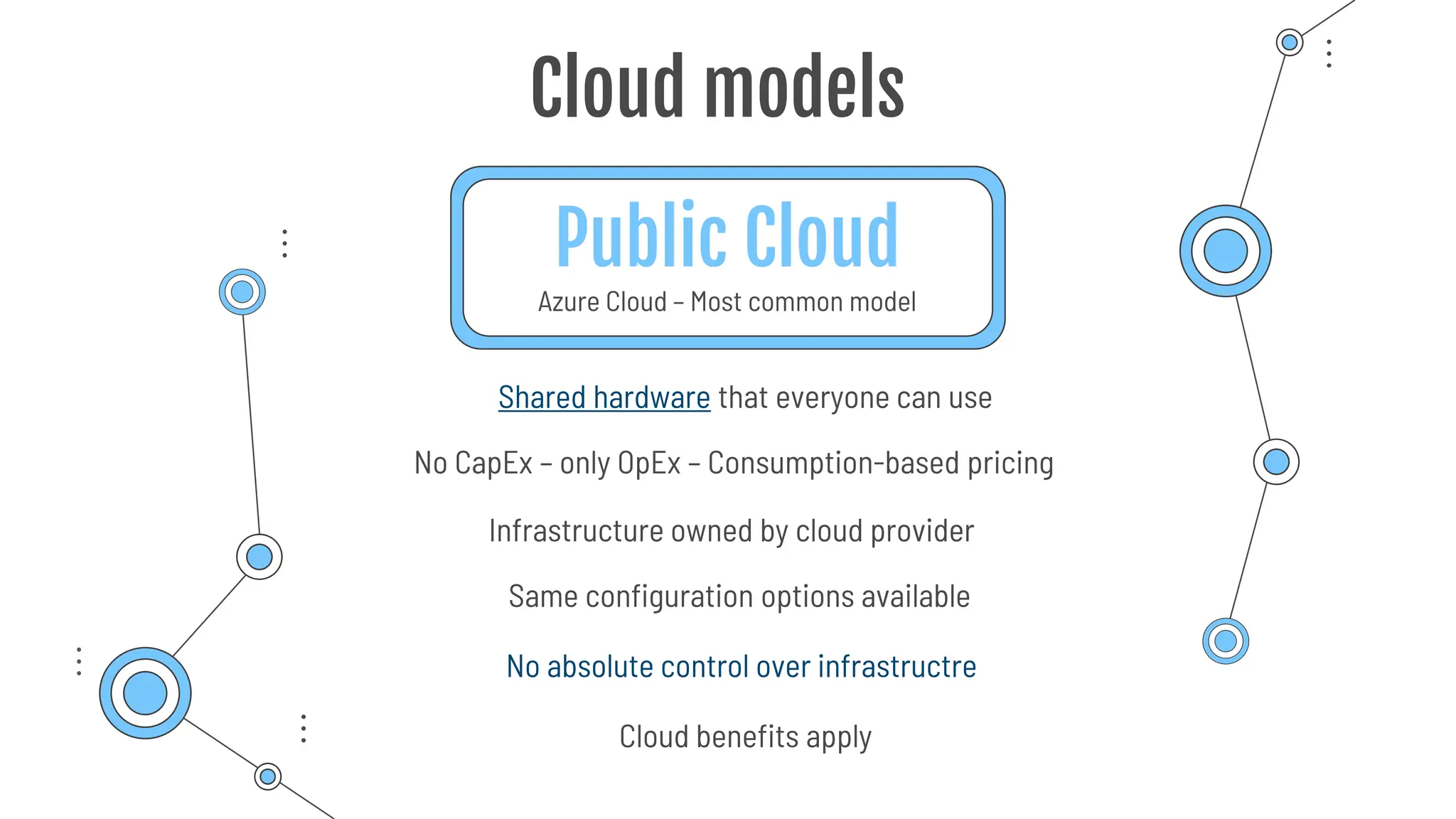
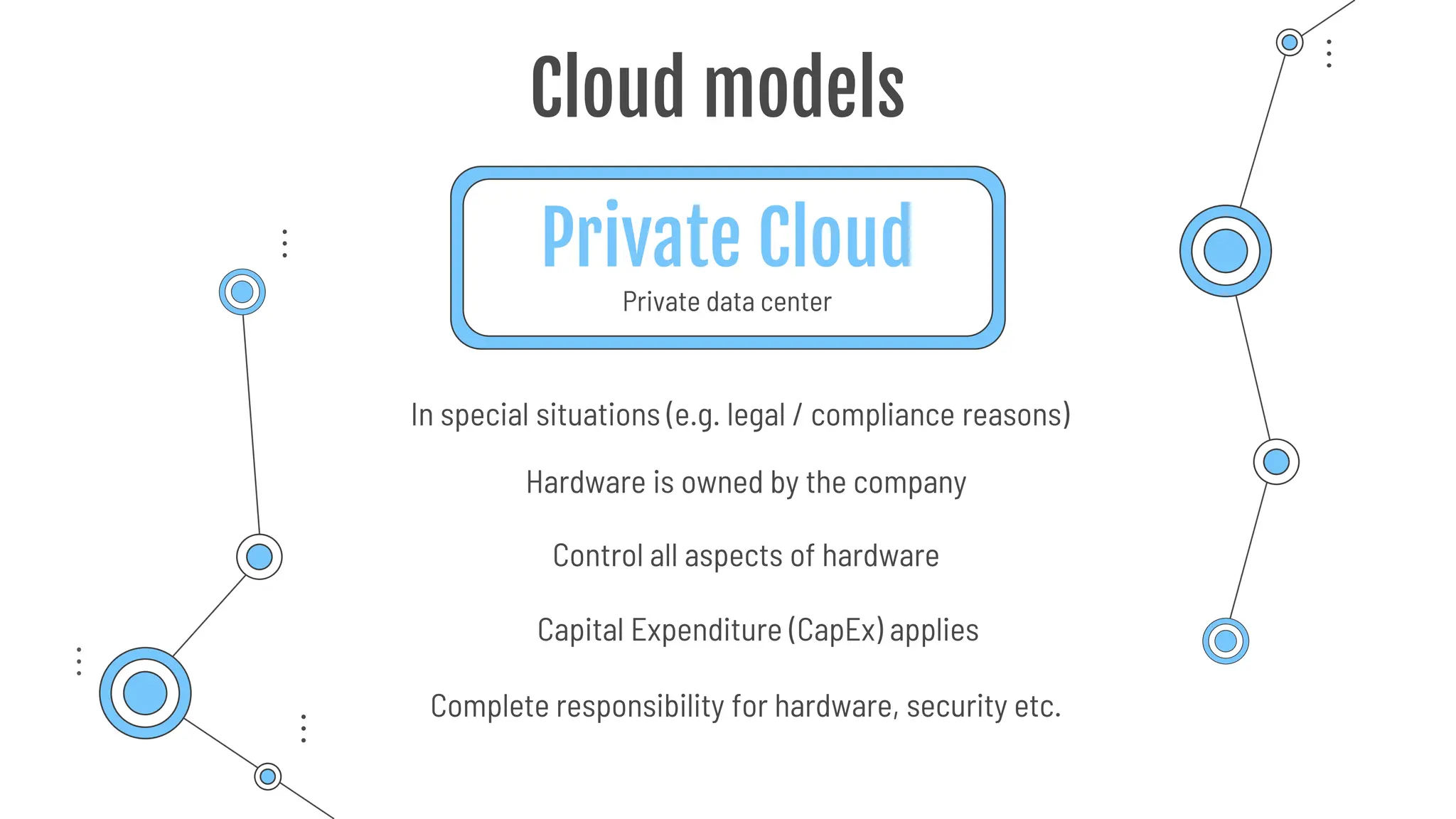
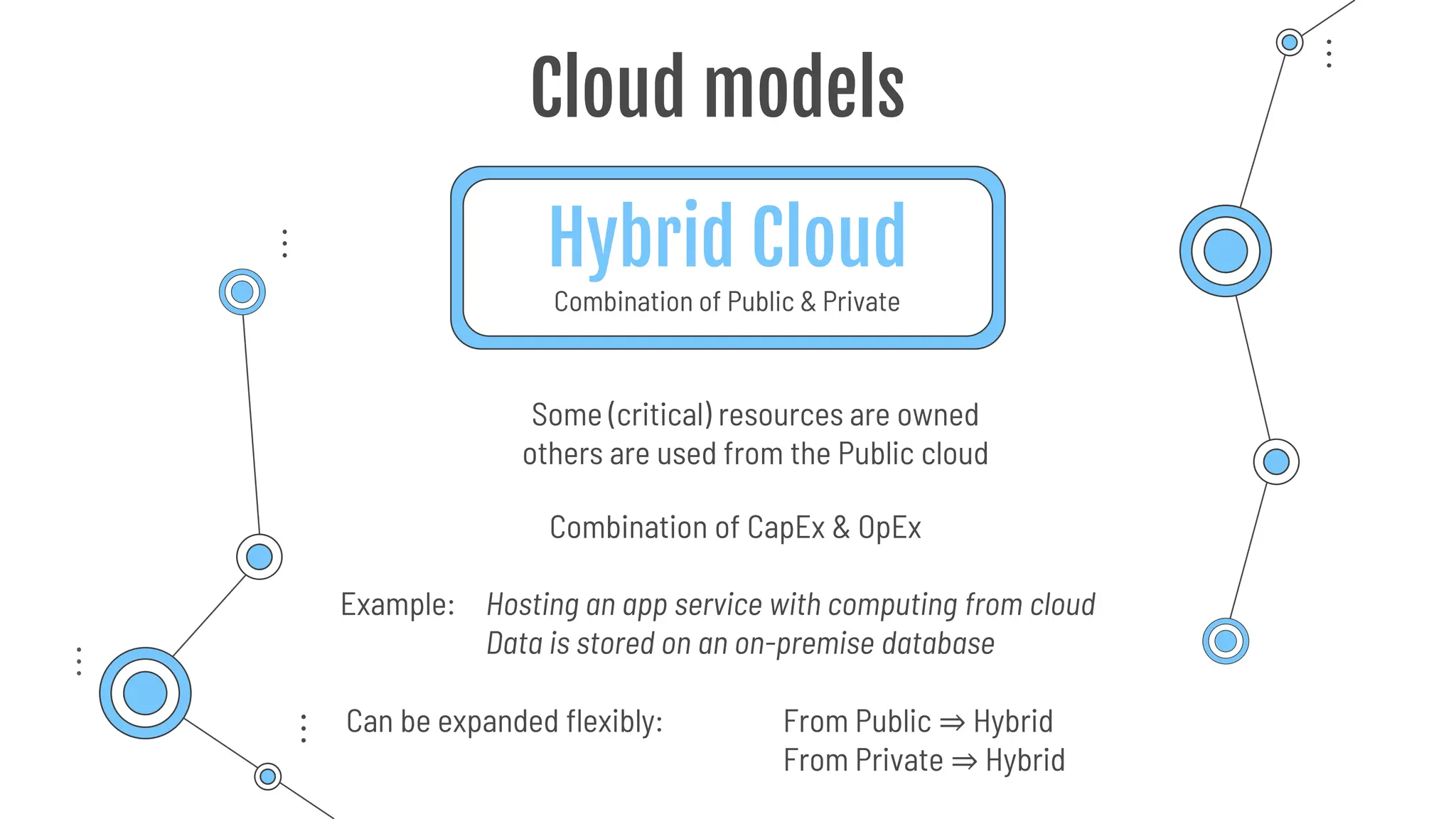
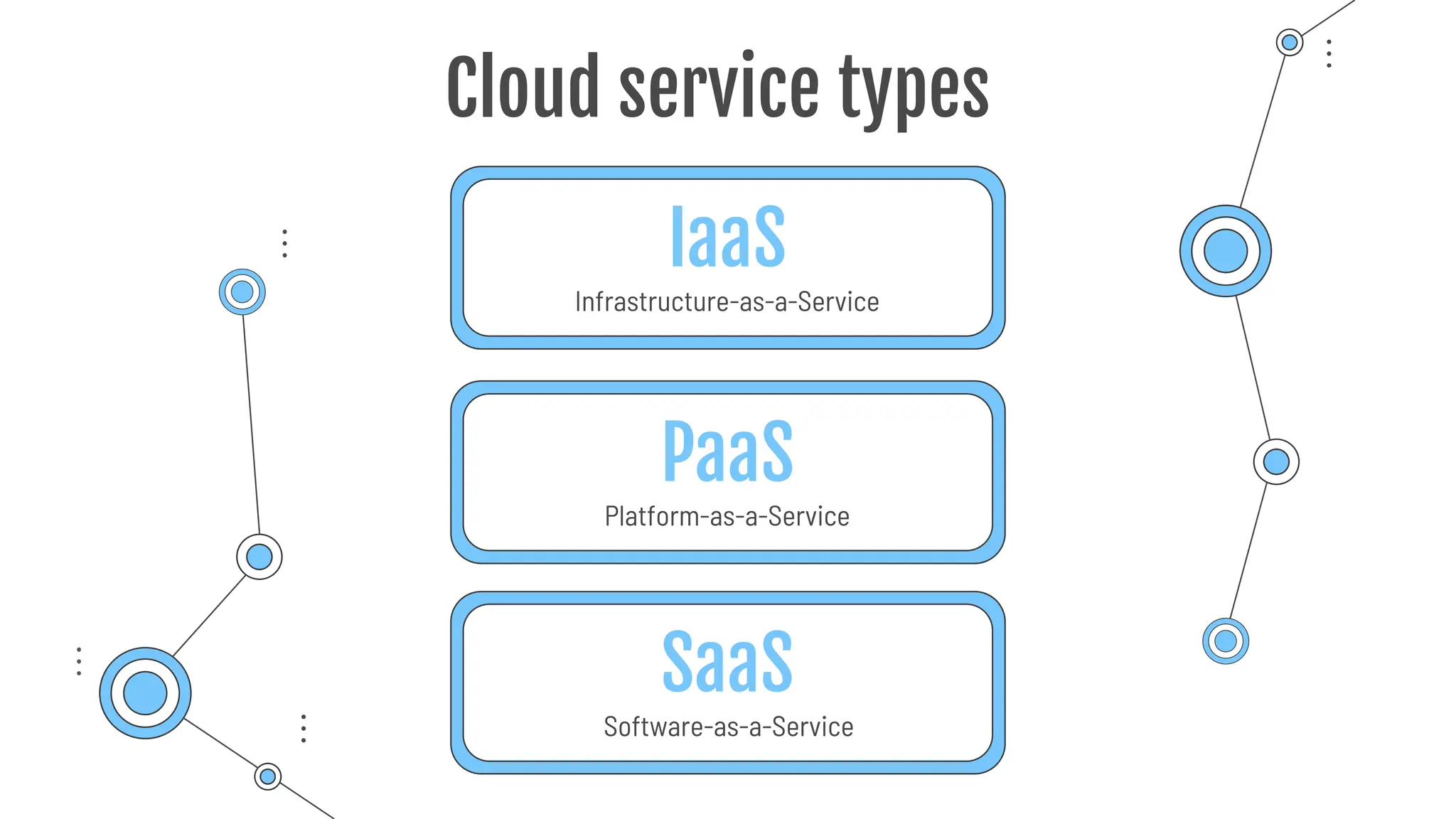
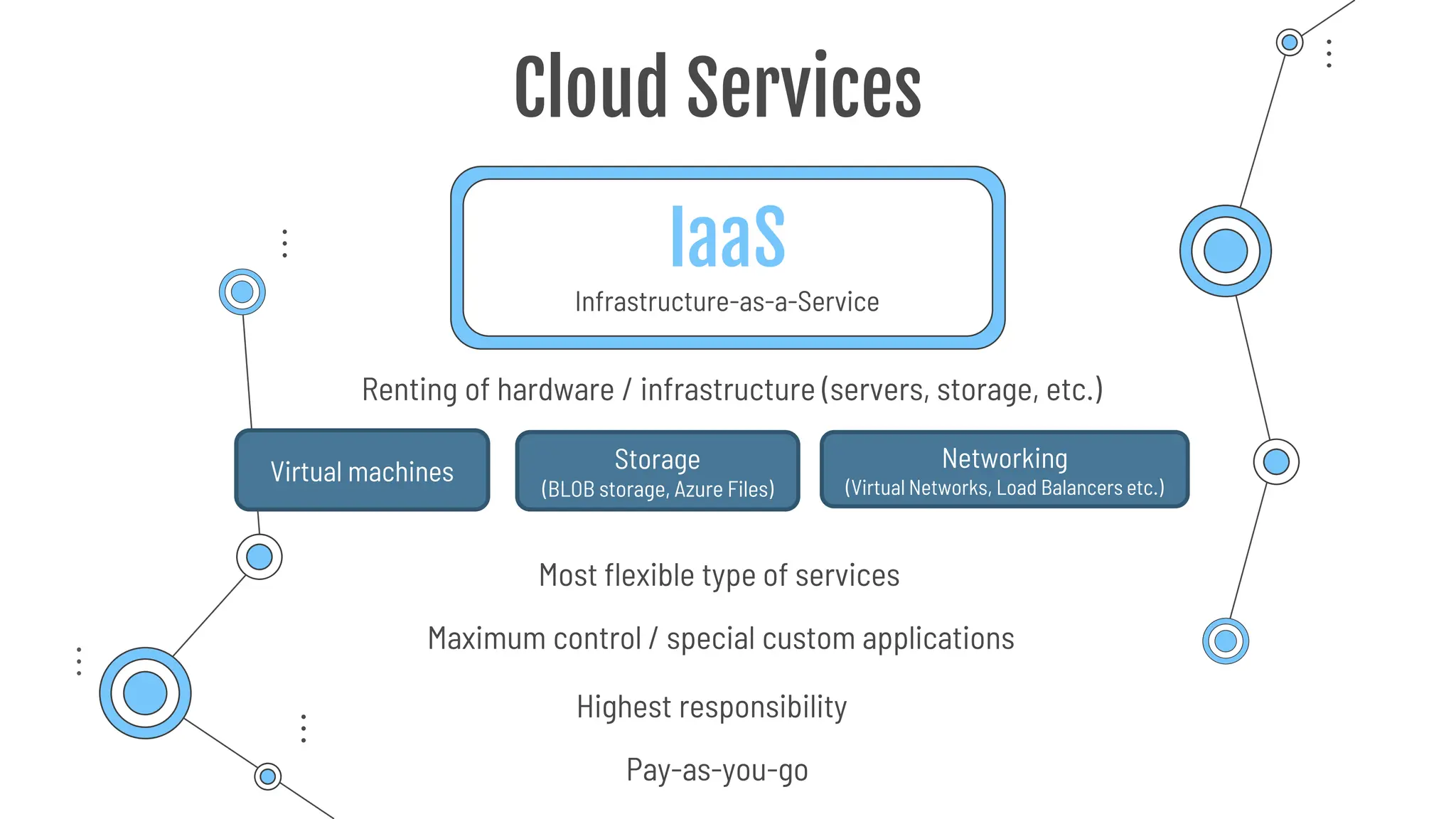
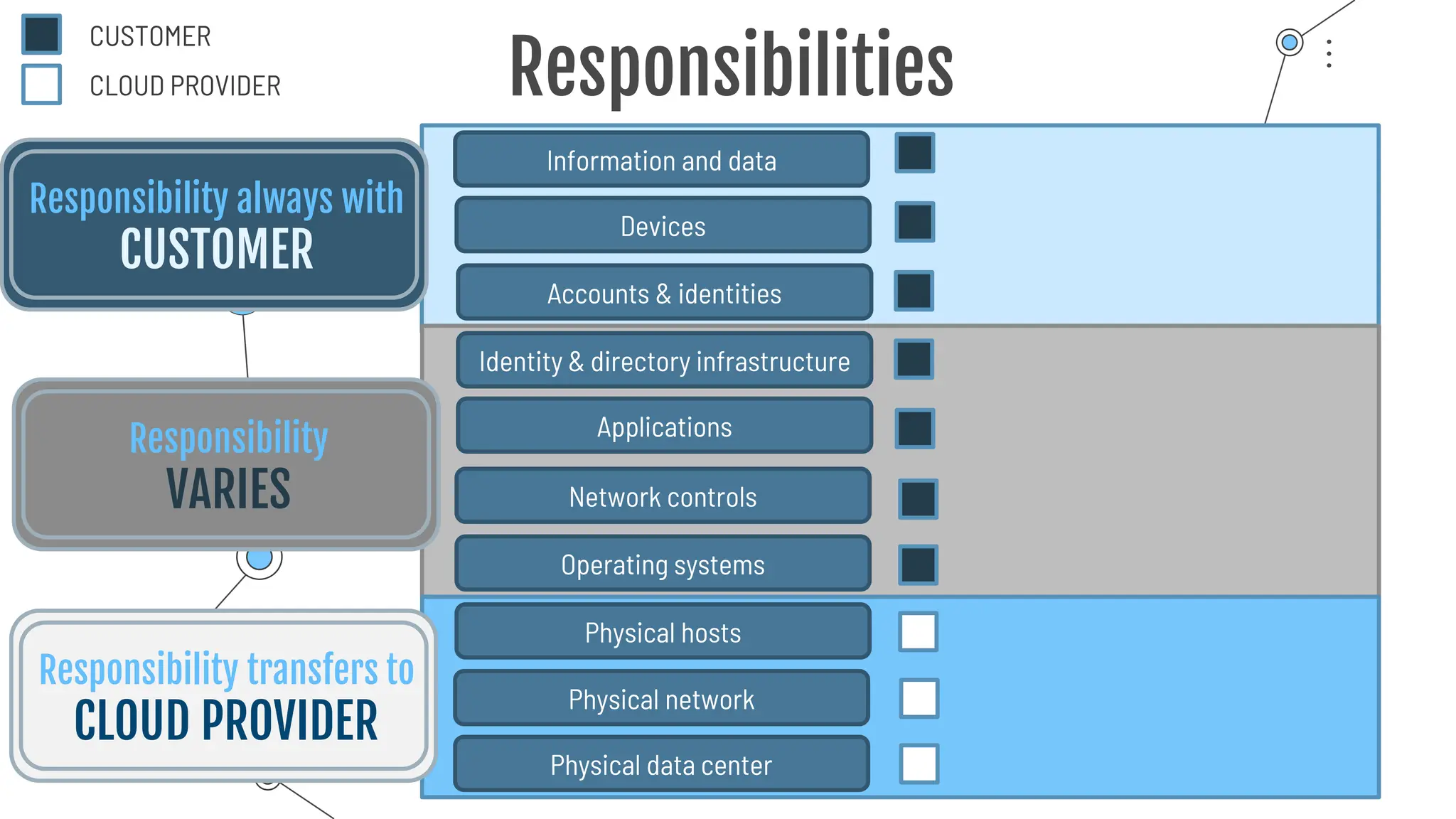
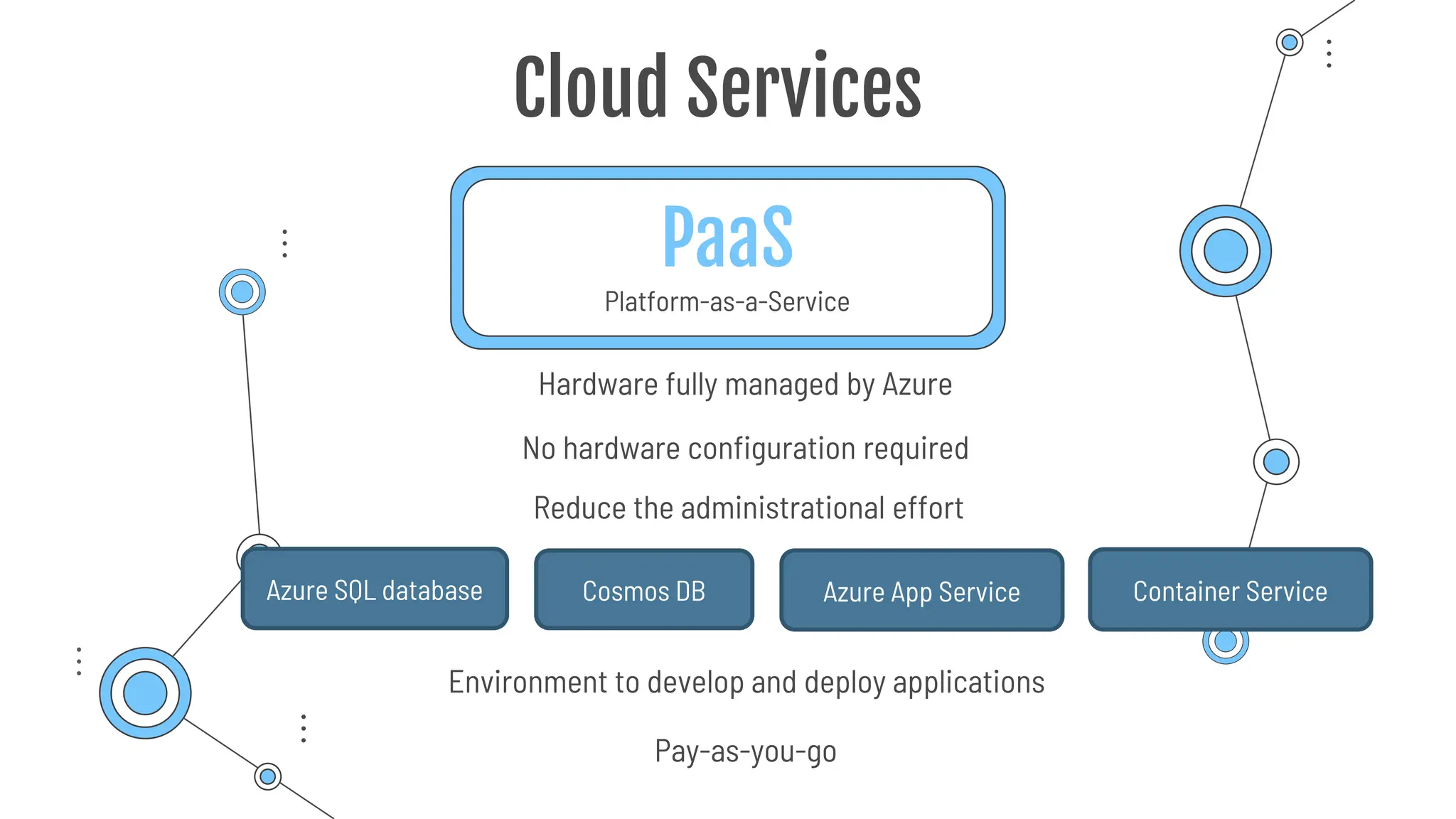
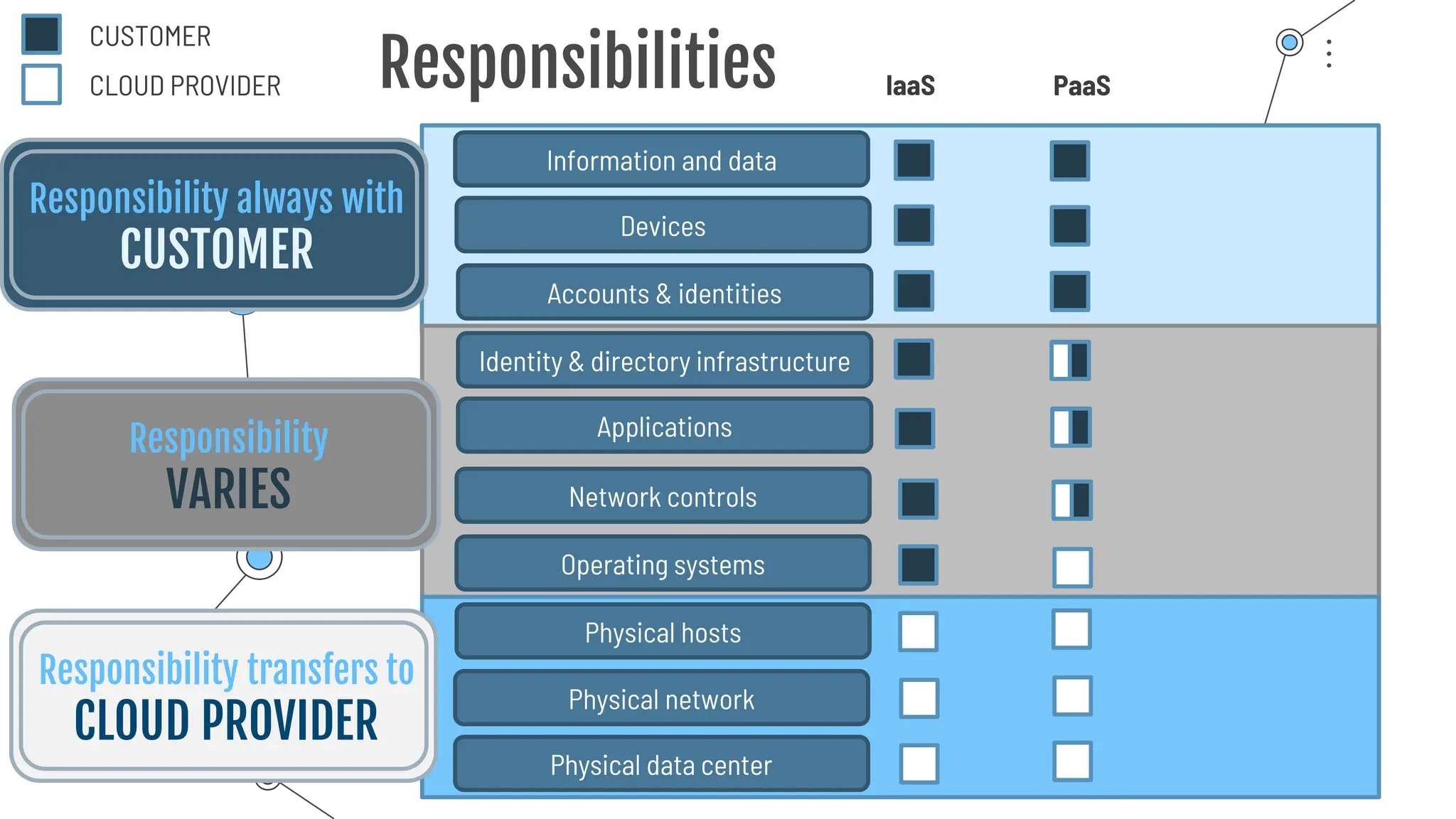
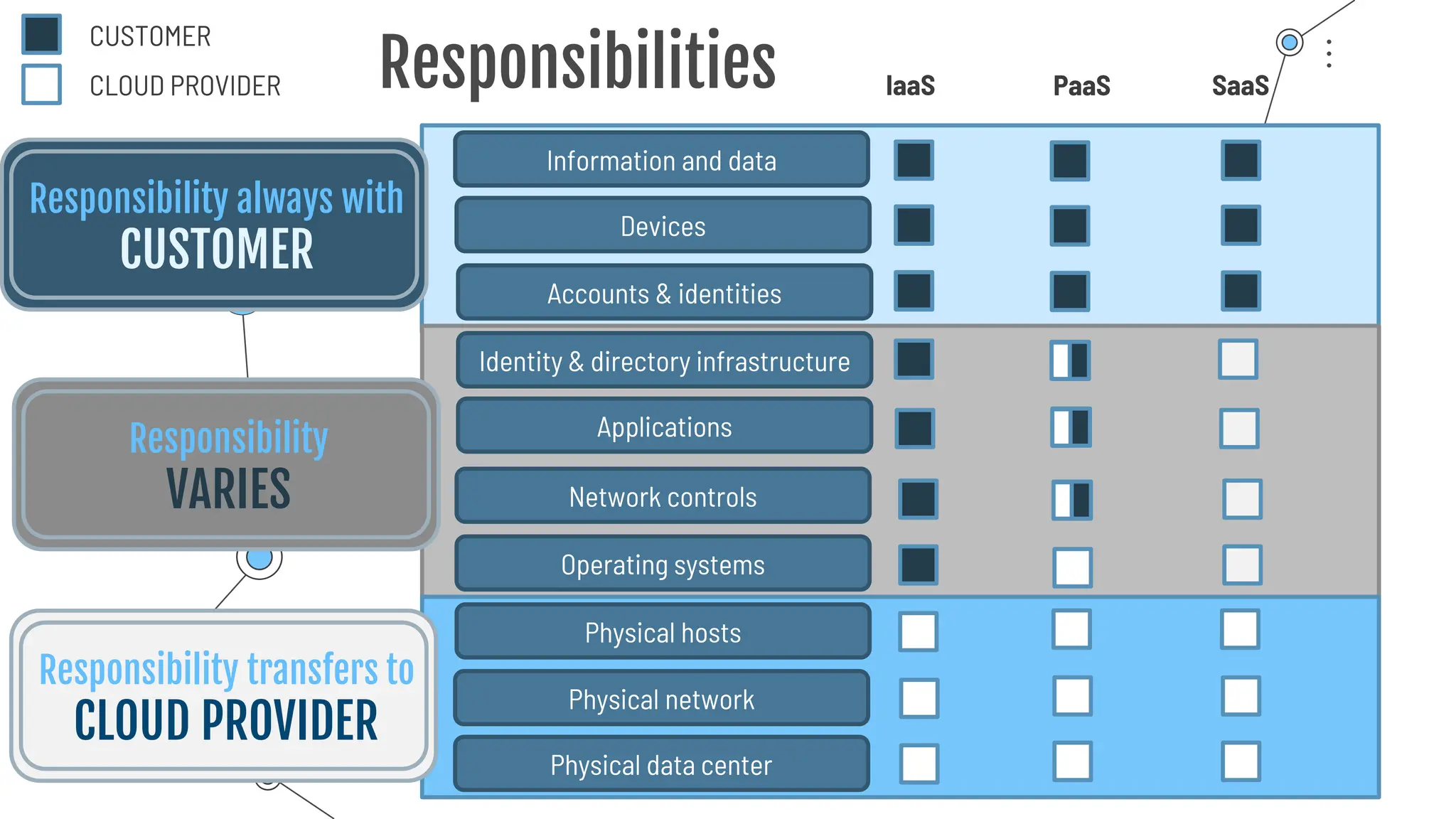
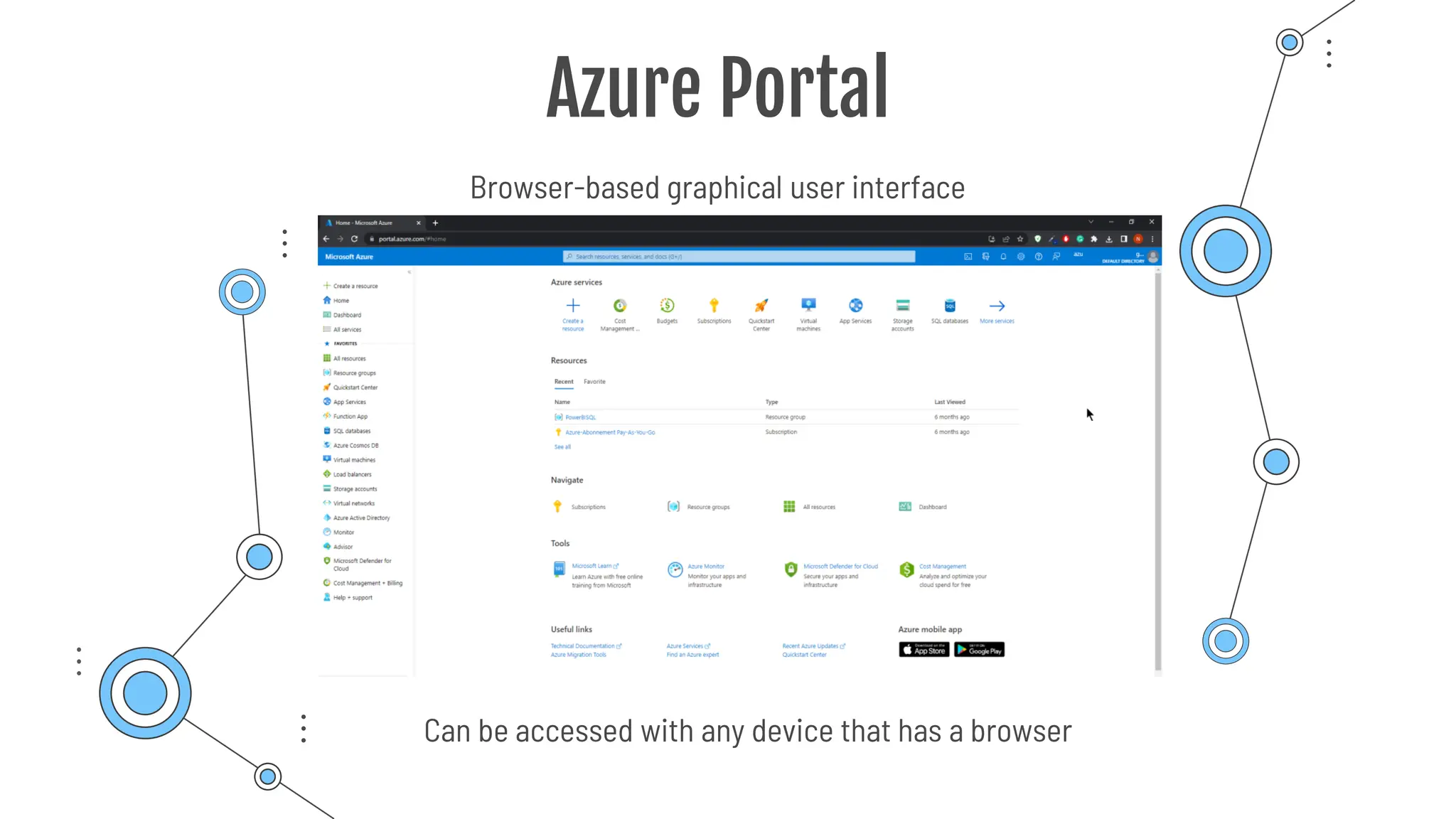
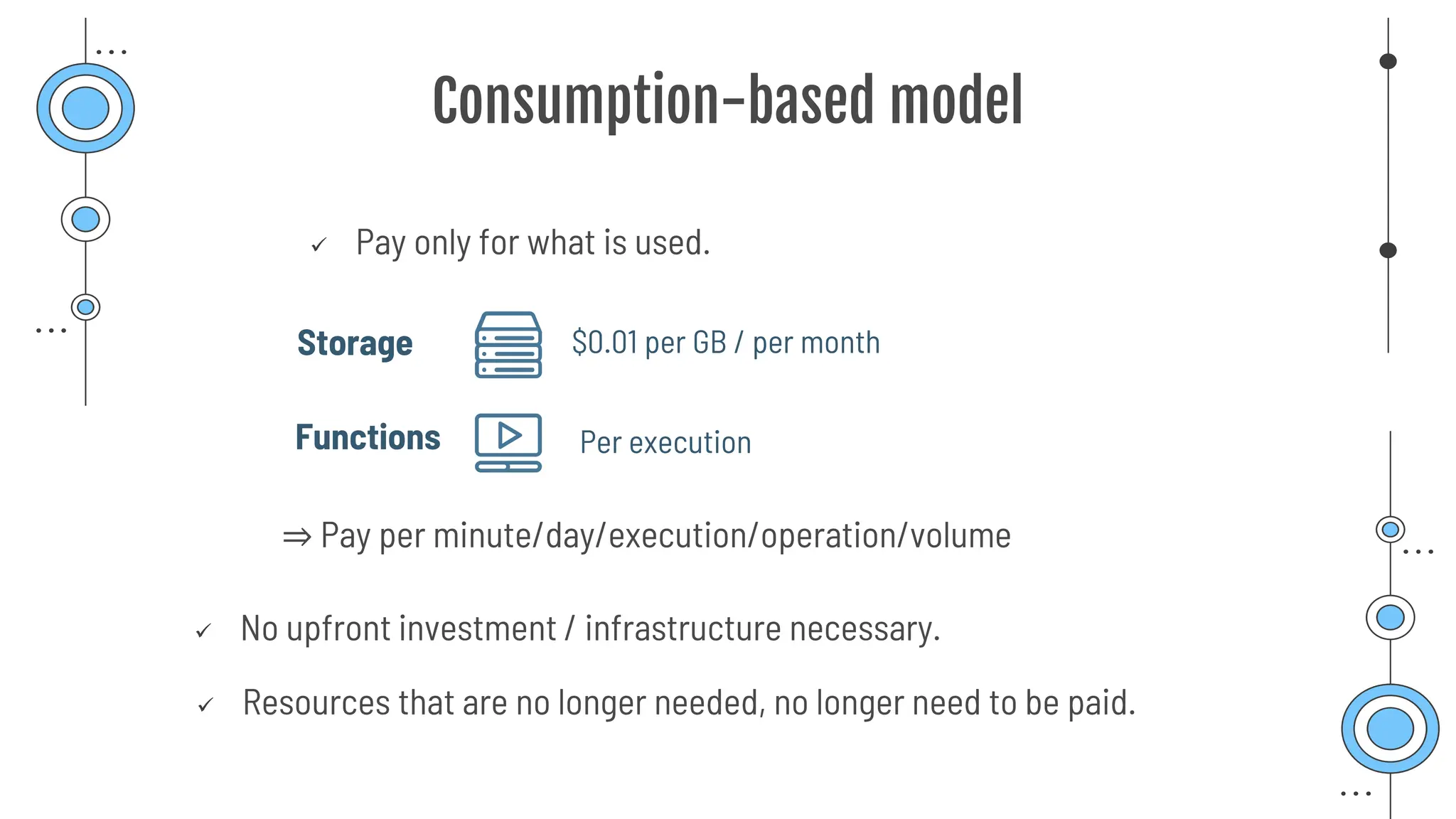
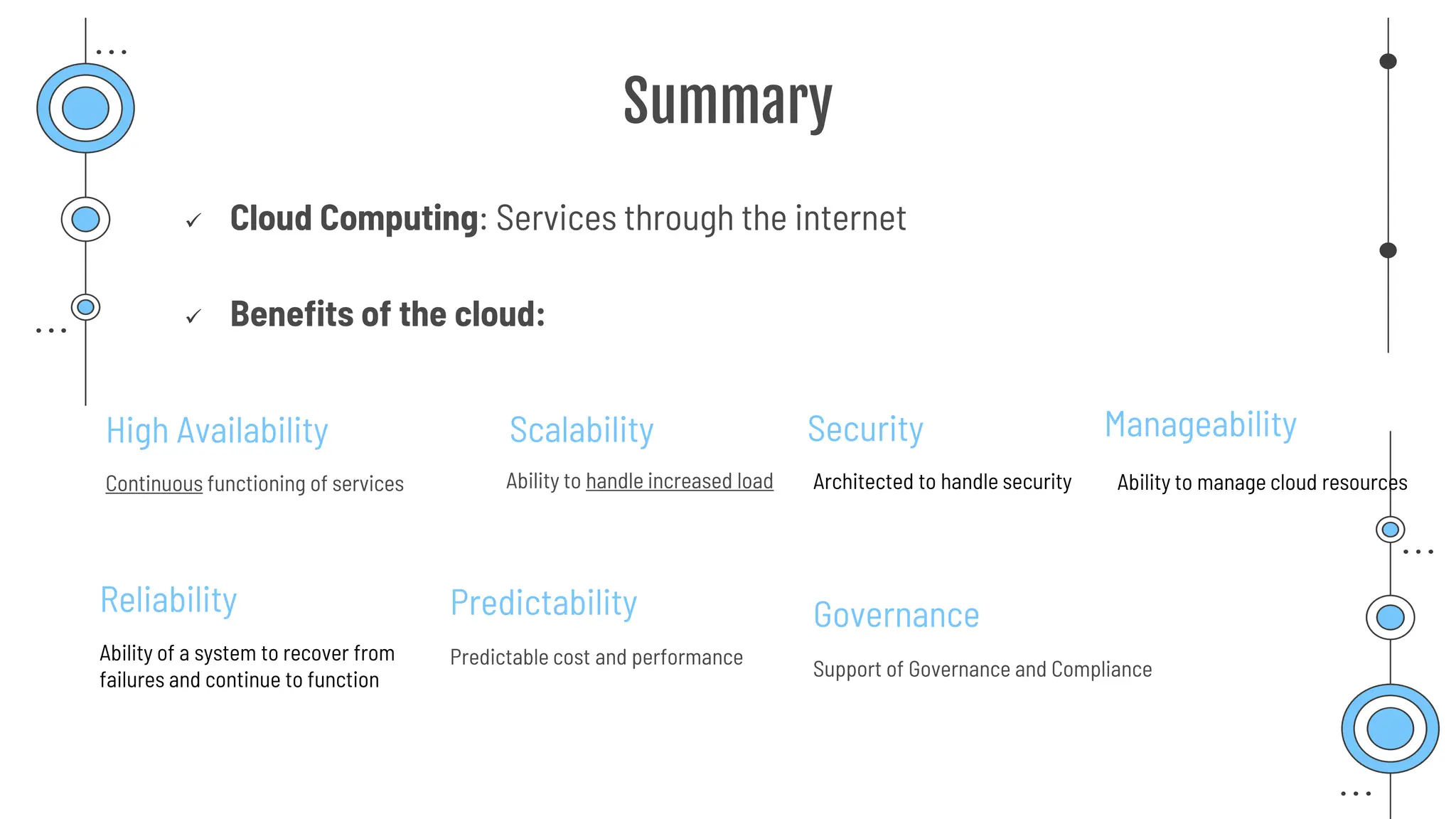
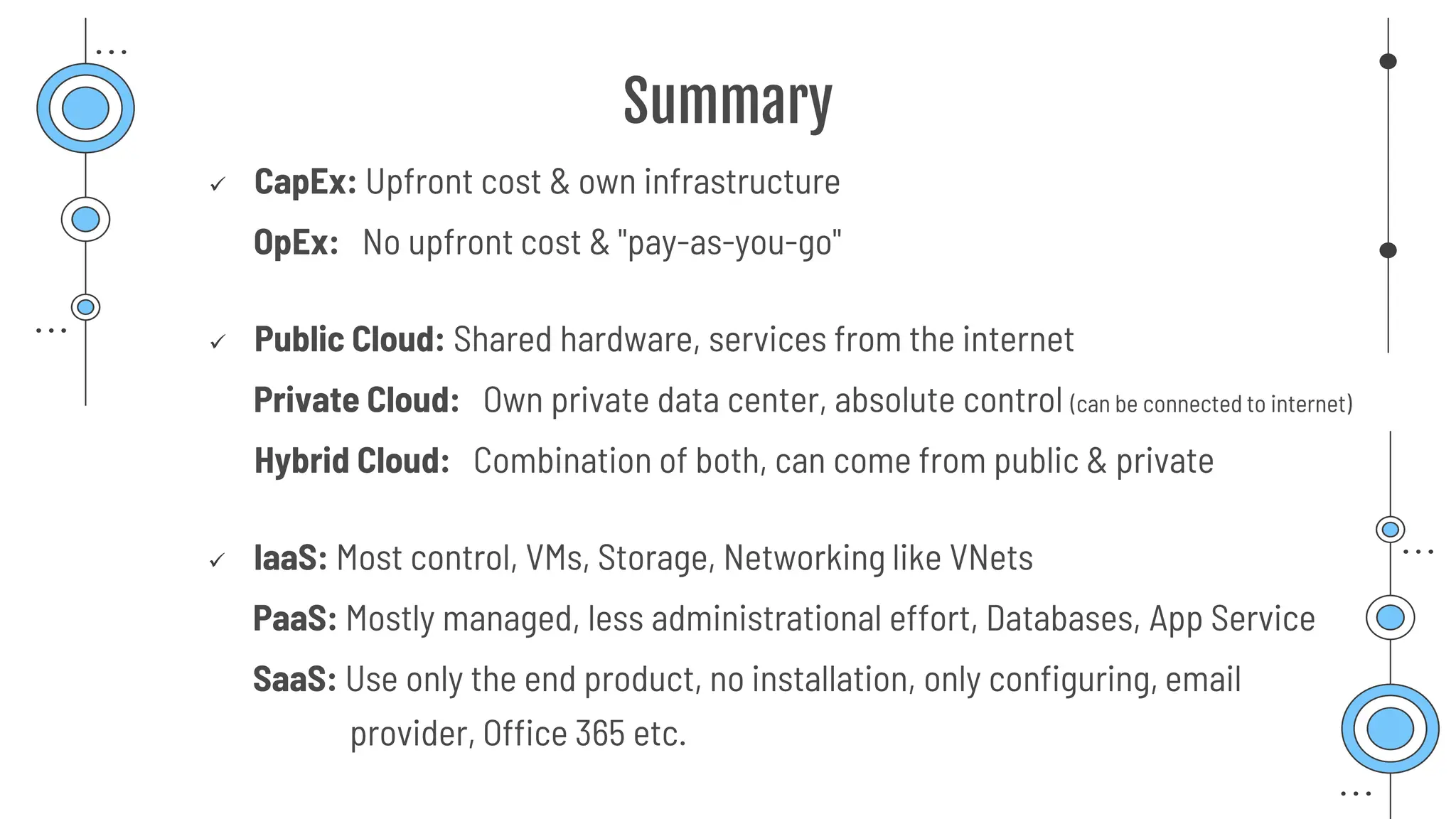
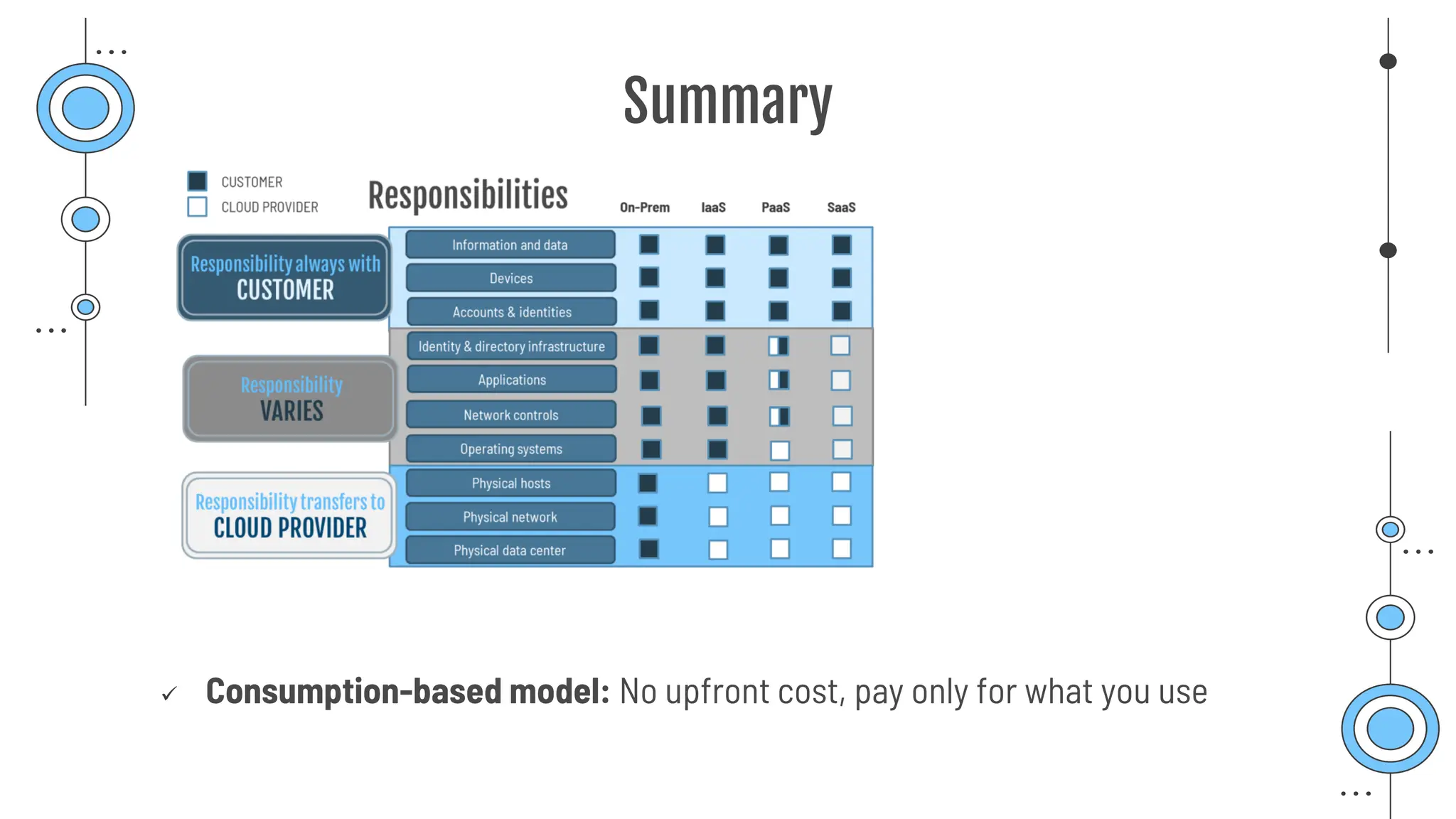
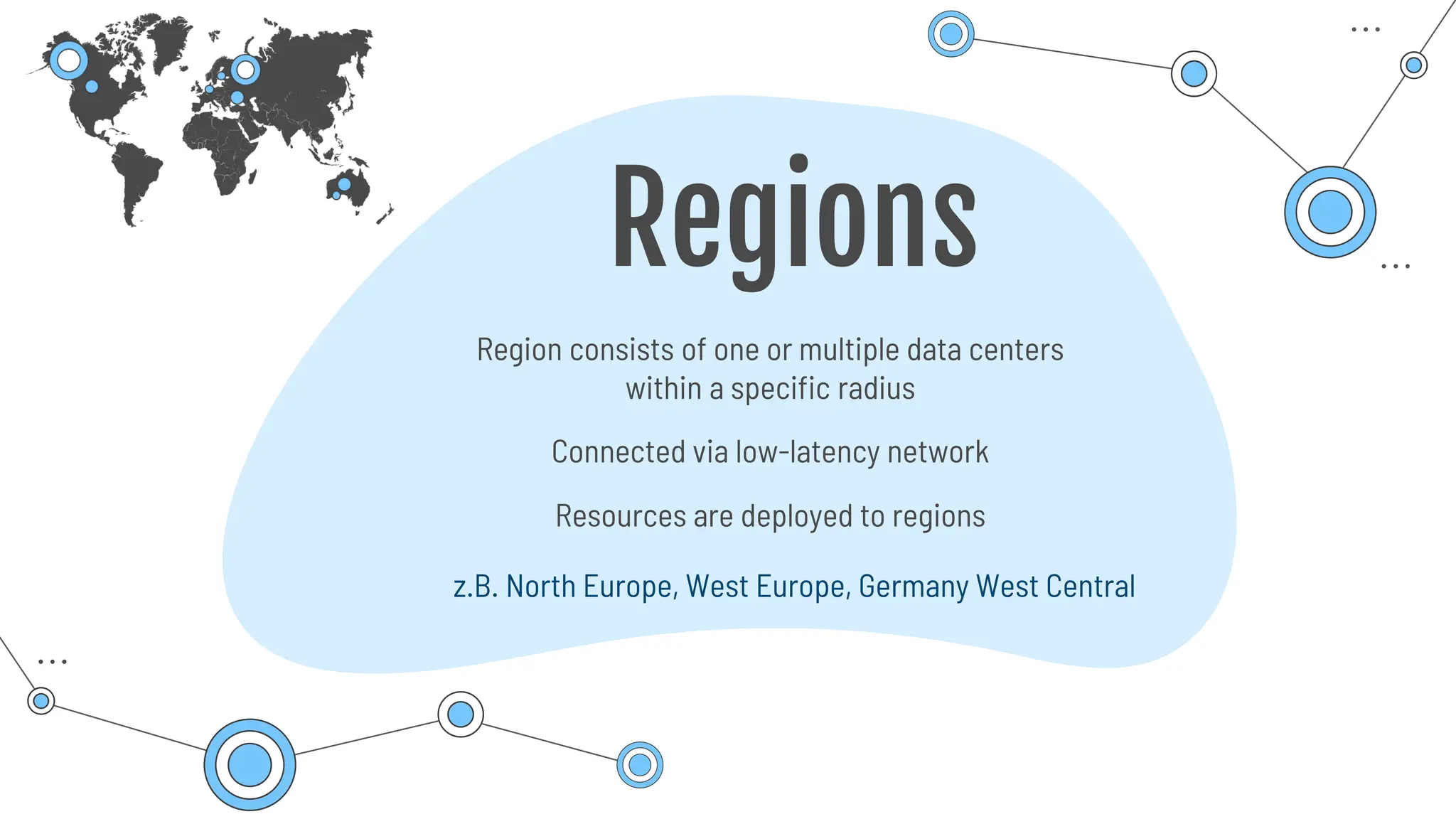
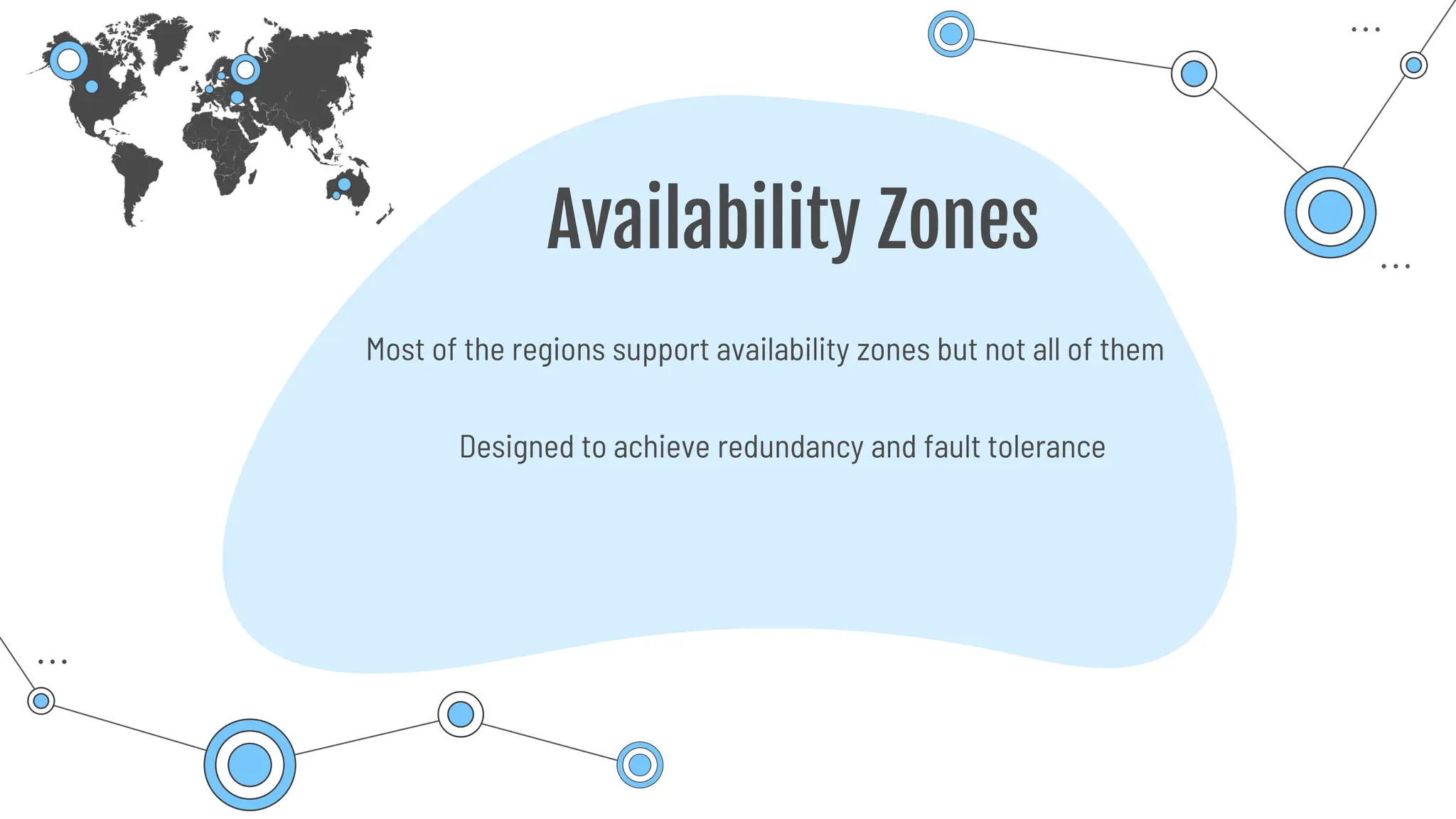
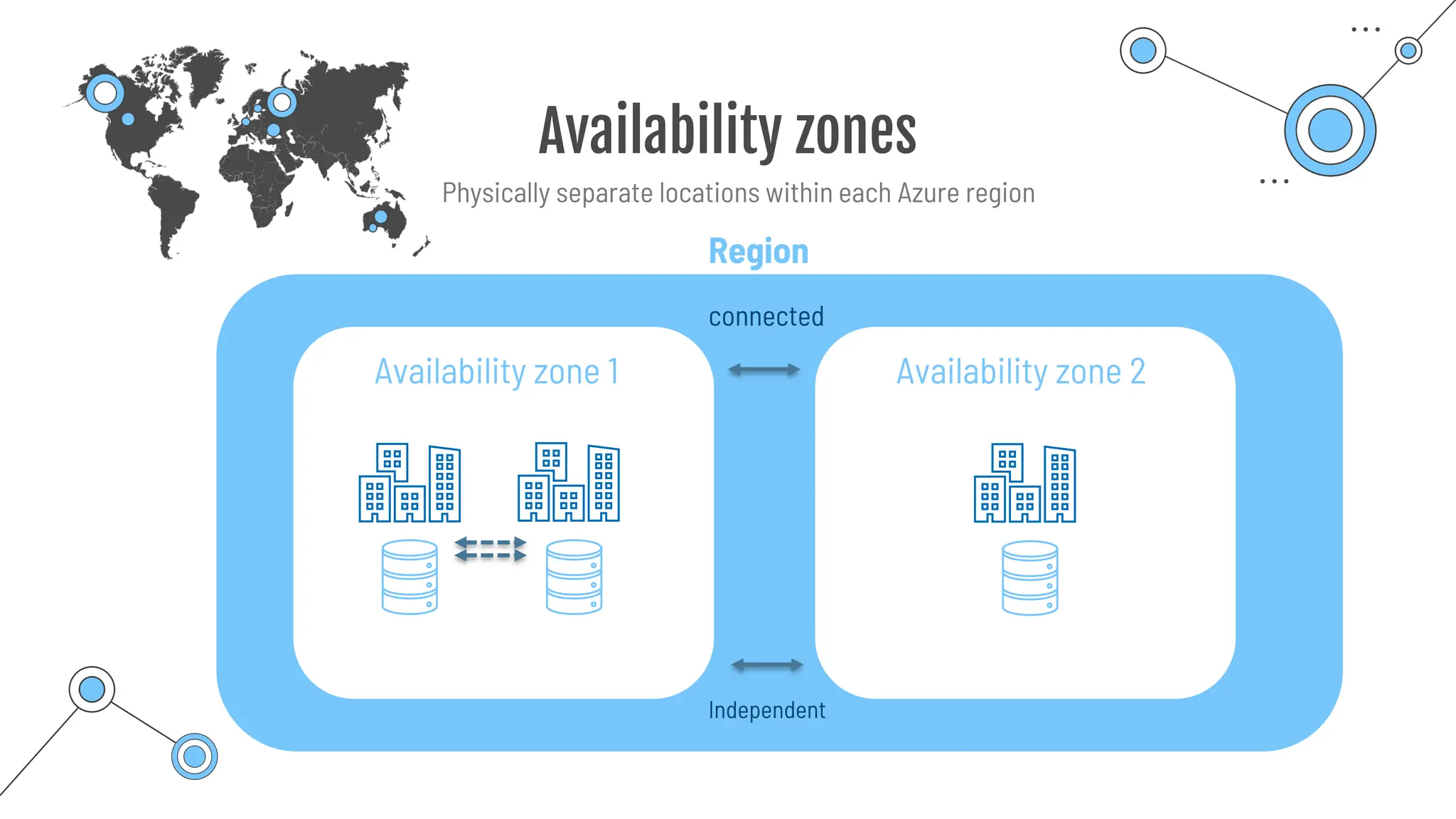
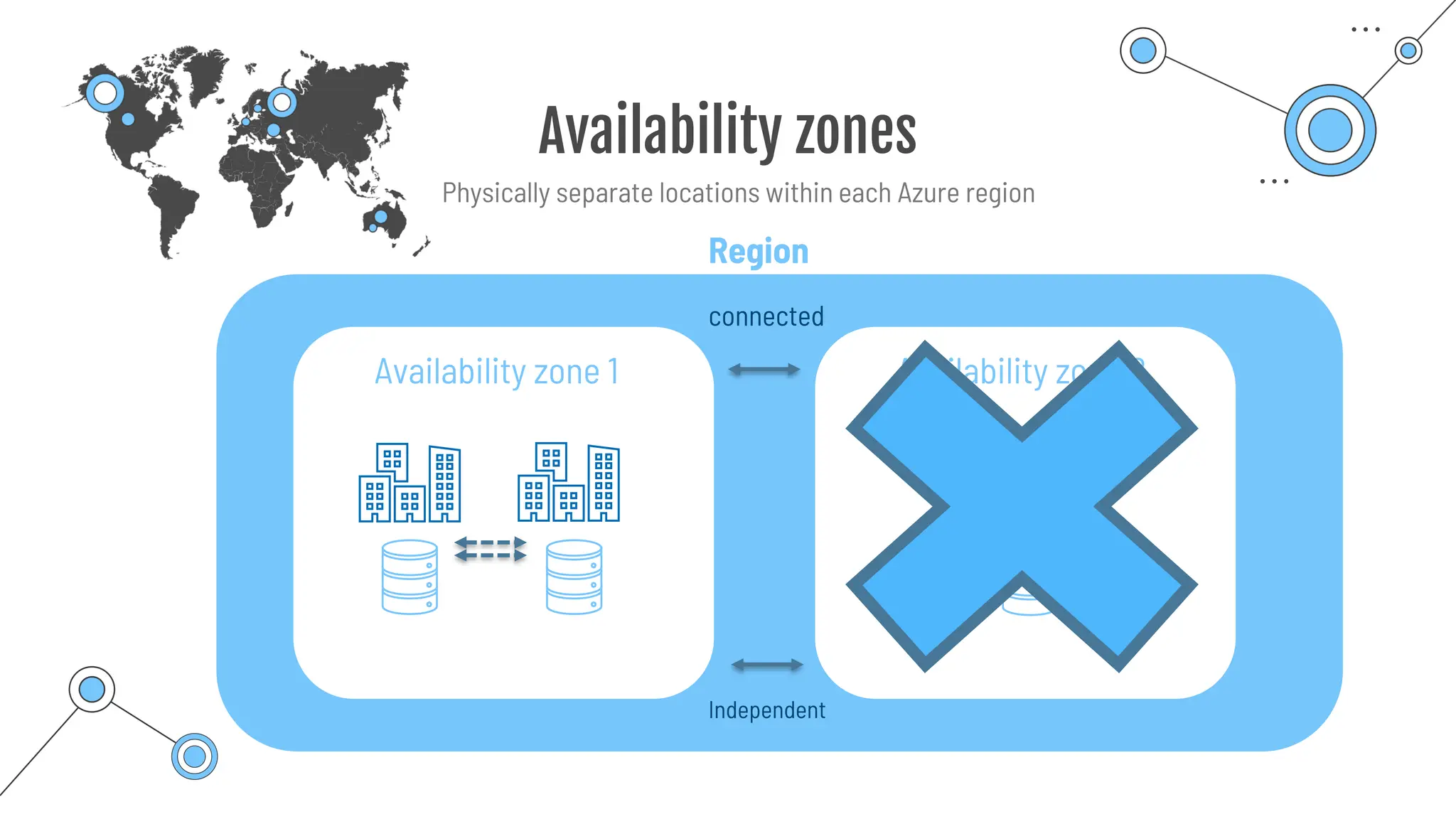
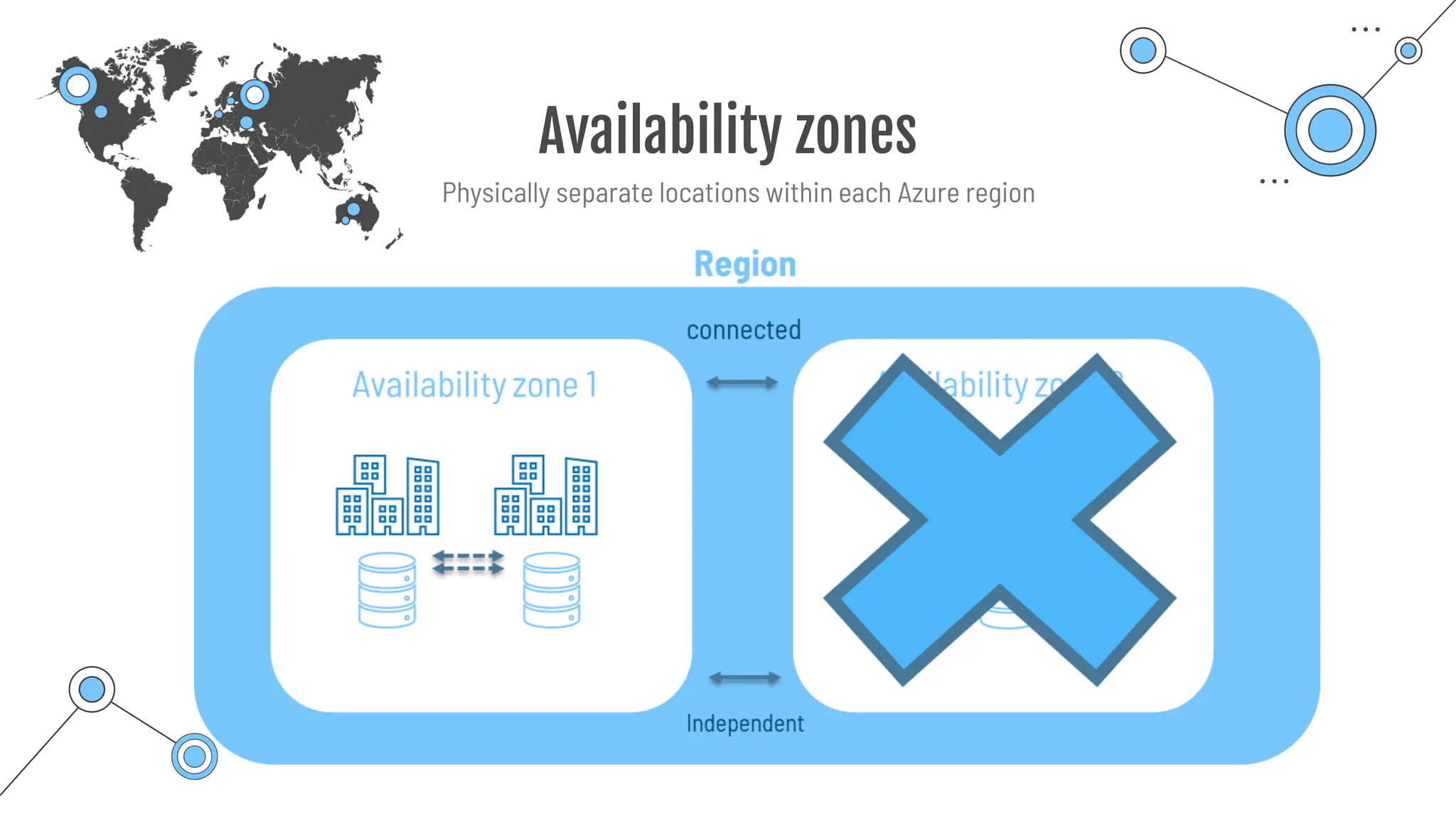
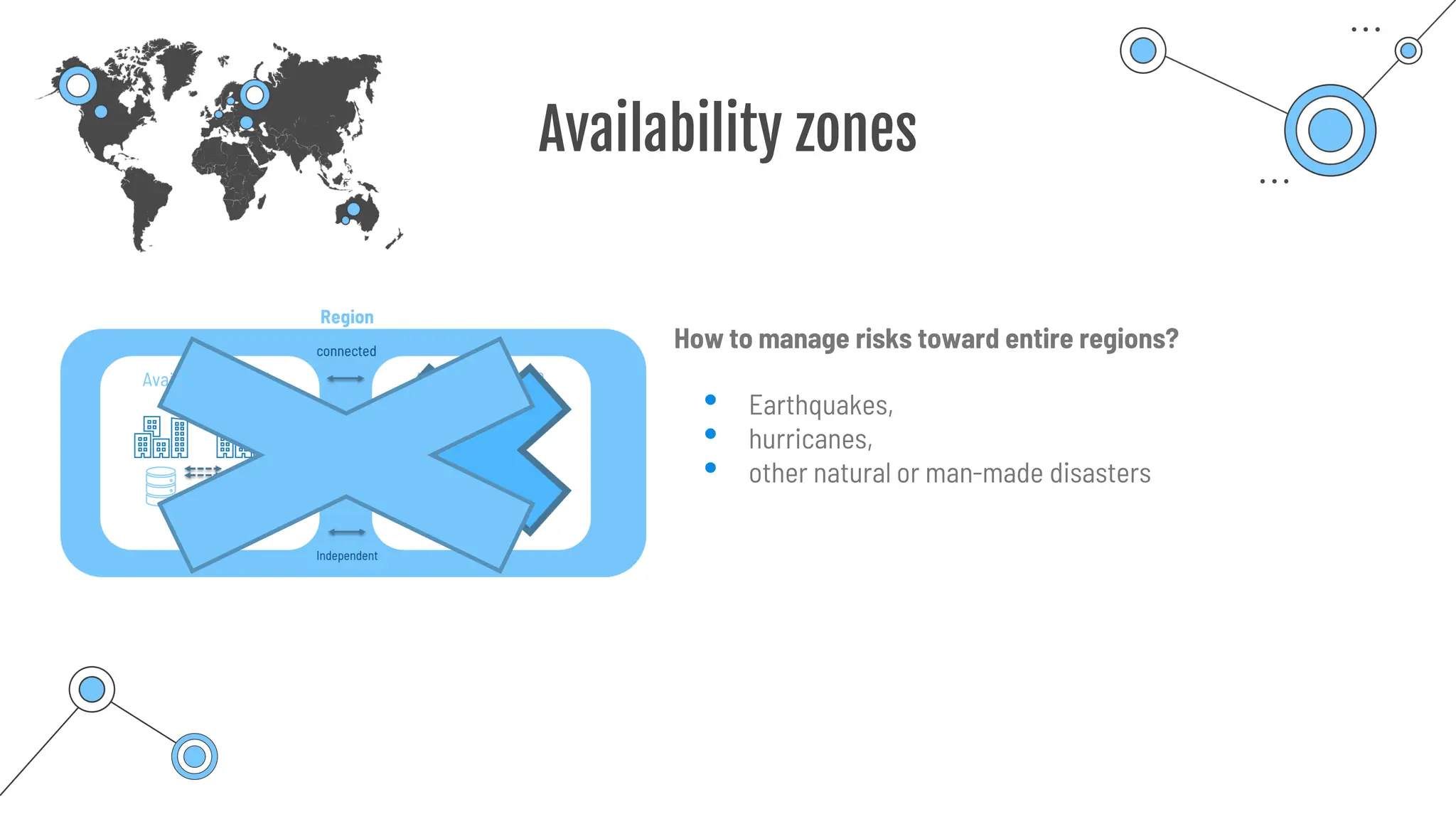
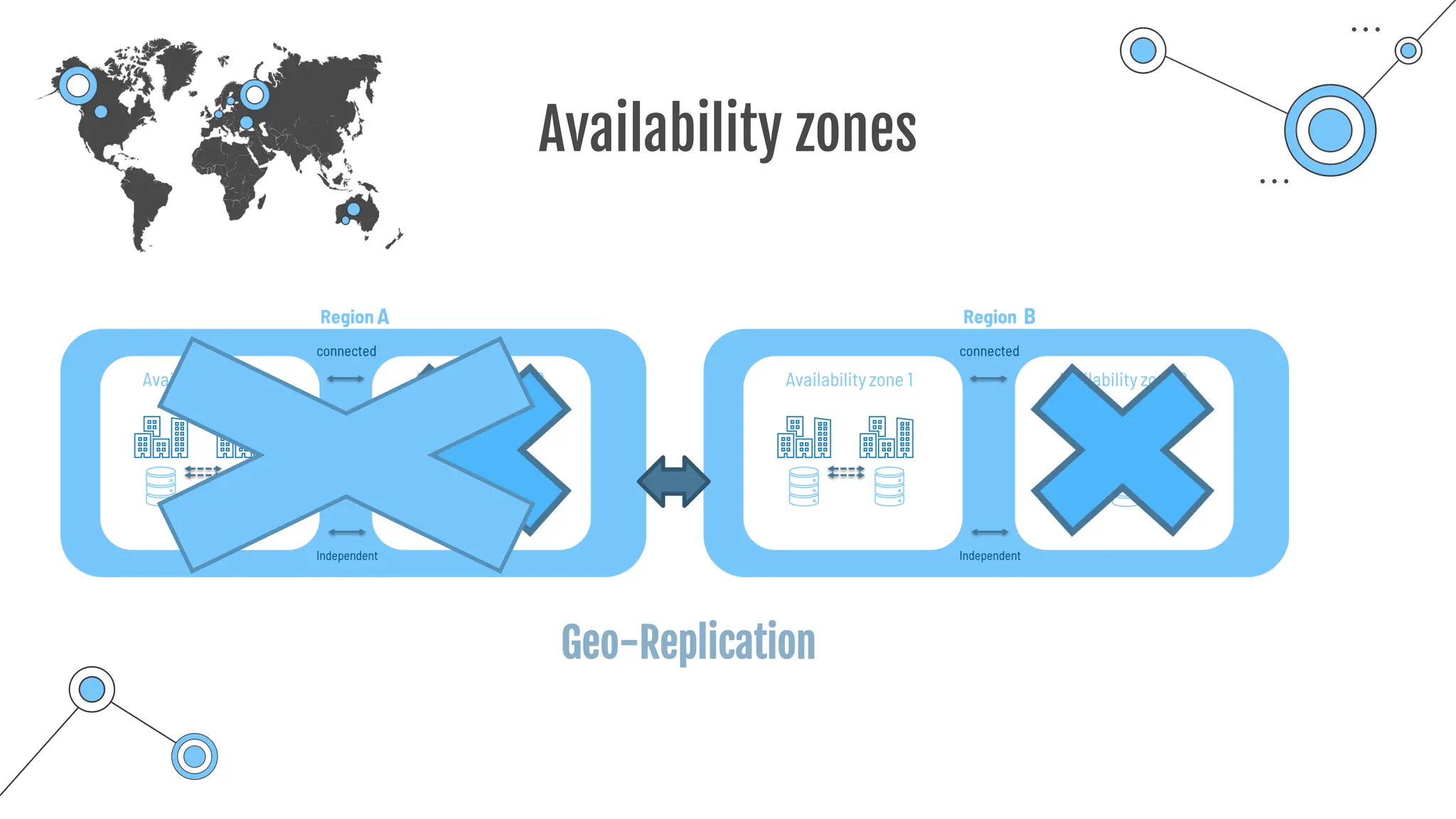
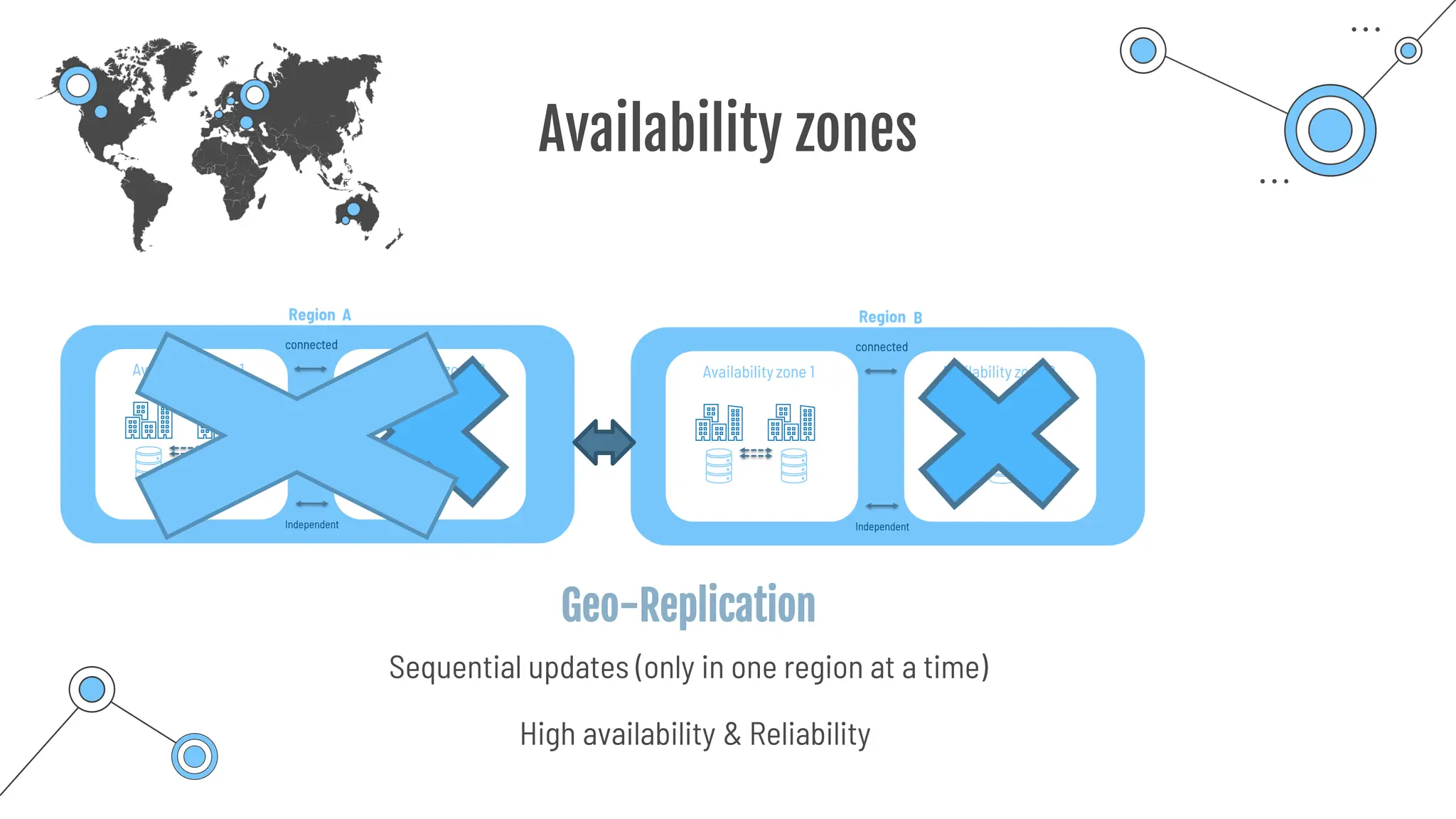
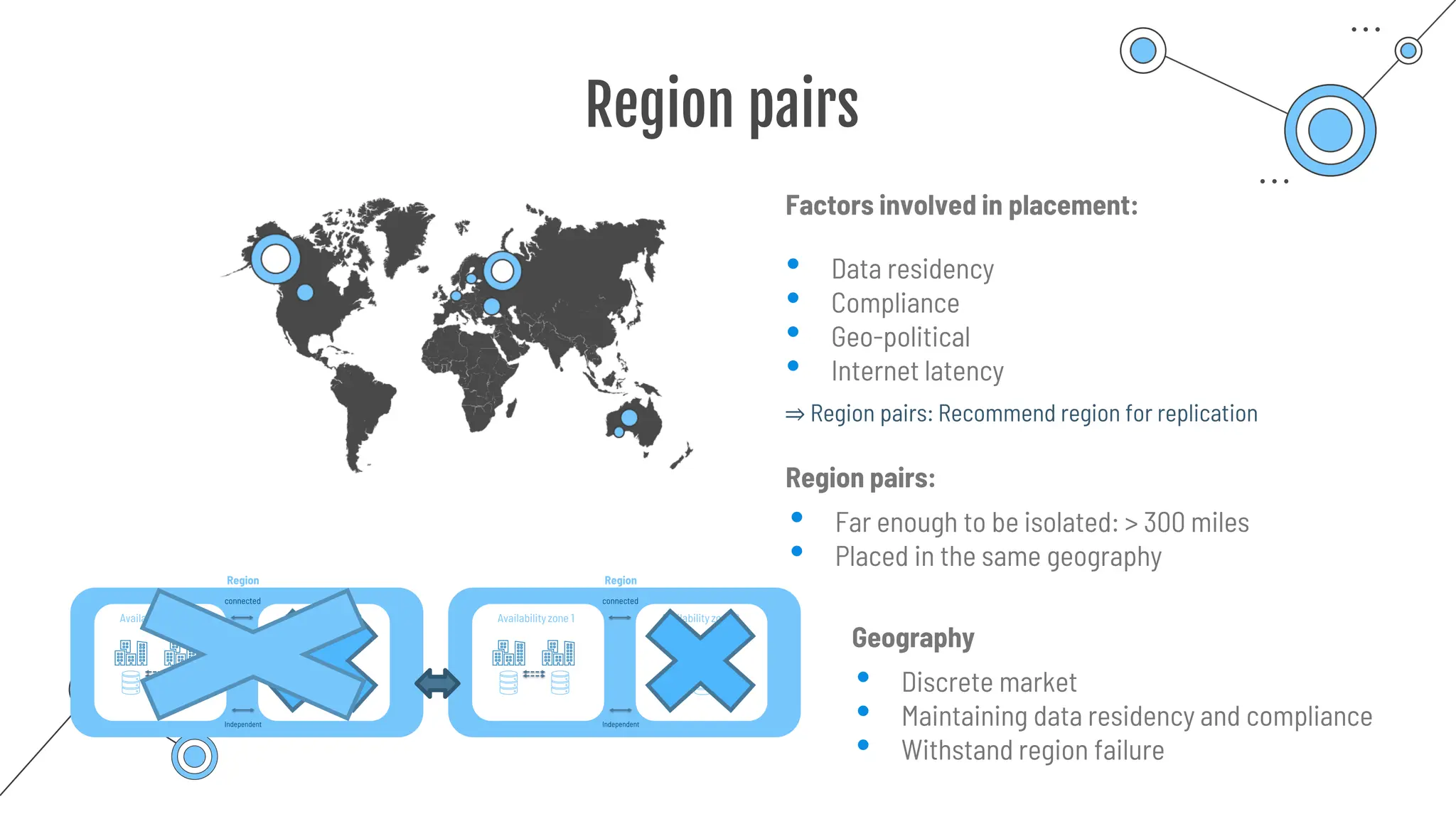
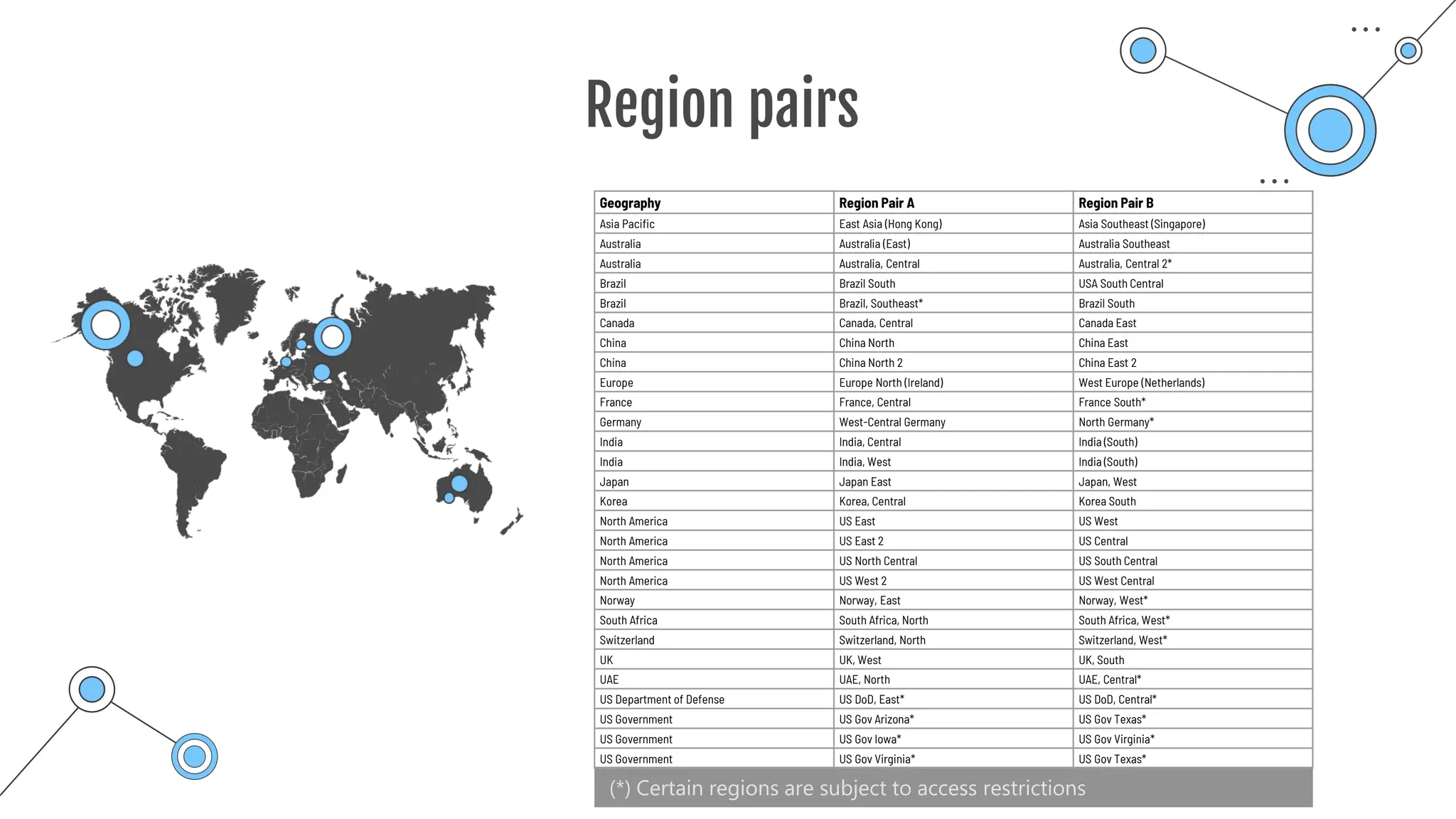
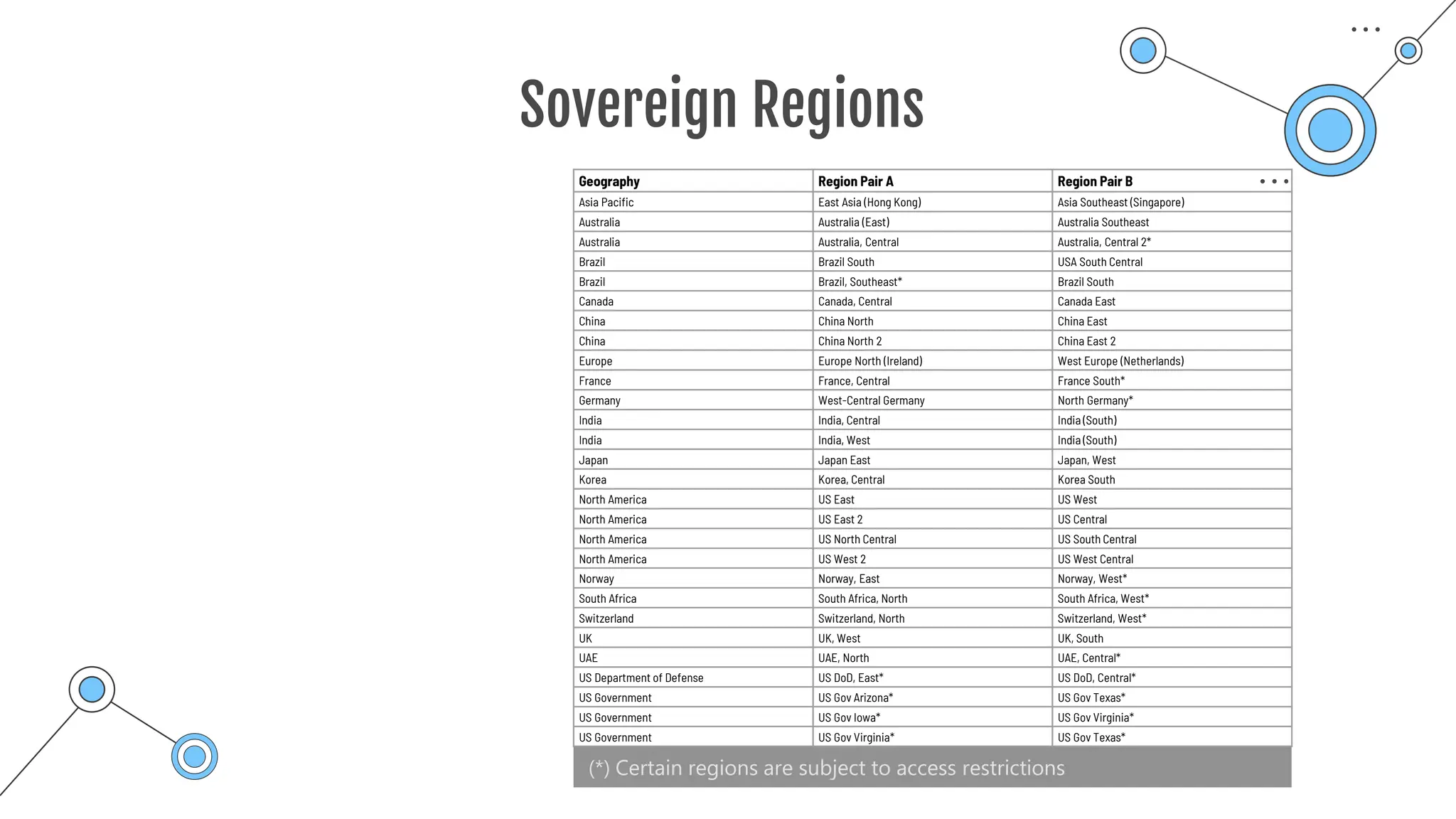
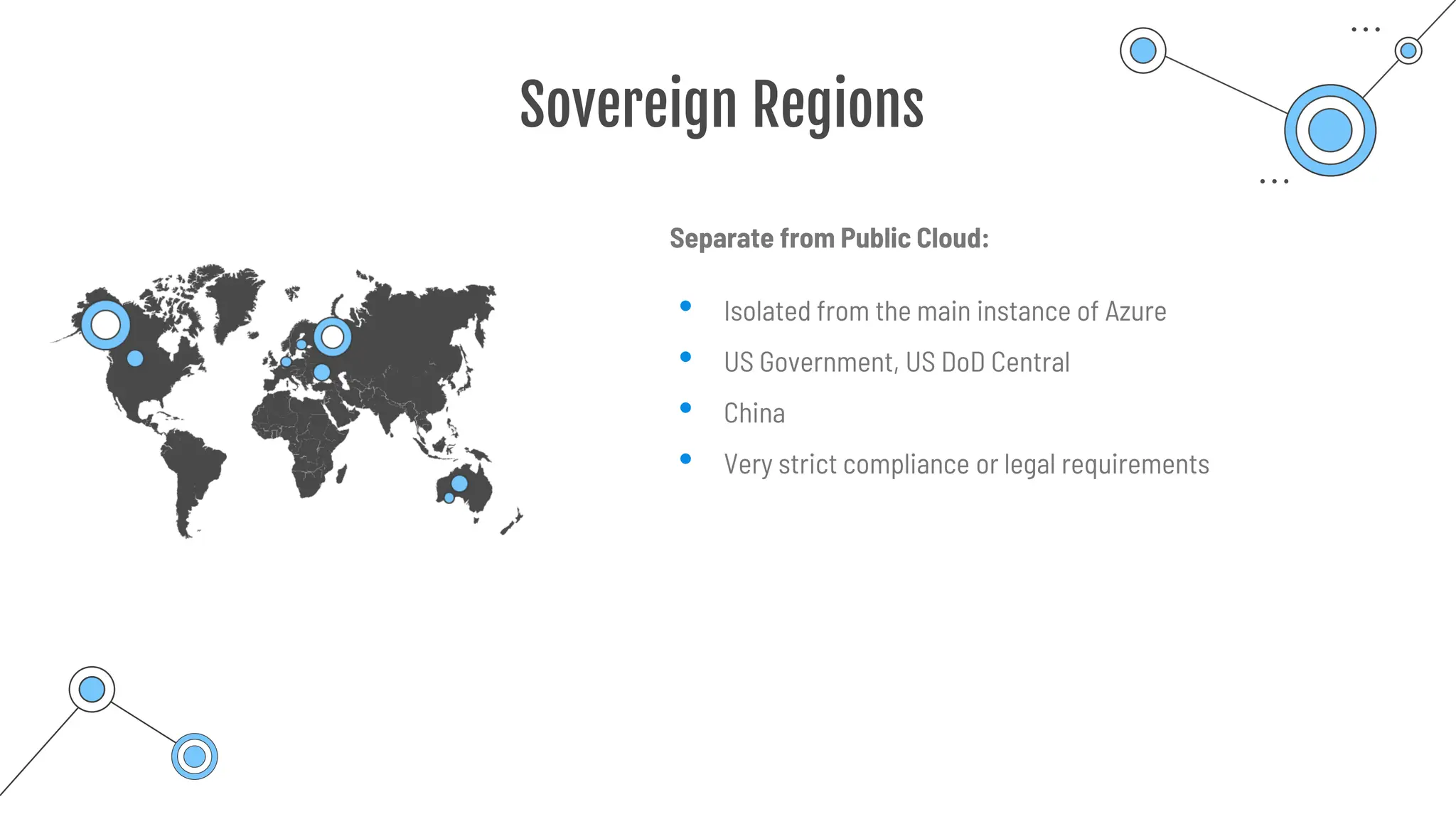
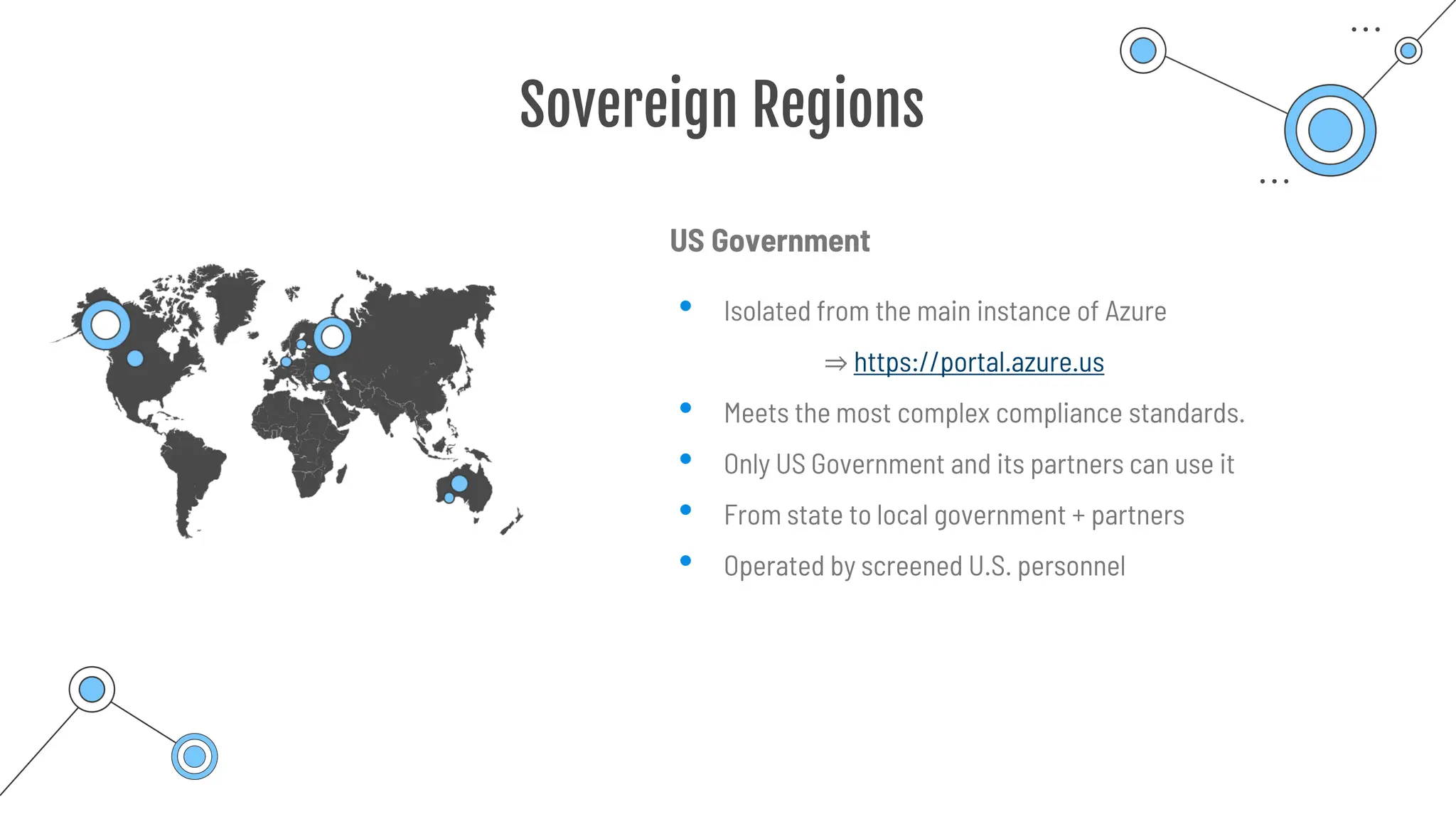
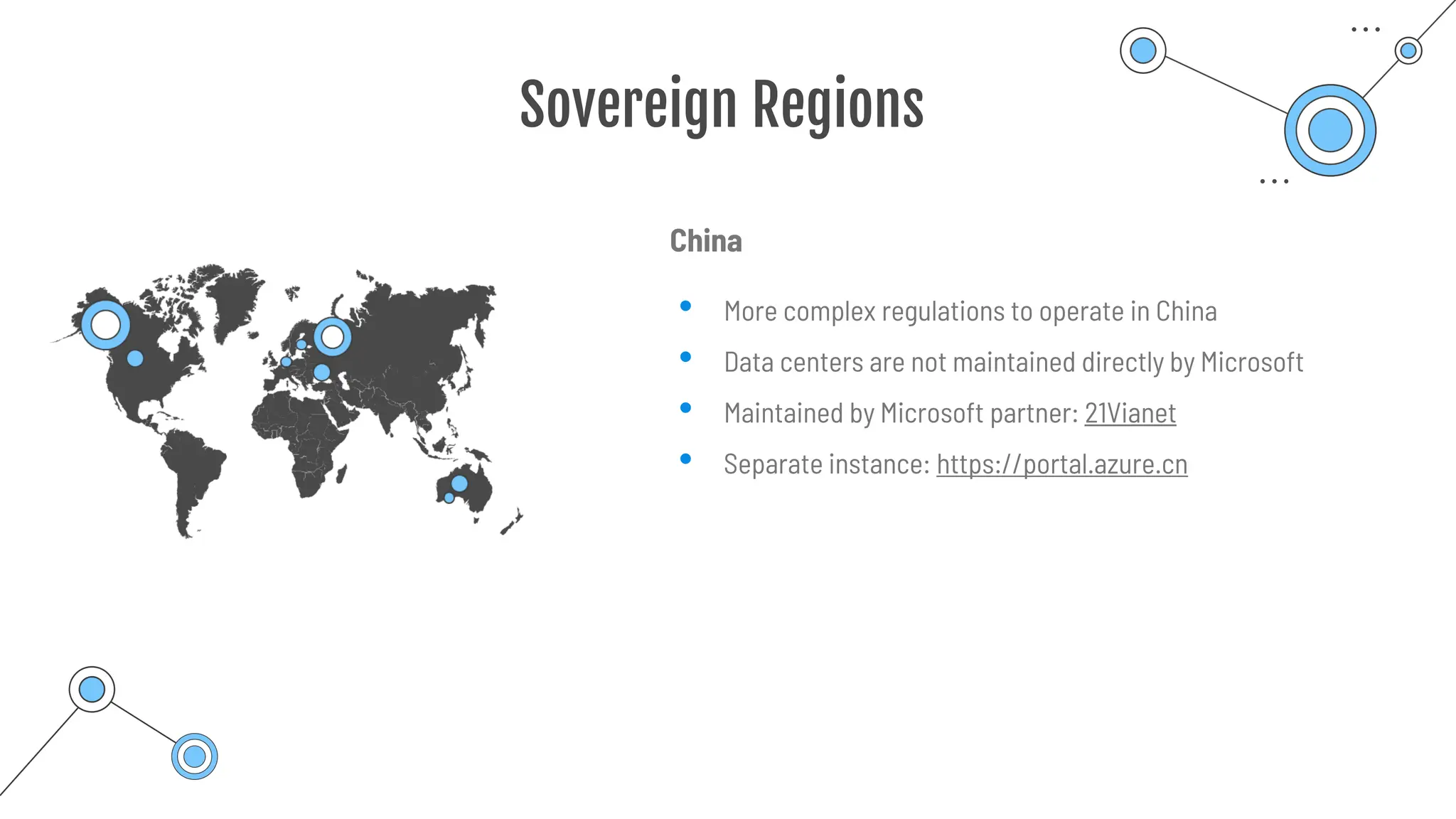
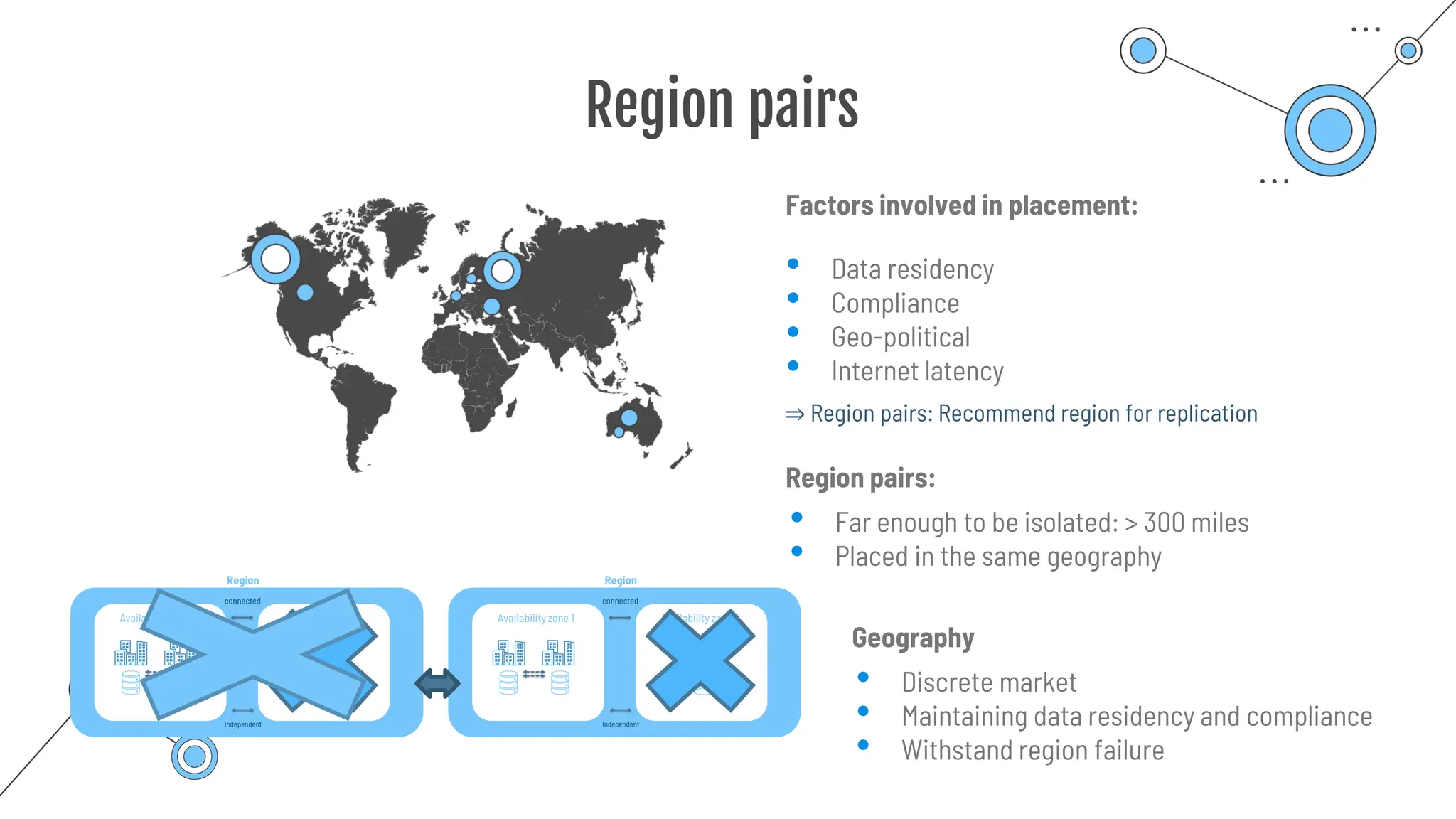
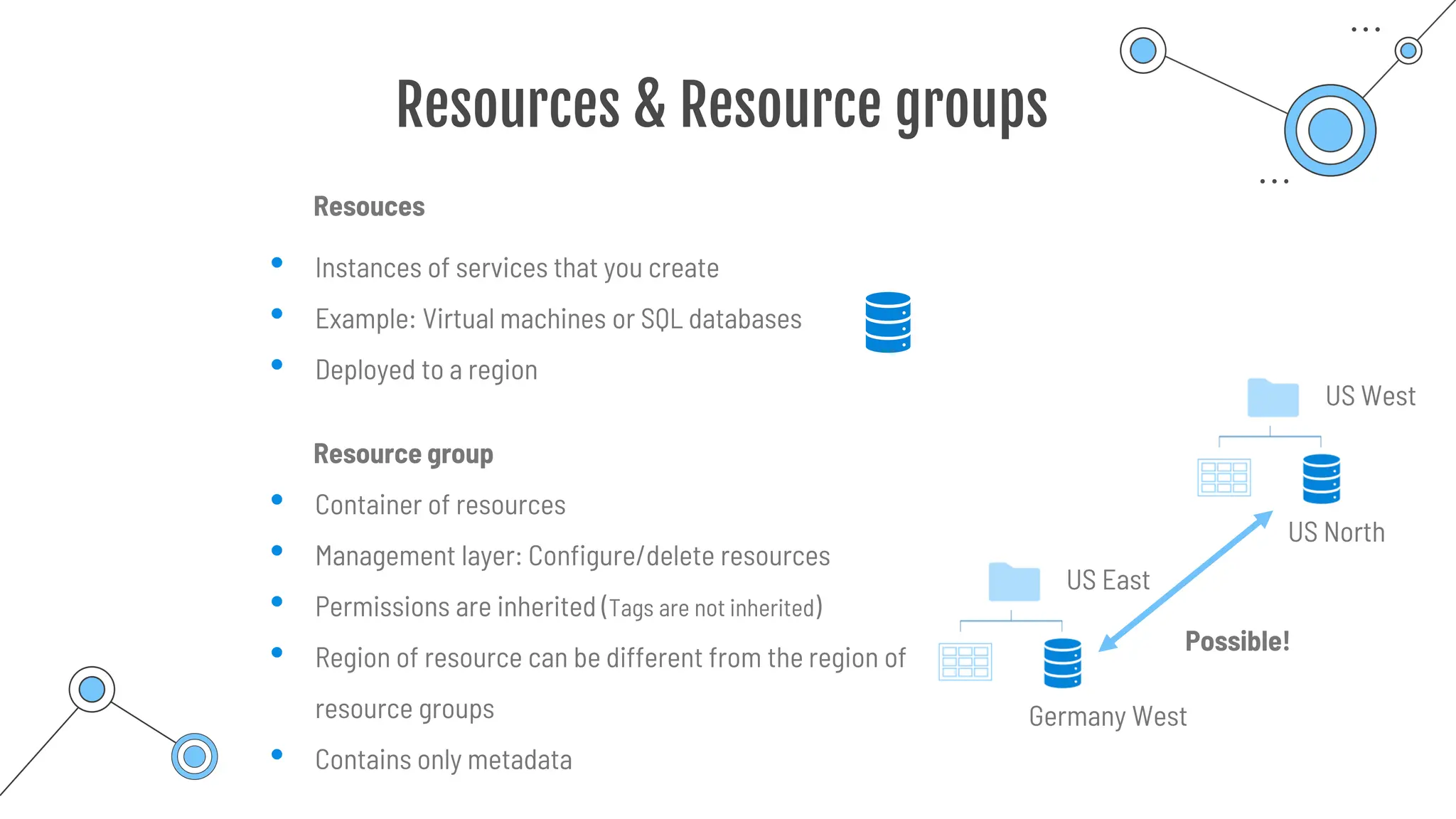
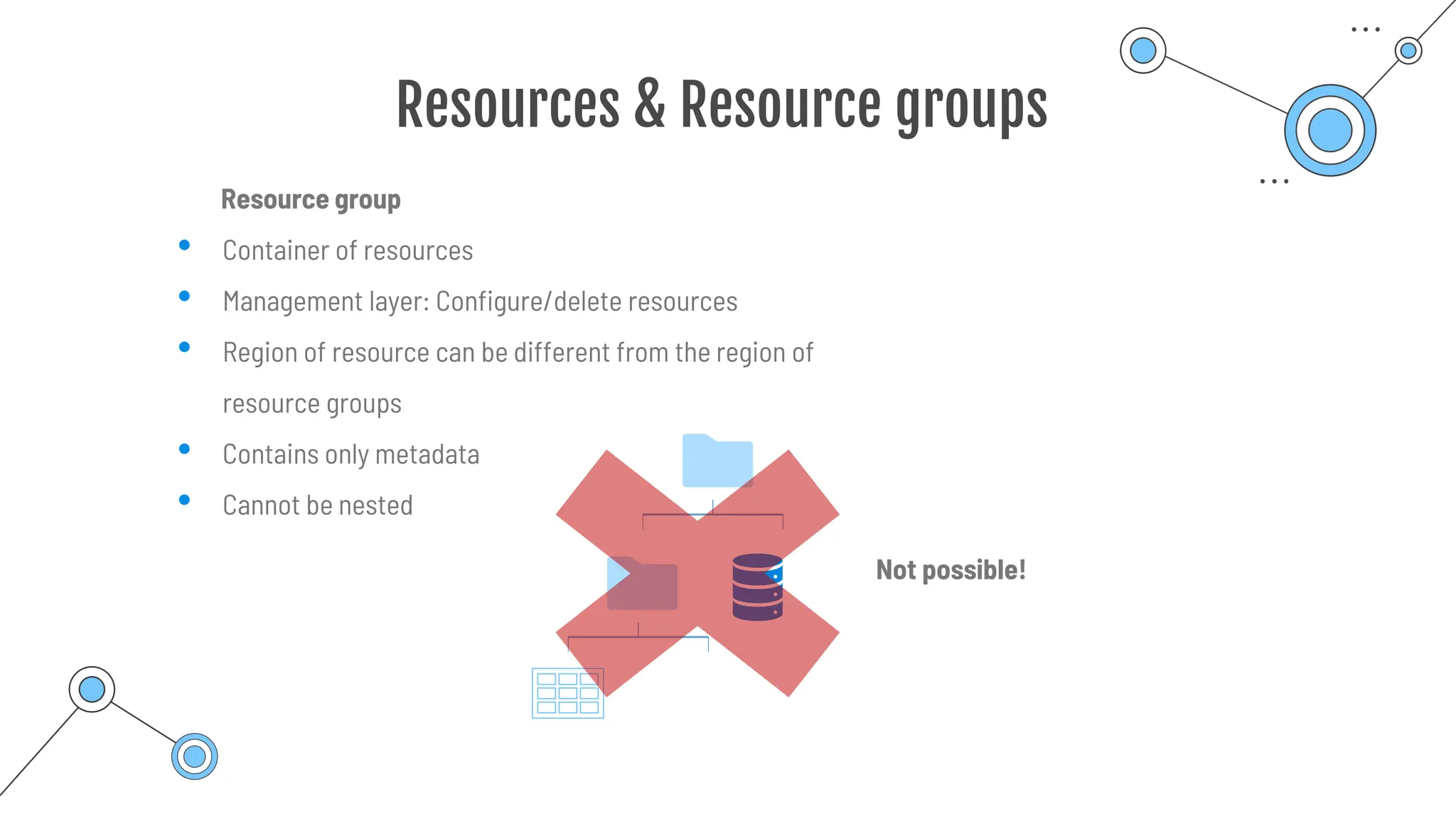
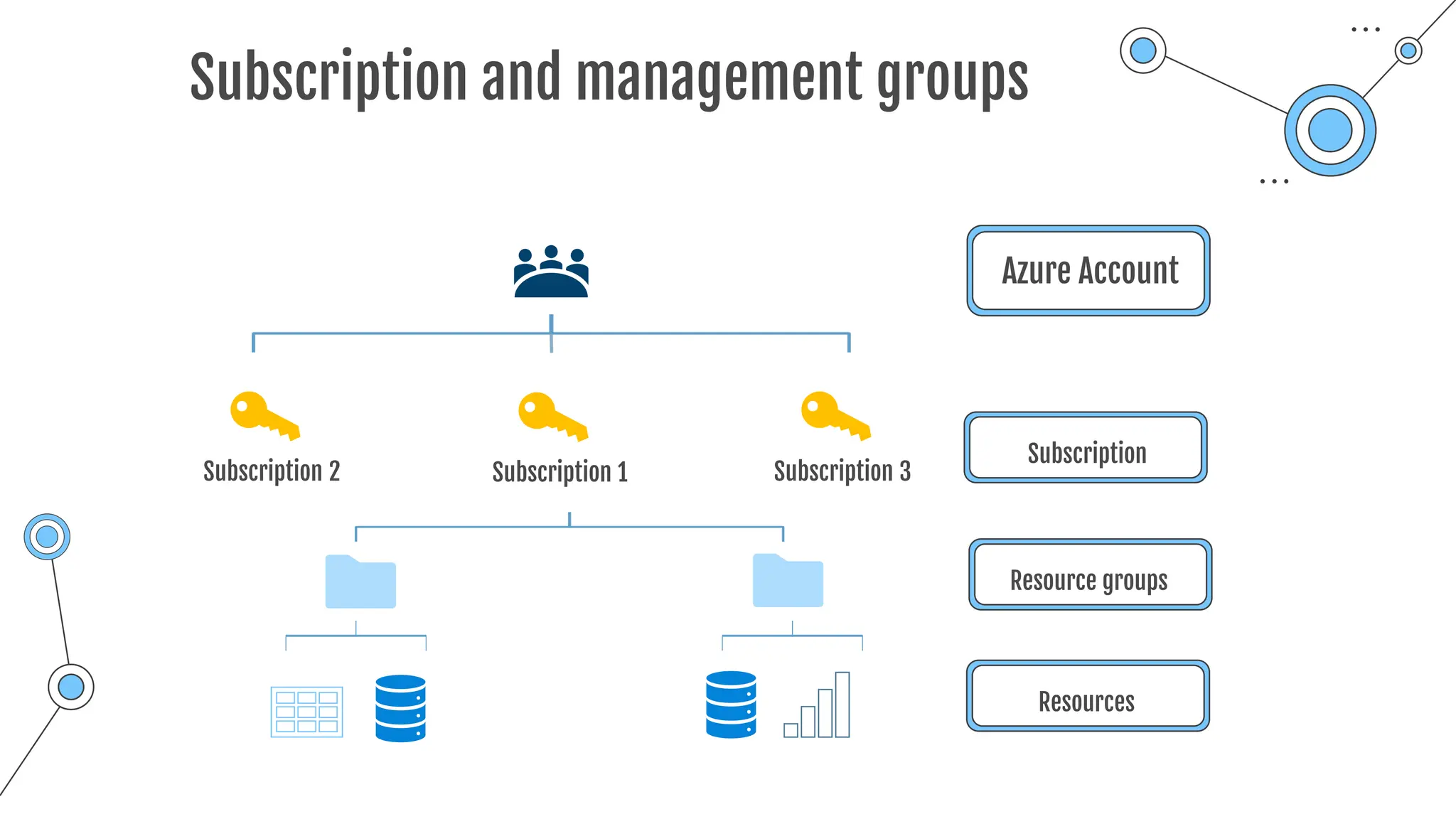
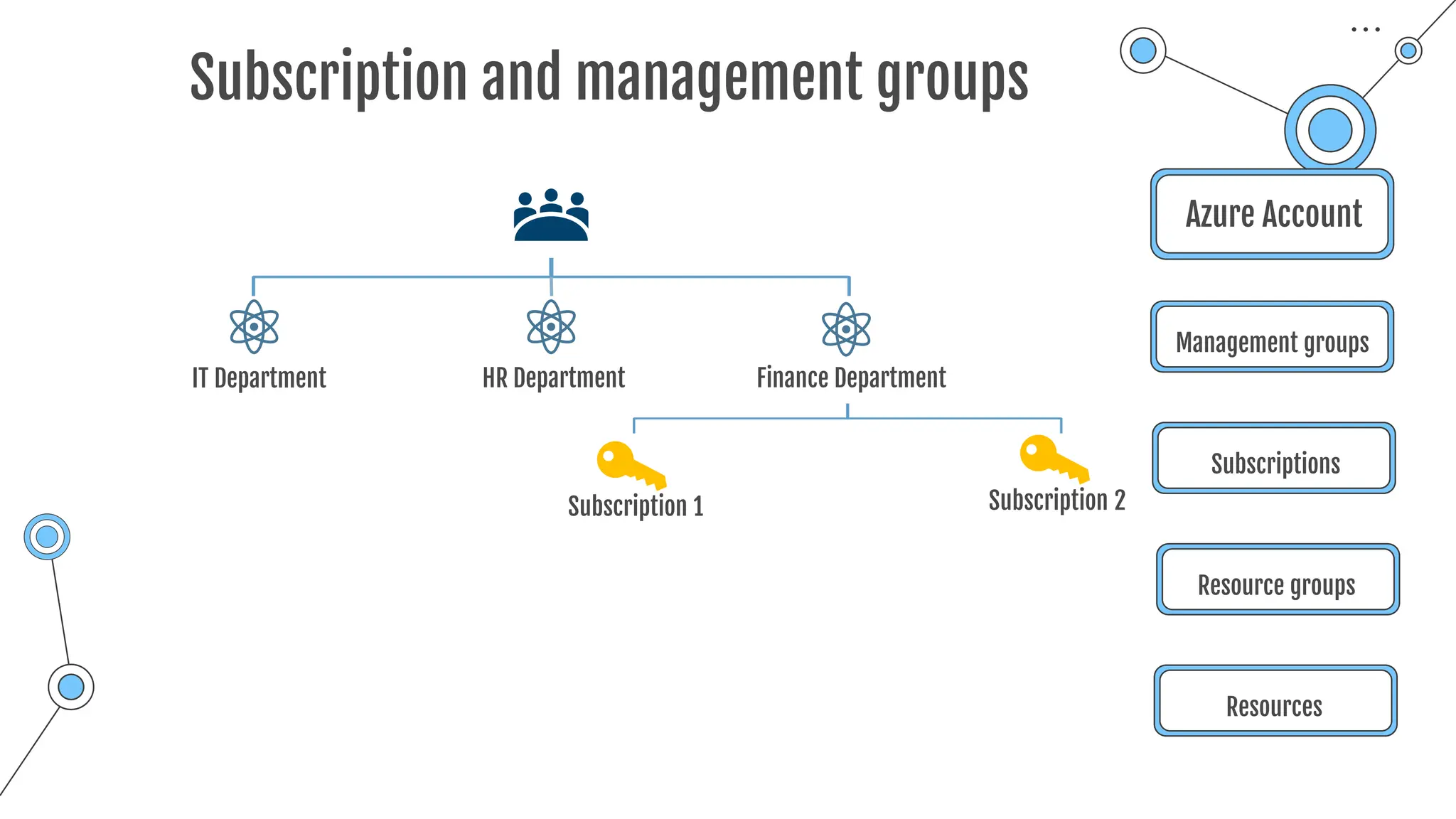
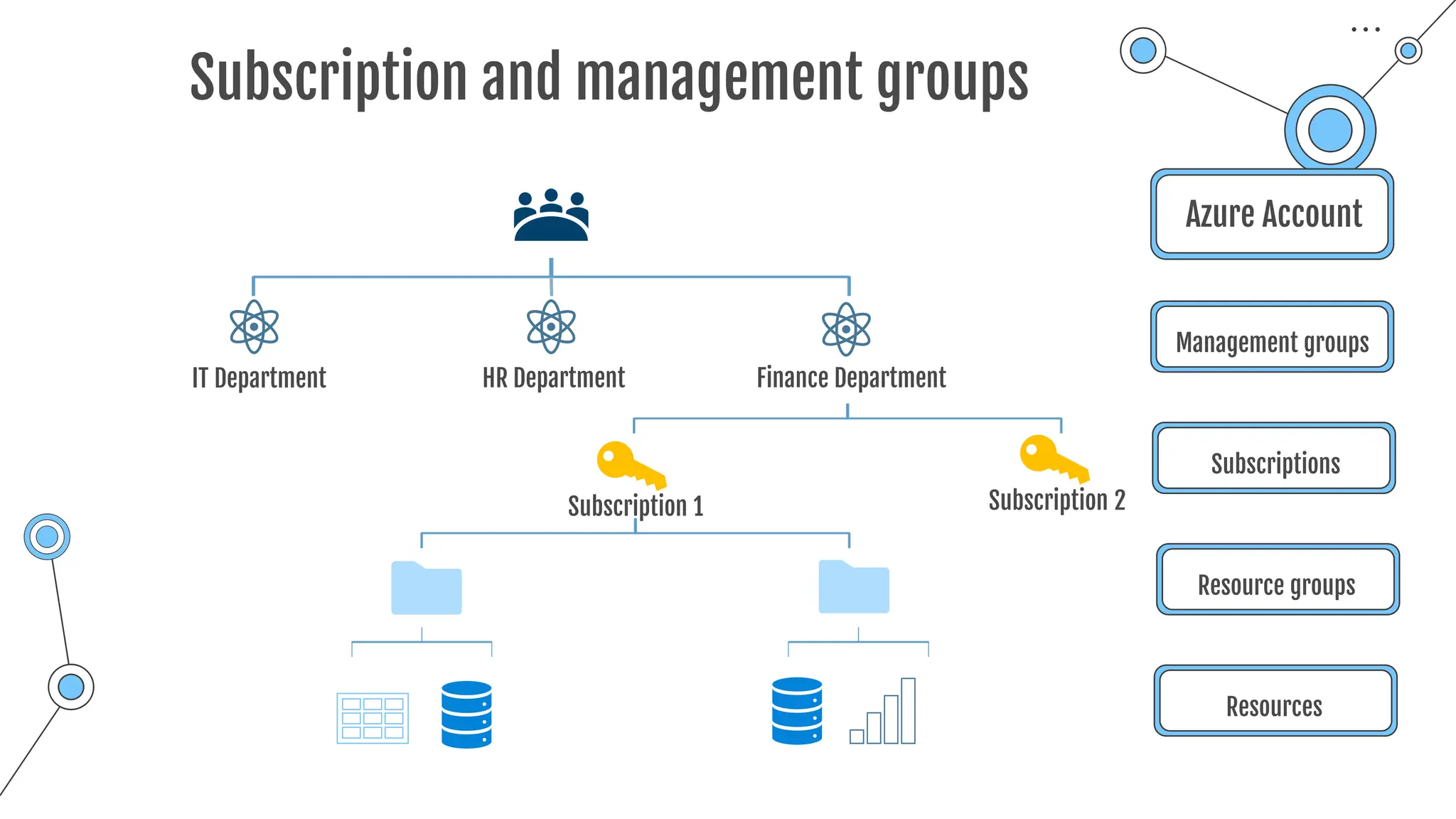
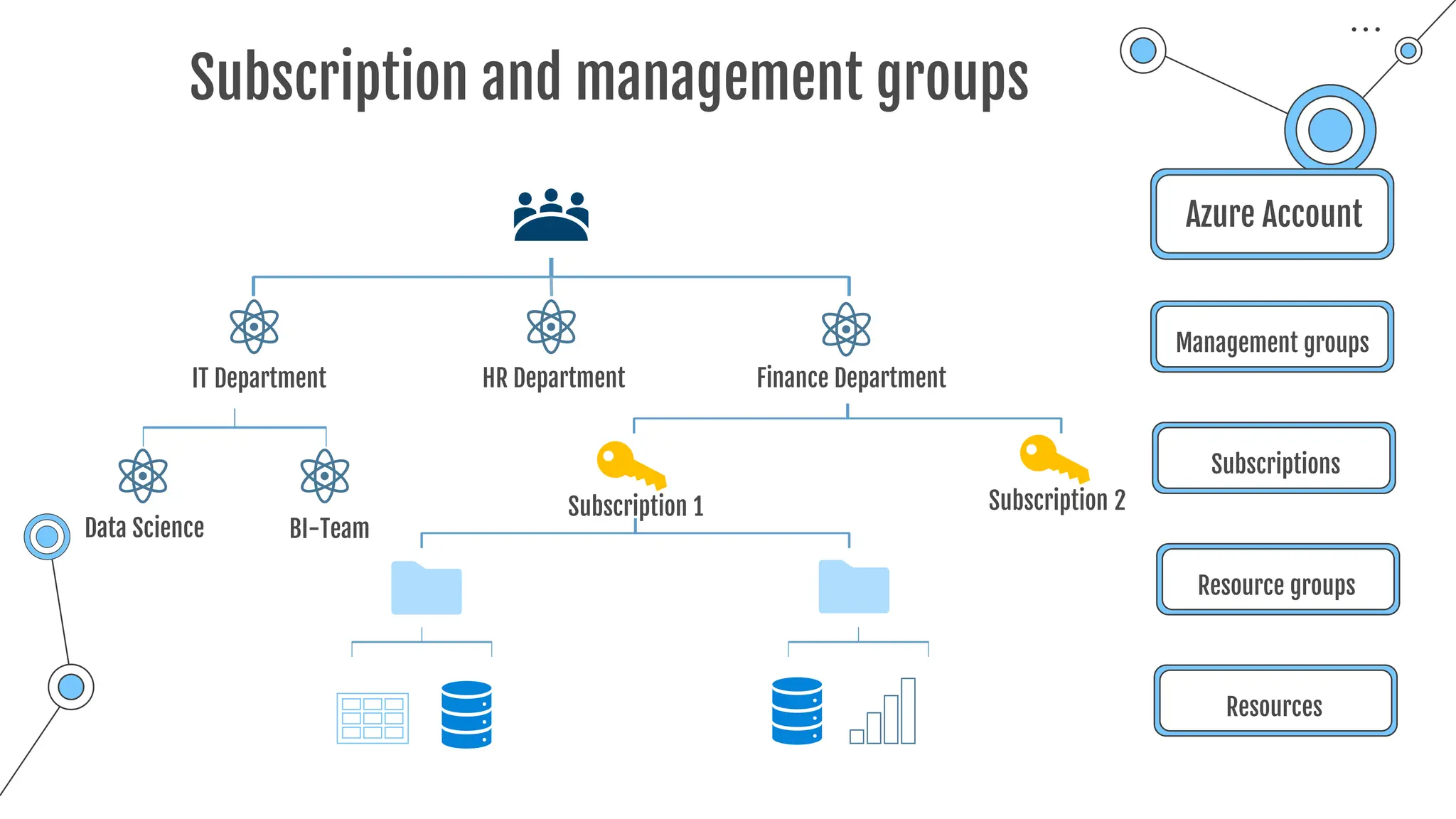
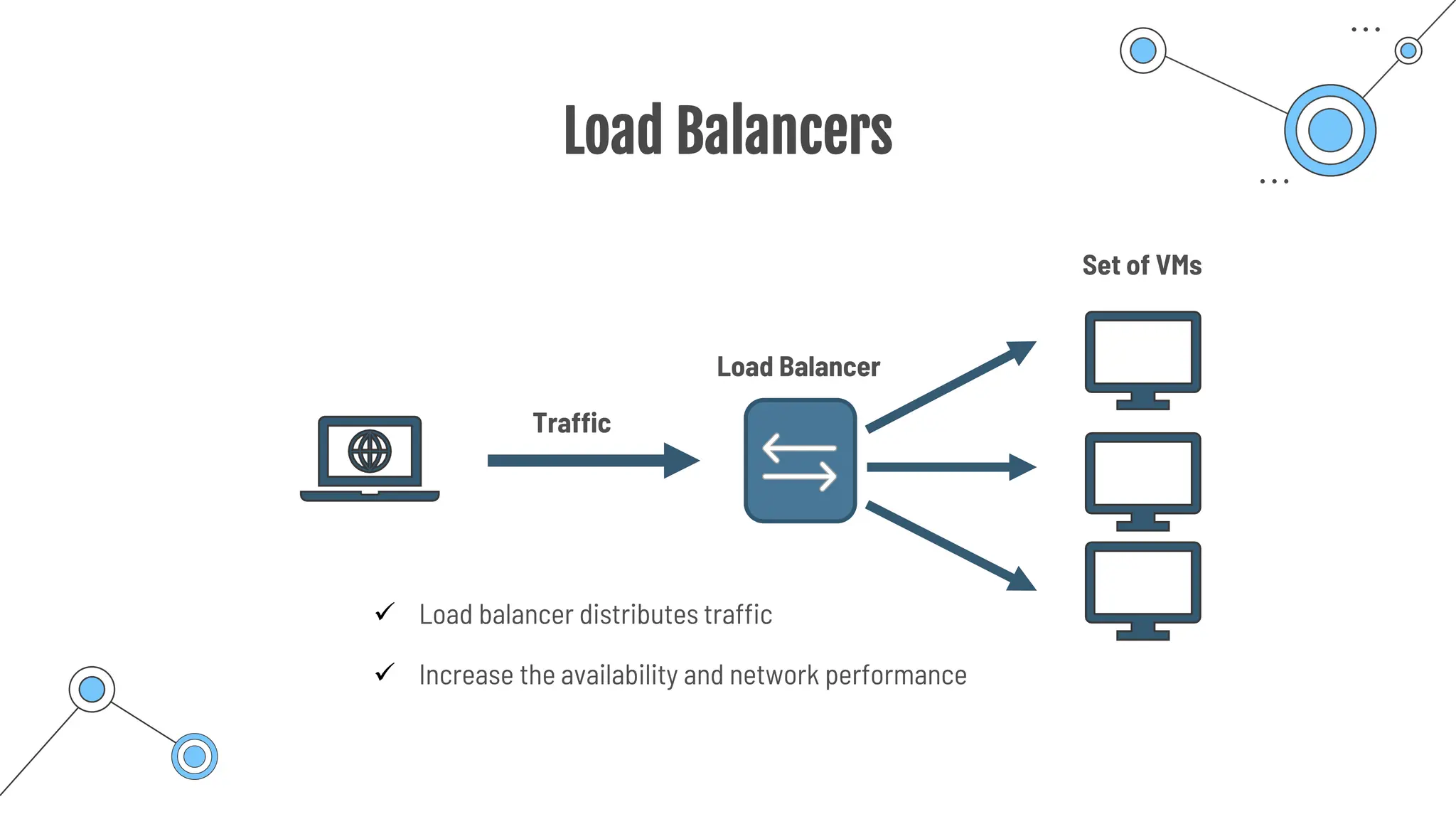
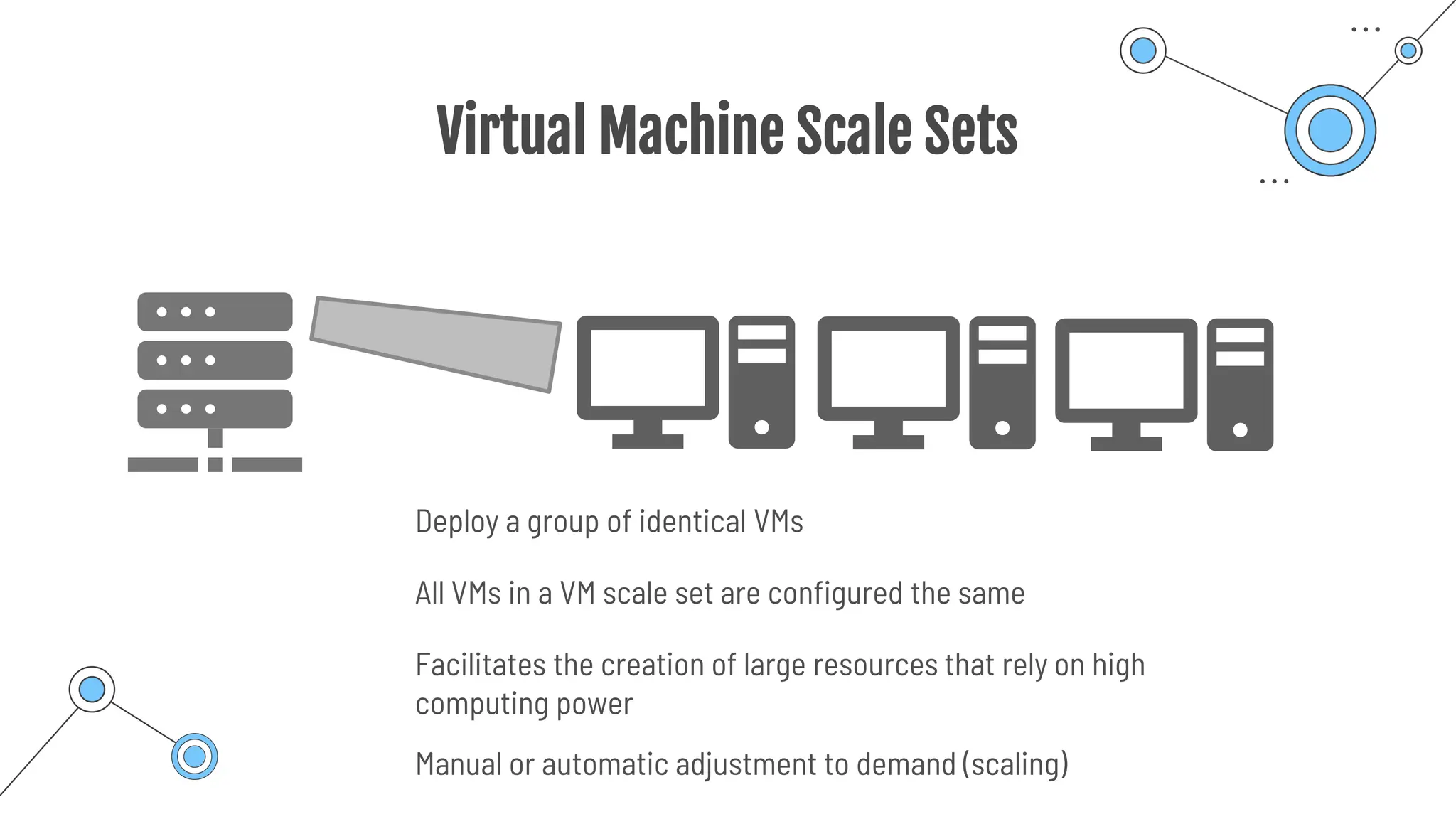
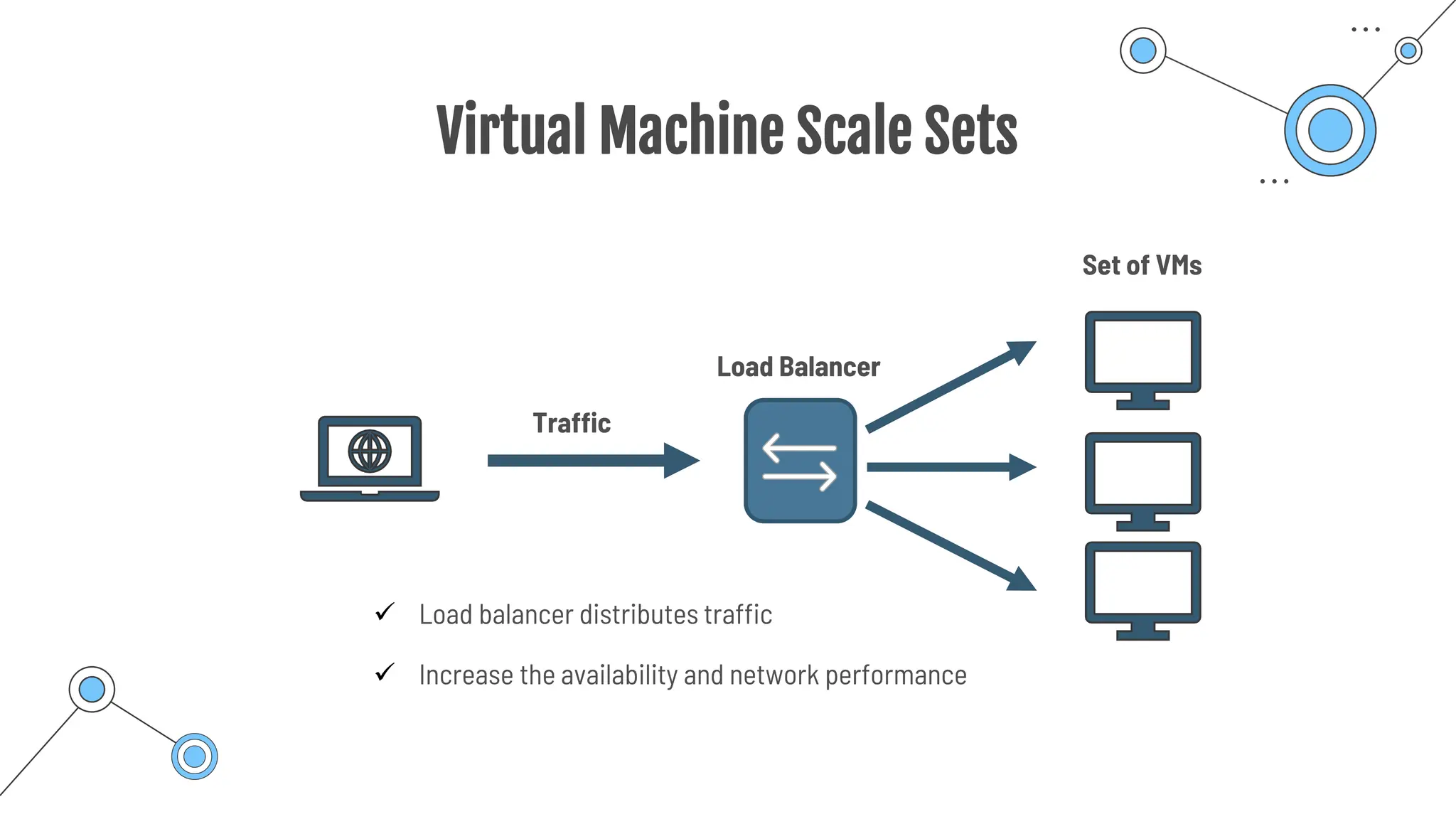
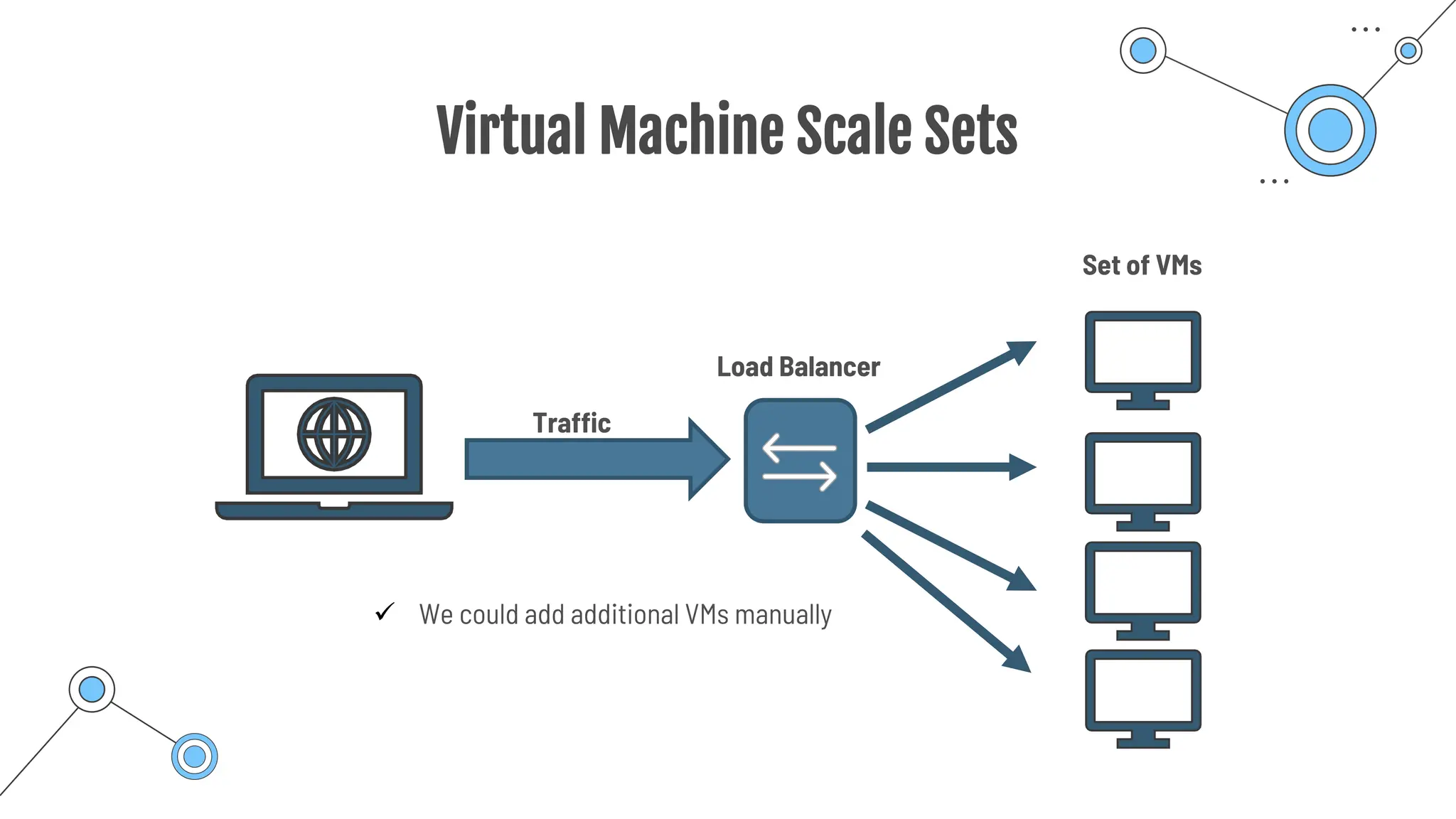
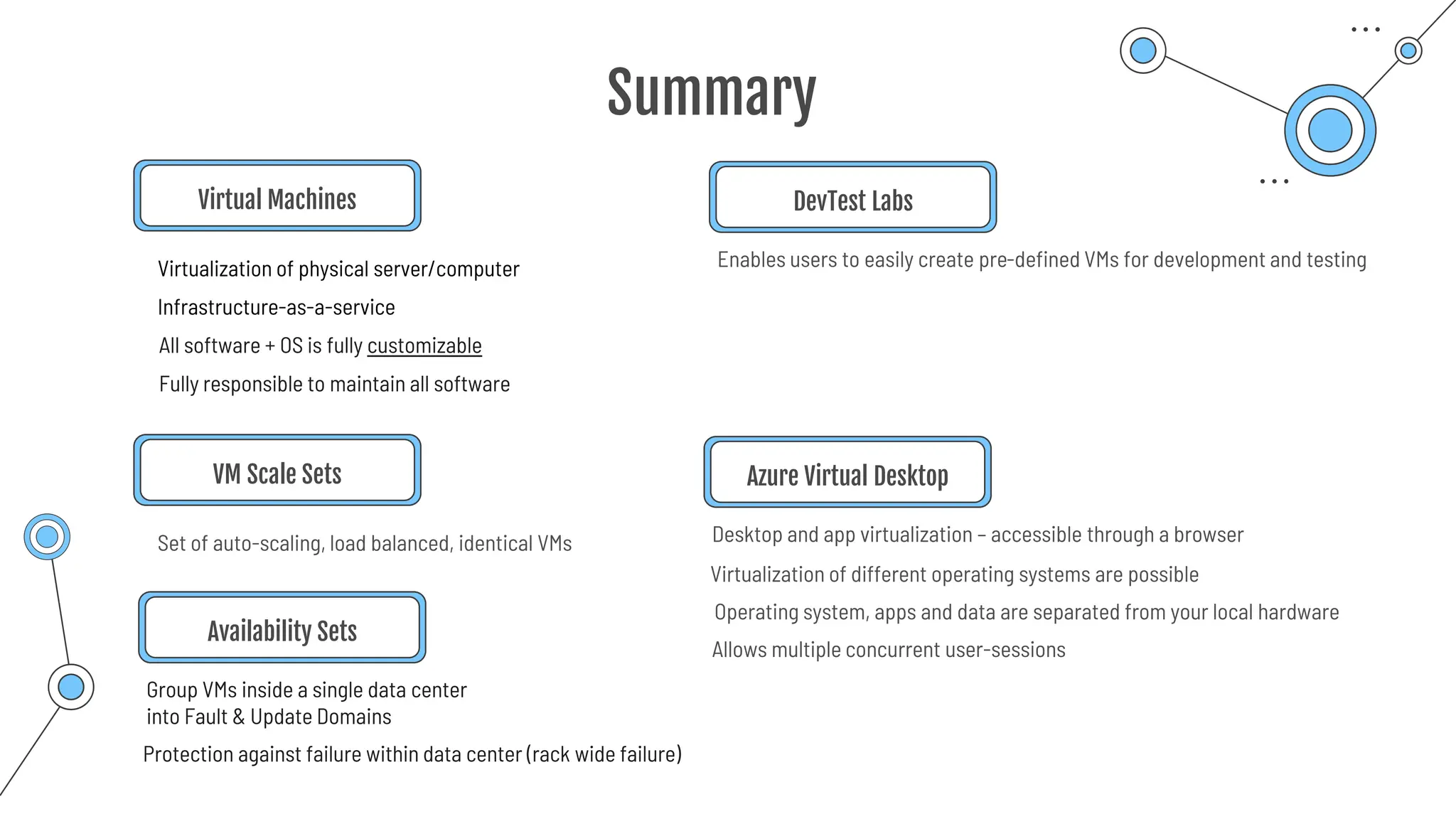
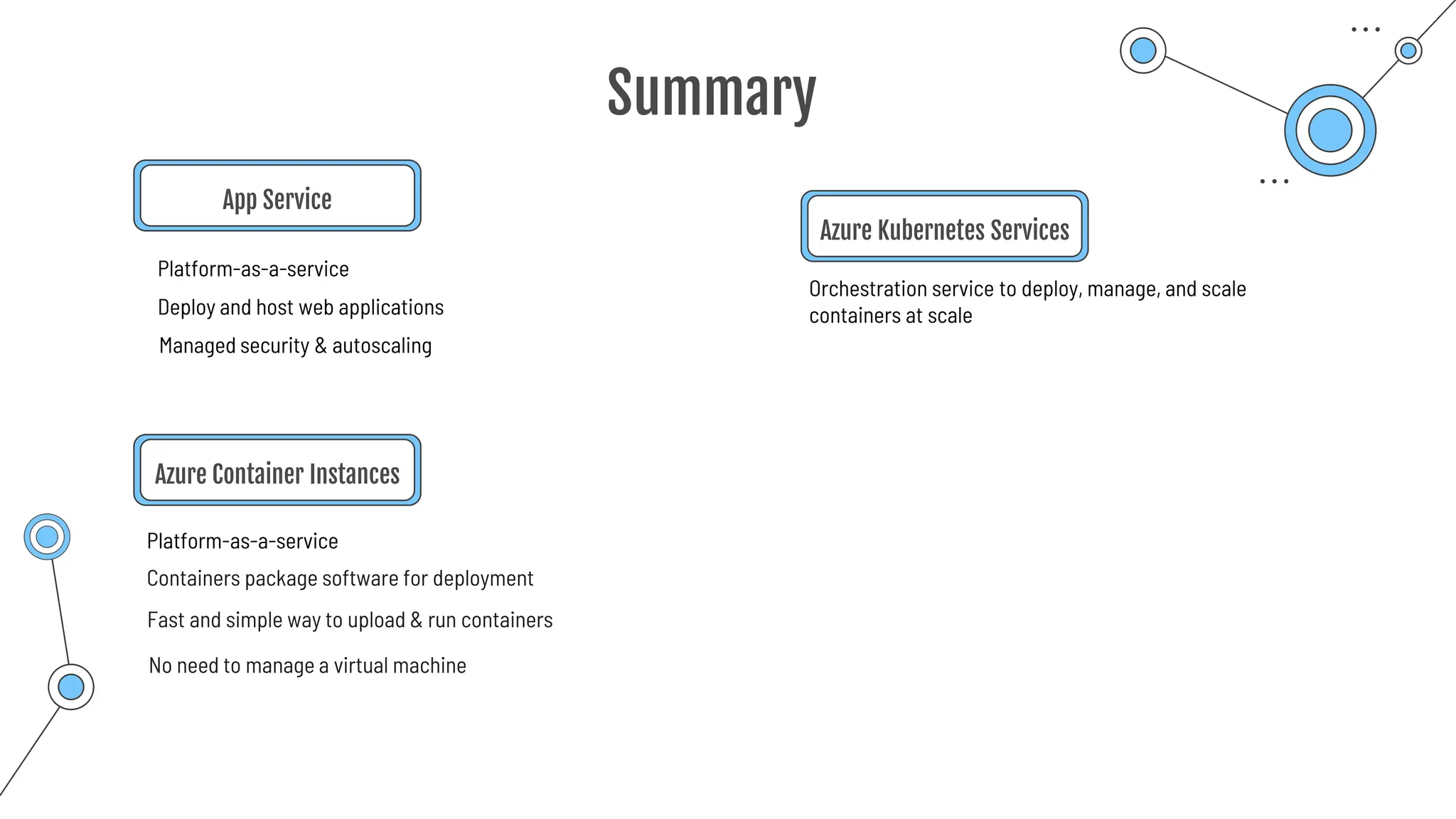
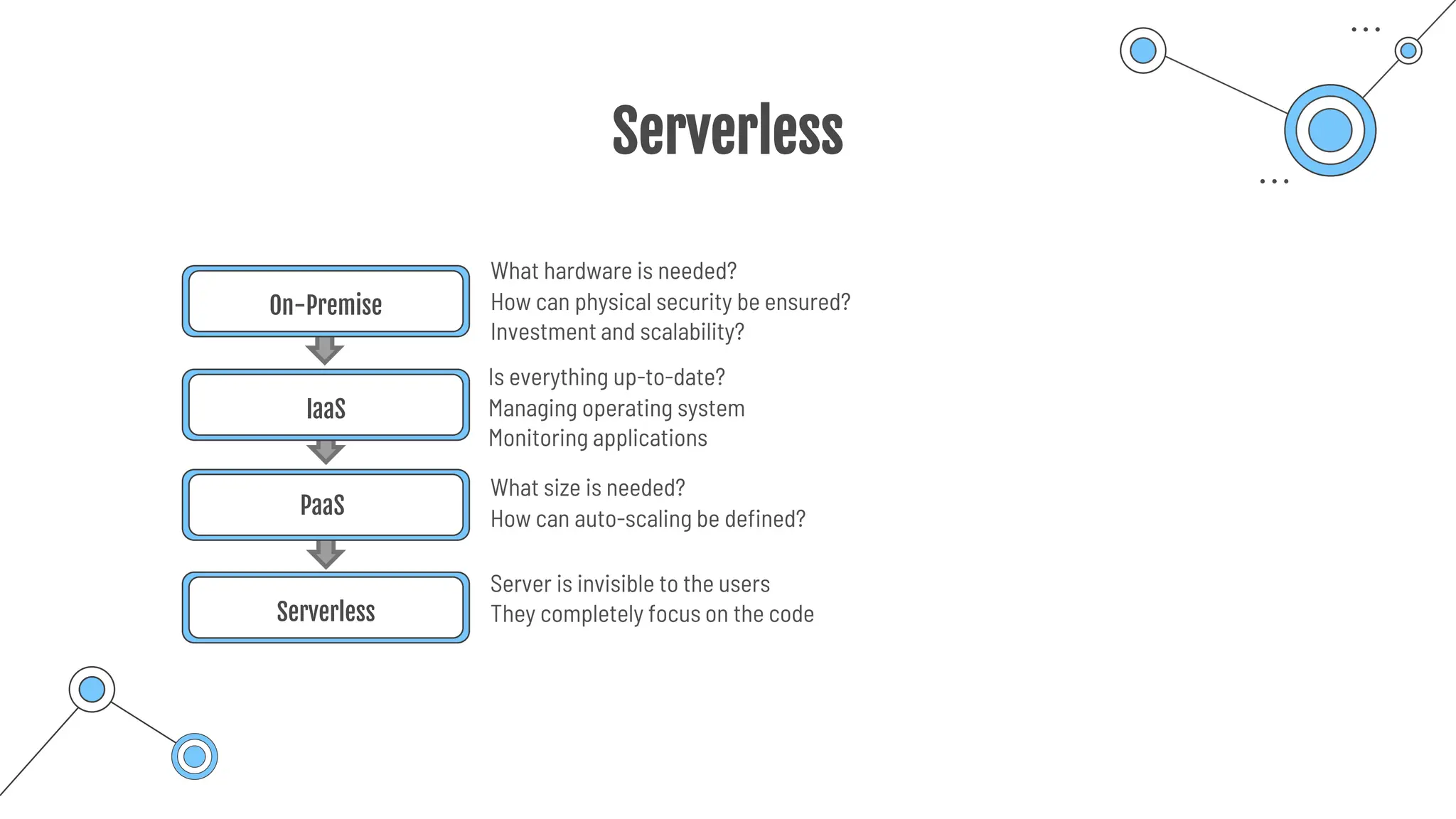
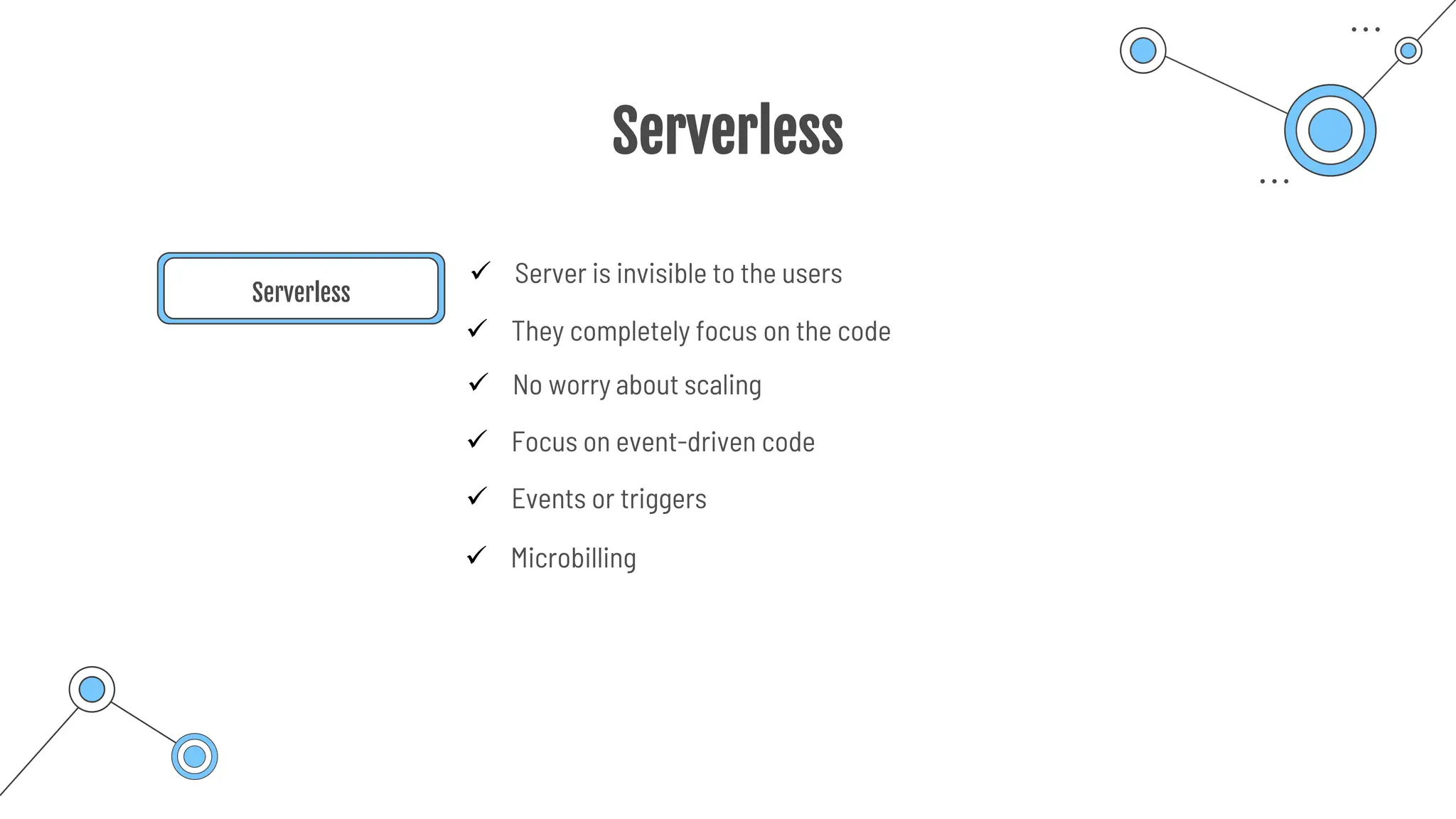
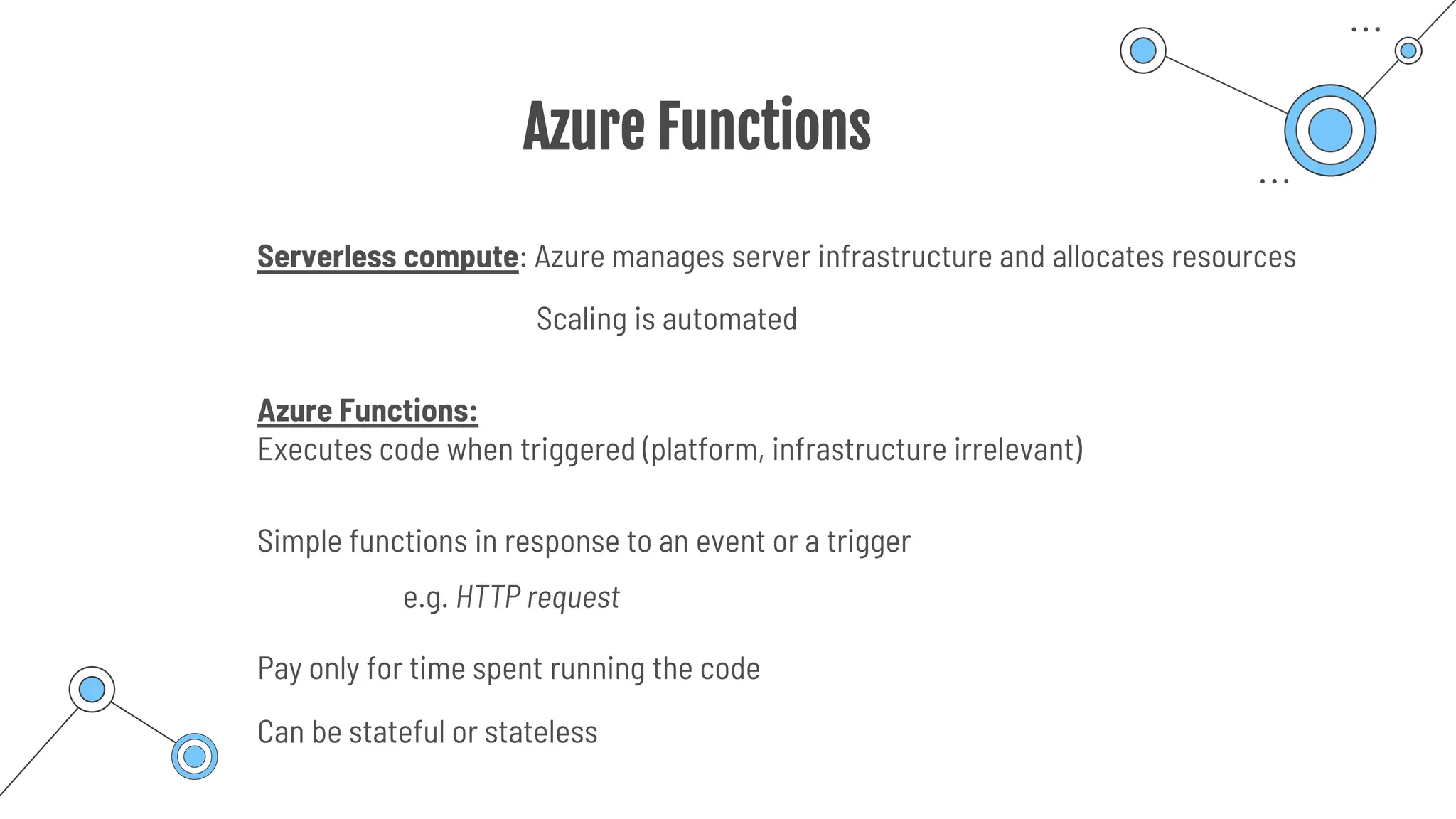
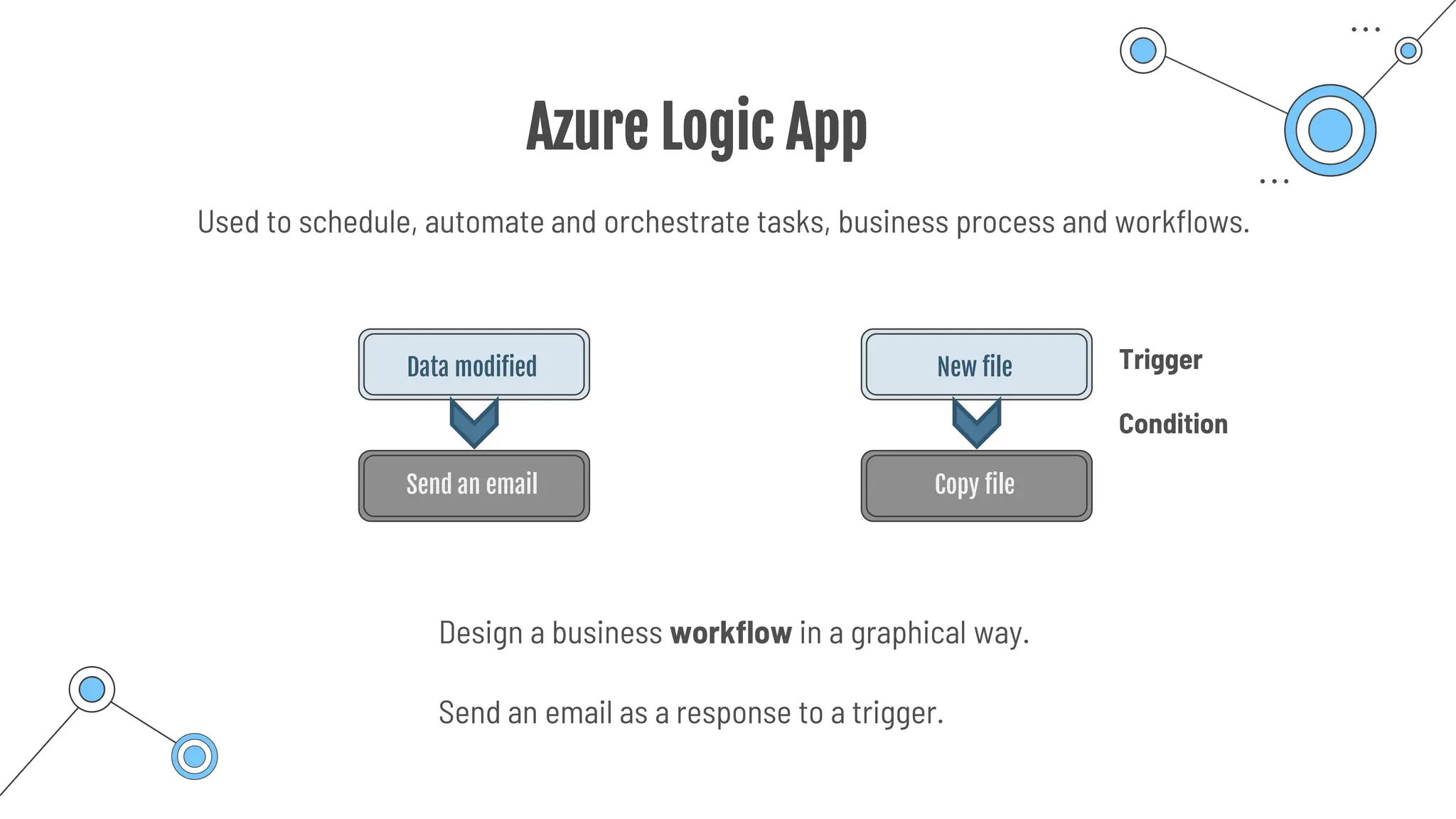
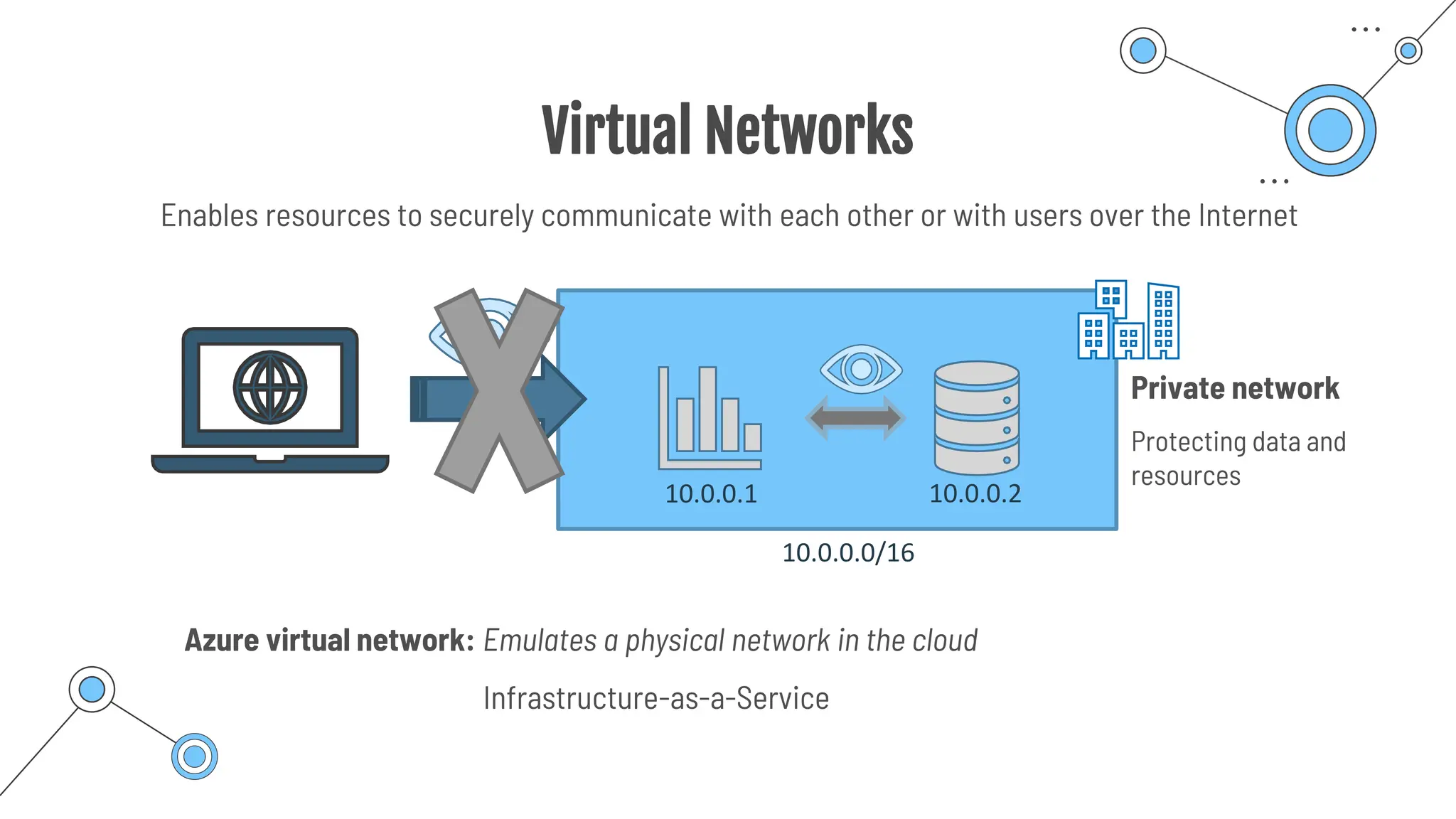
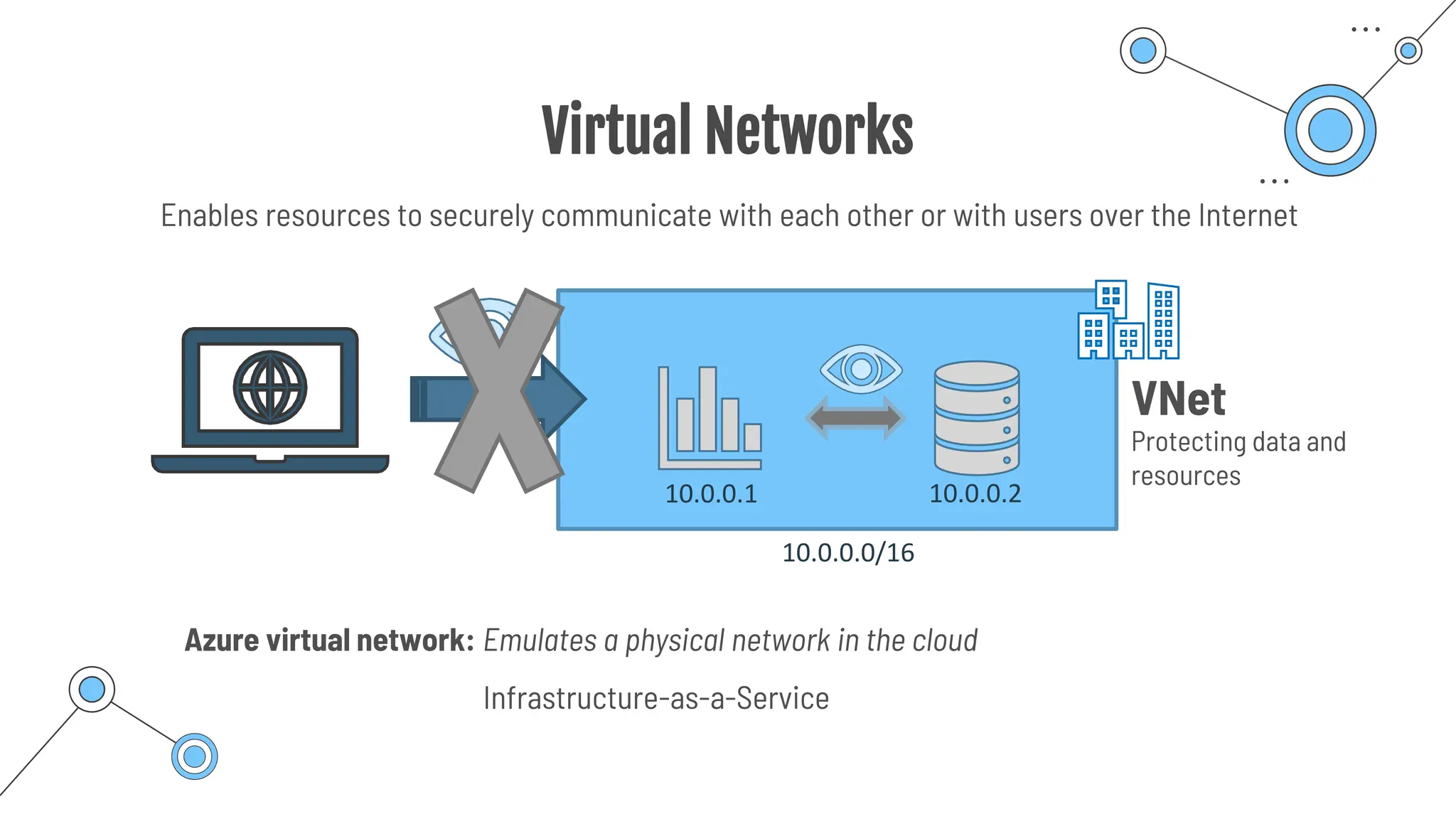
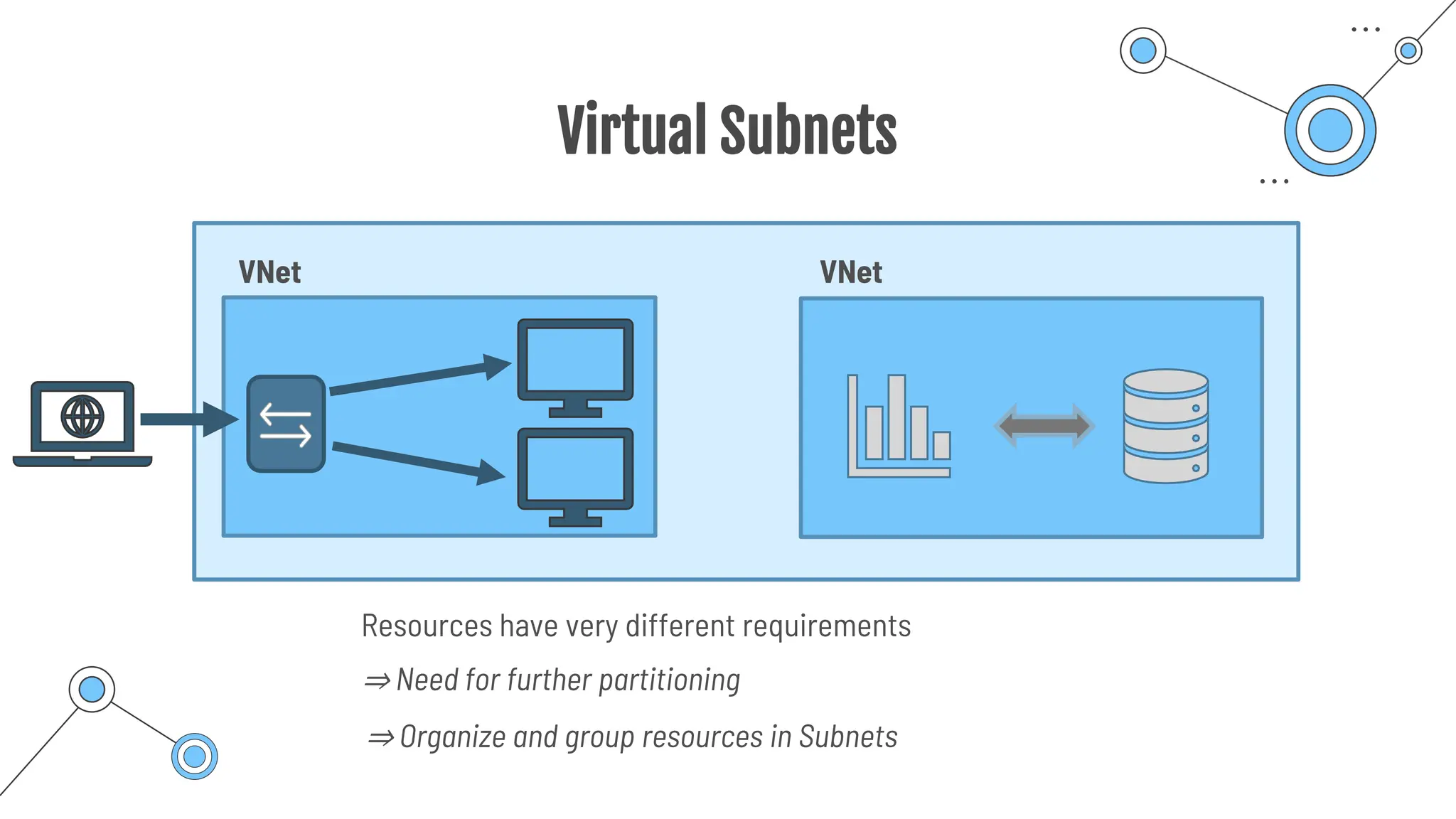
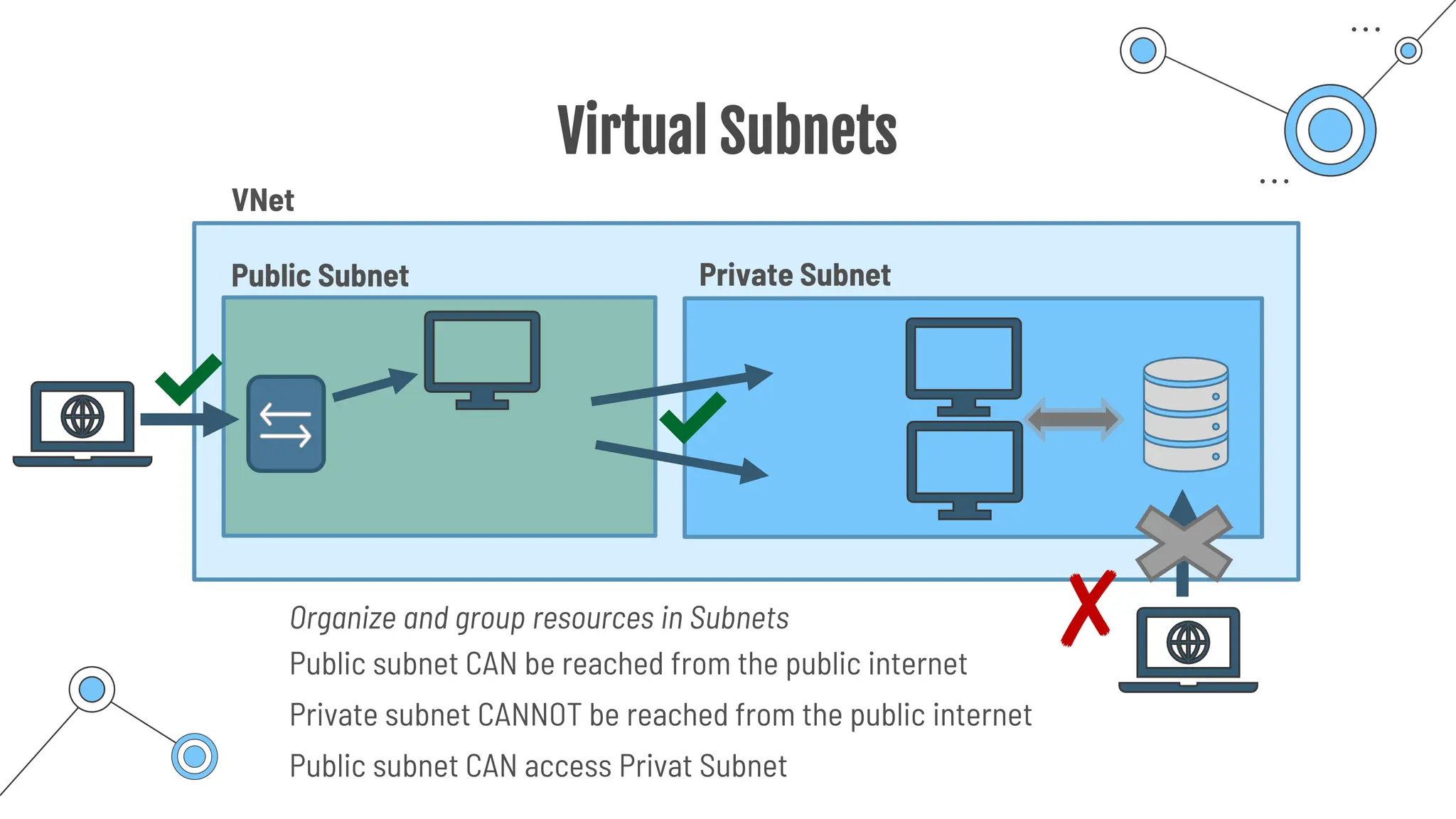
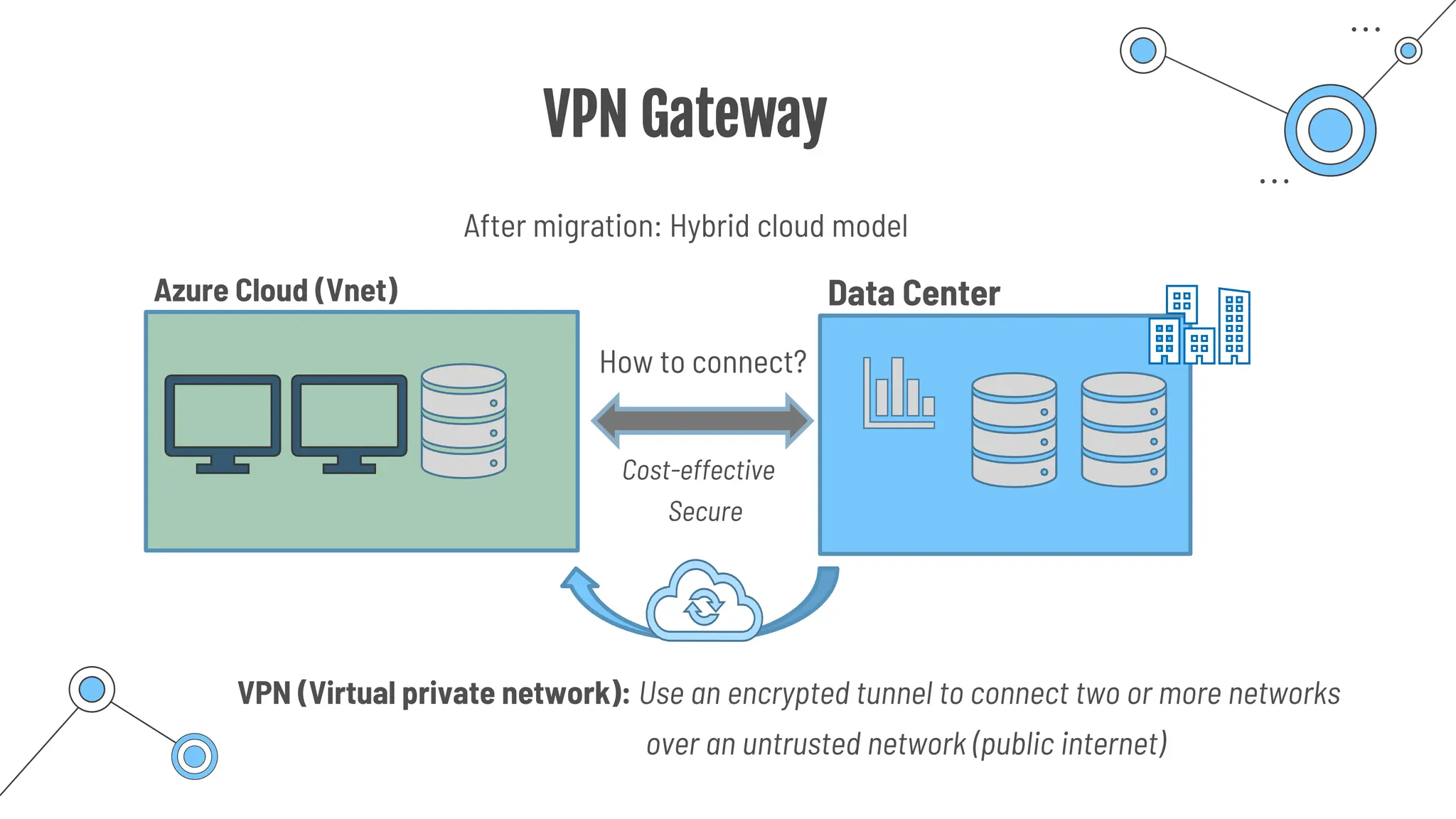
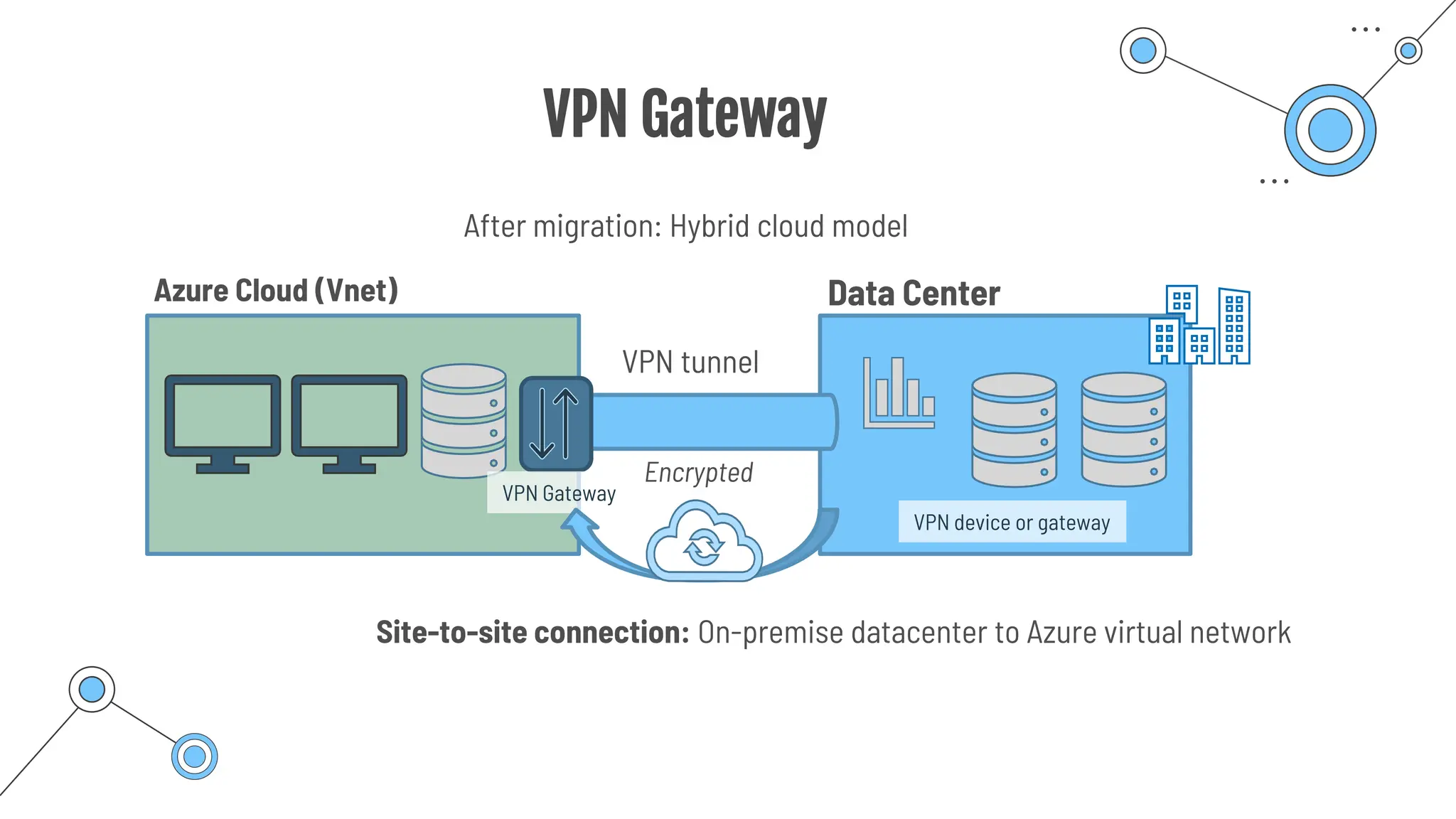
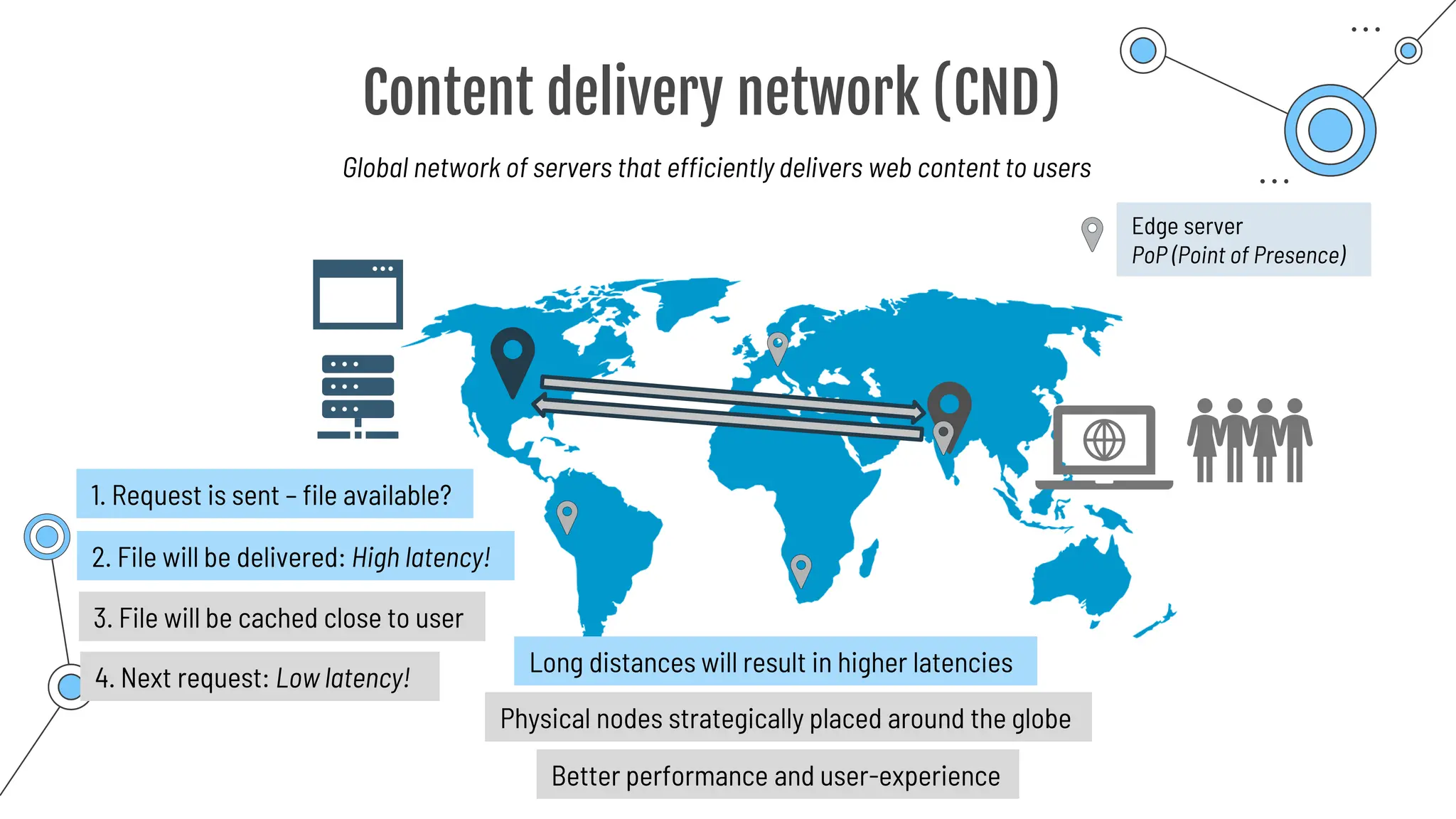
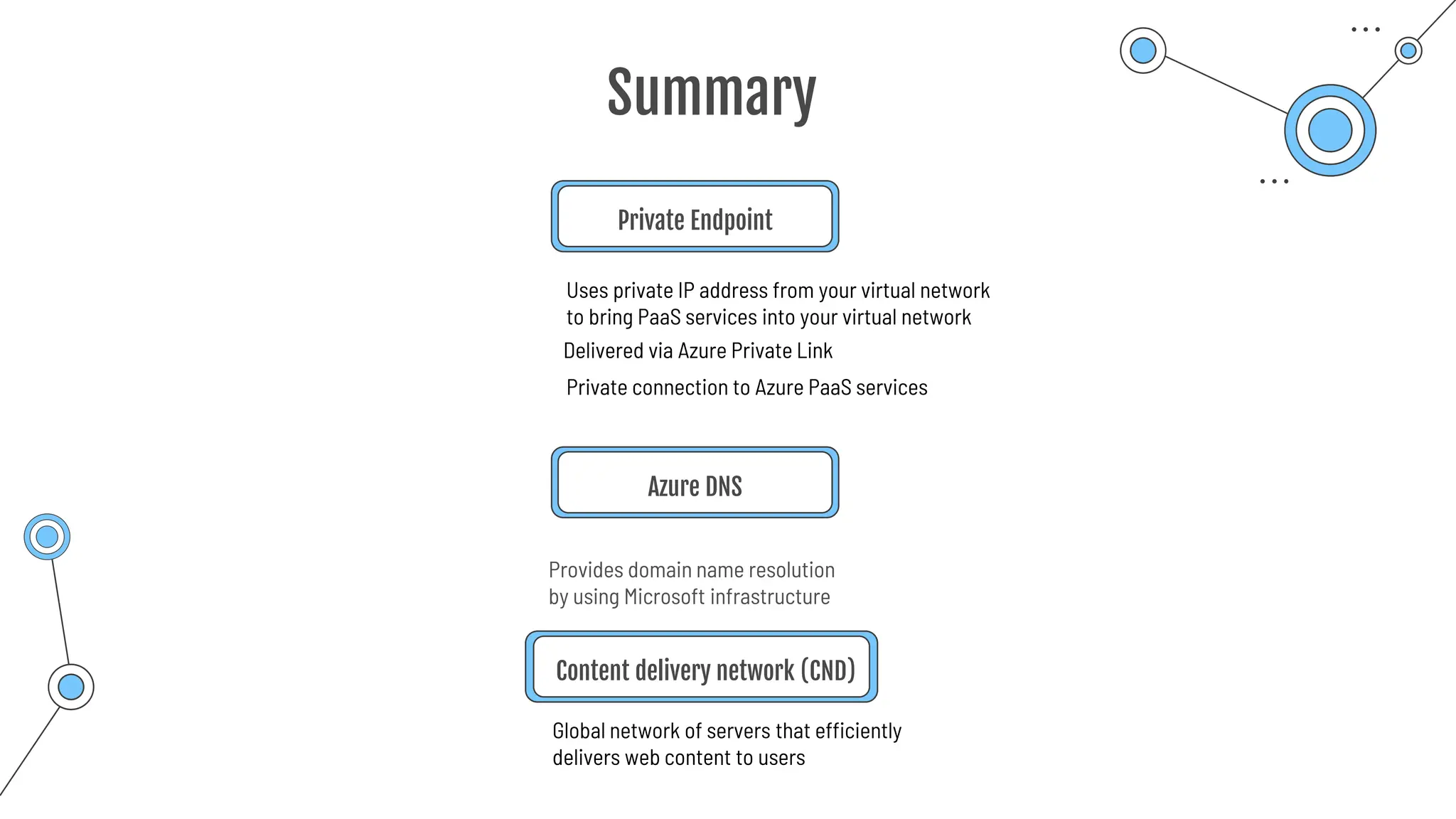
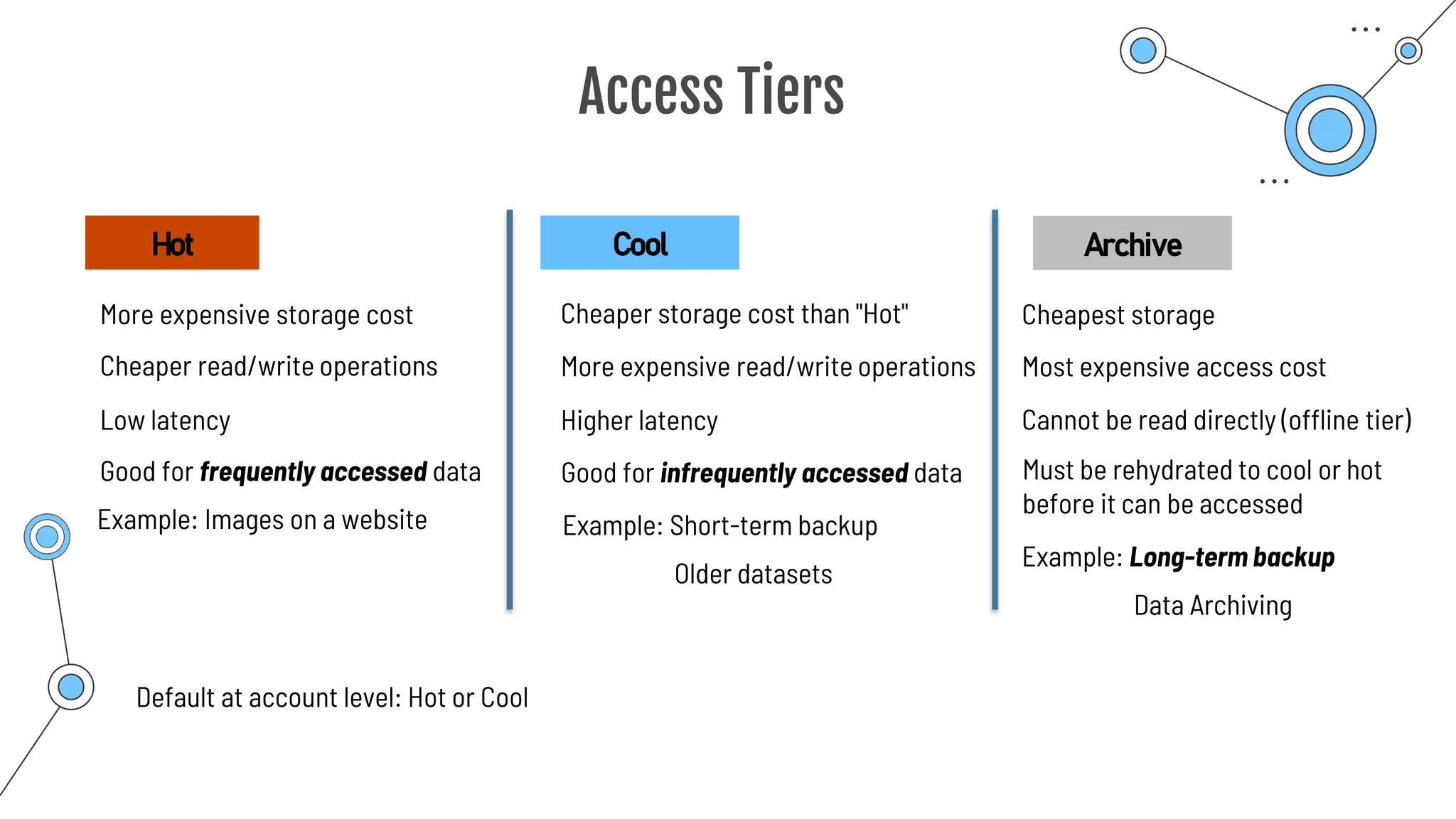
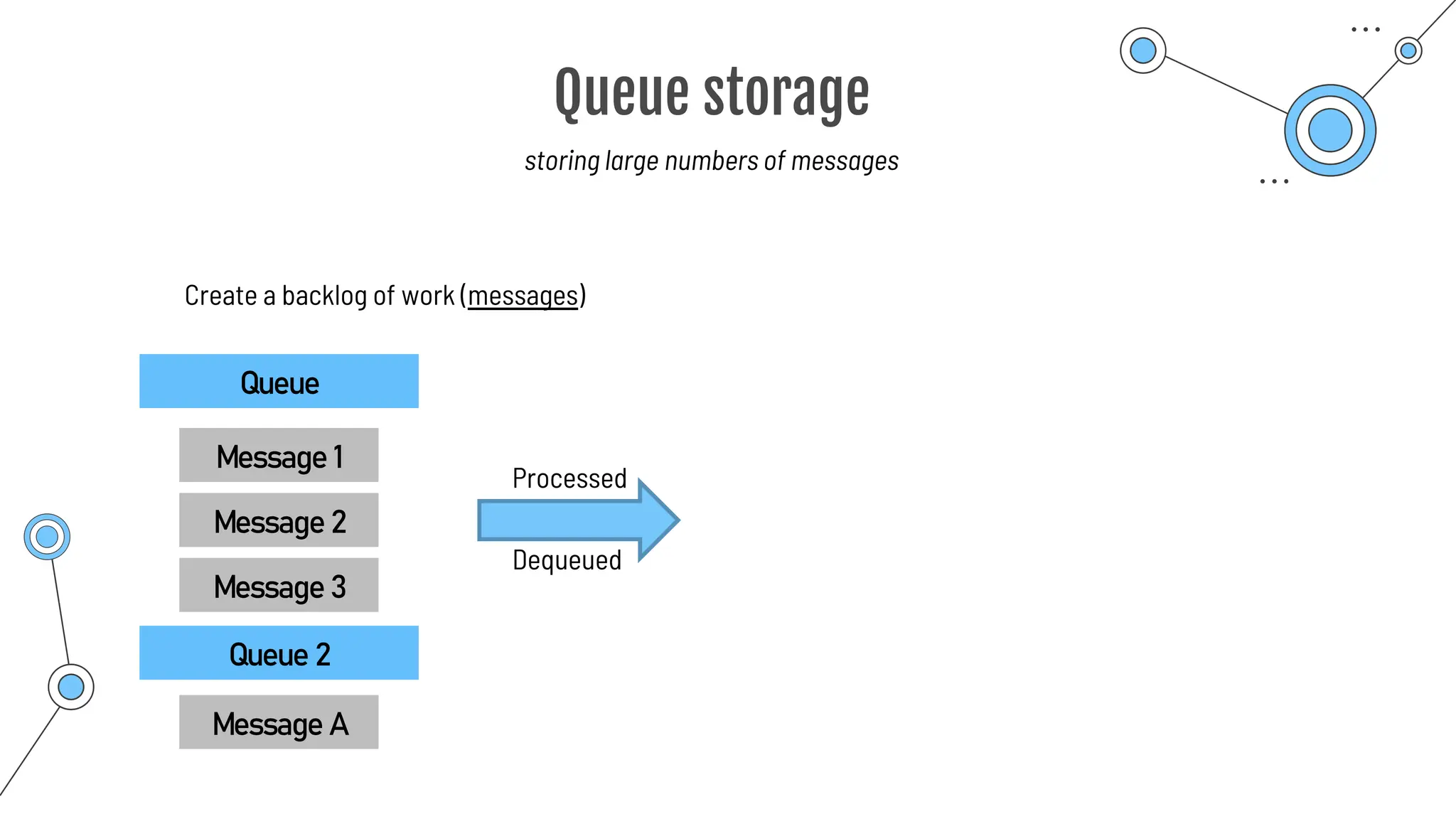
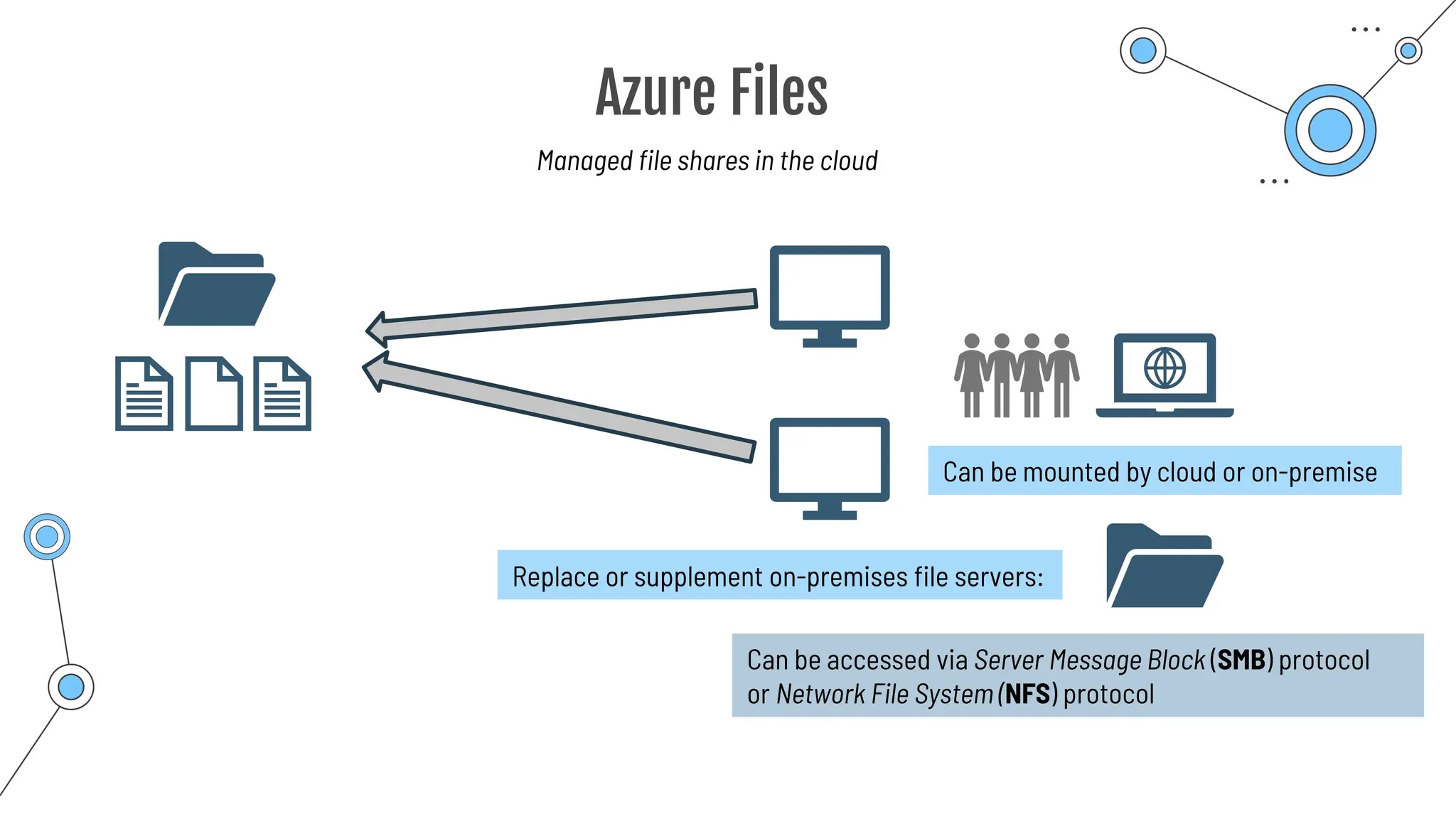
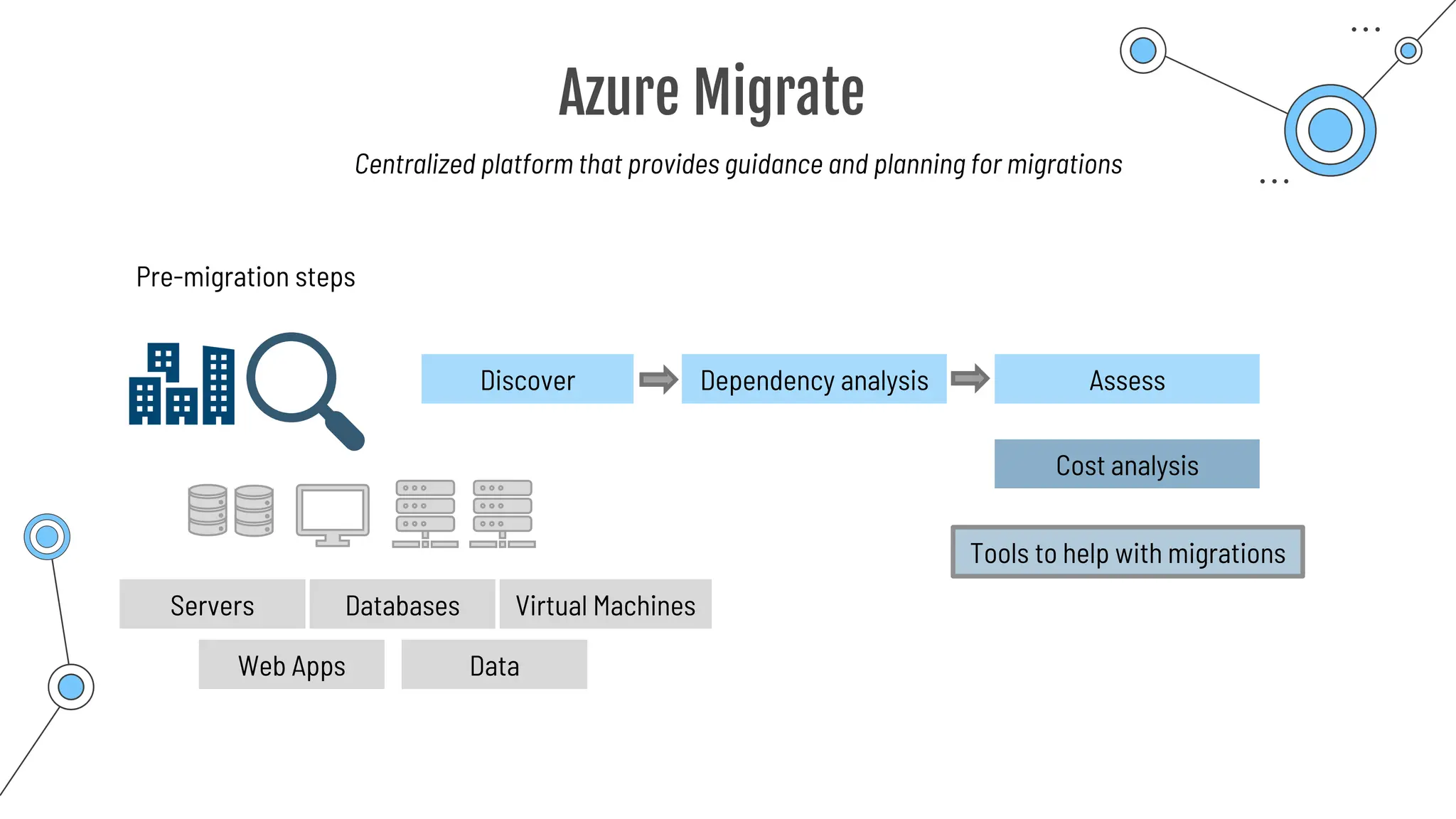
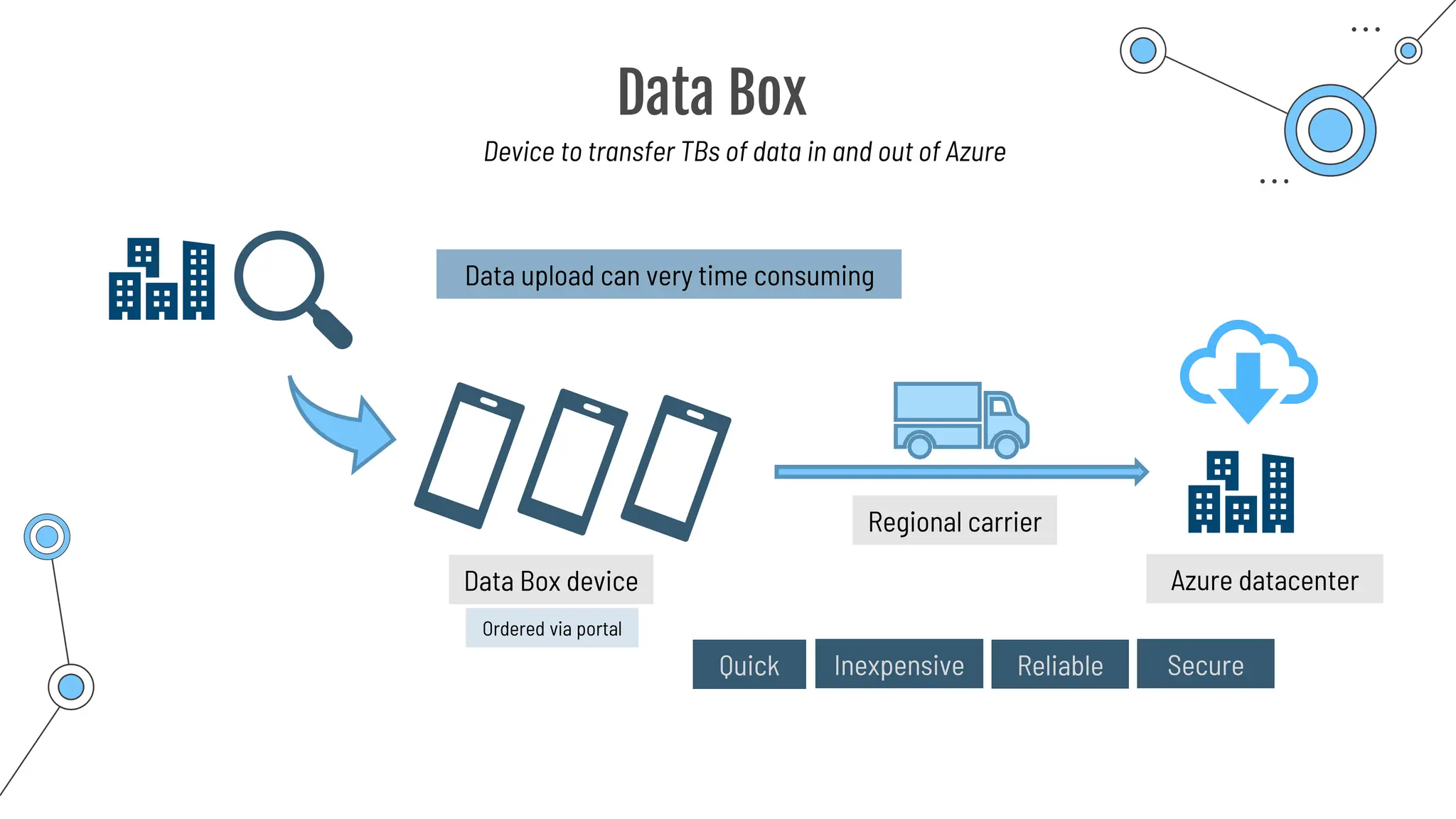
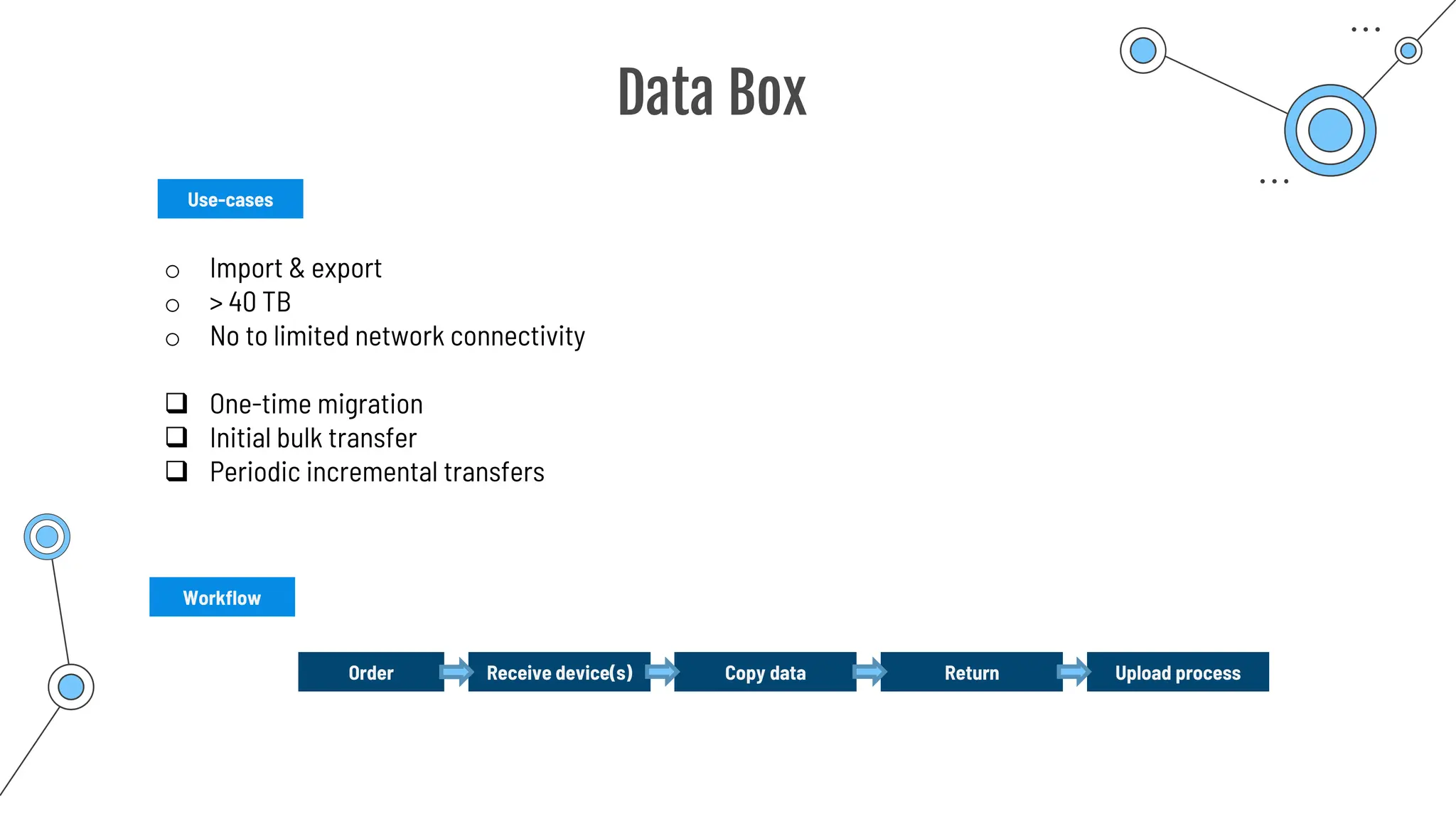
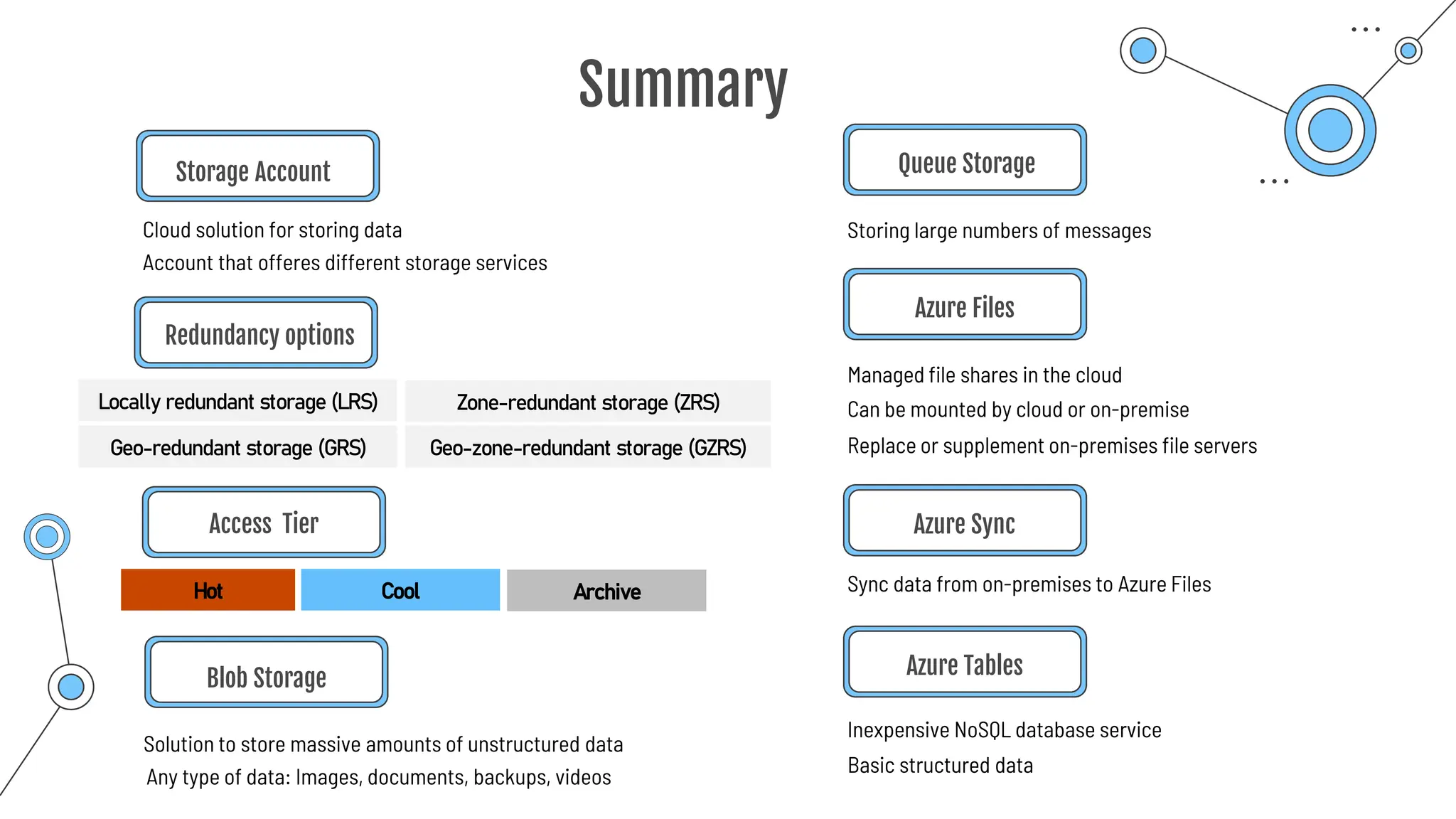
The document provides a comprehensive guide to the AZ-900 exam, a foundational certification in Azure. It covers important topics such as exam structure, cloud computing benefits, different service models (IaaS, PaaS, SaaS), and resource management strategies. Key points include the importance of understanding Azure's services, preparation tips for achieving a passing score, and the significance of public, private, and hybrid cloud models.






































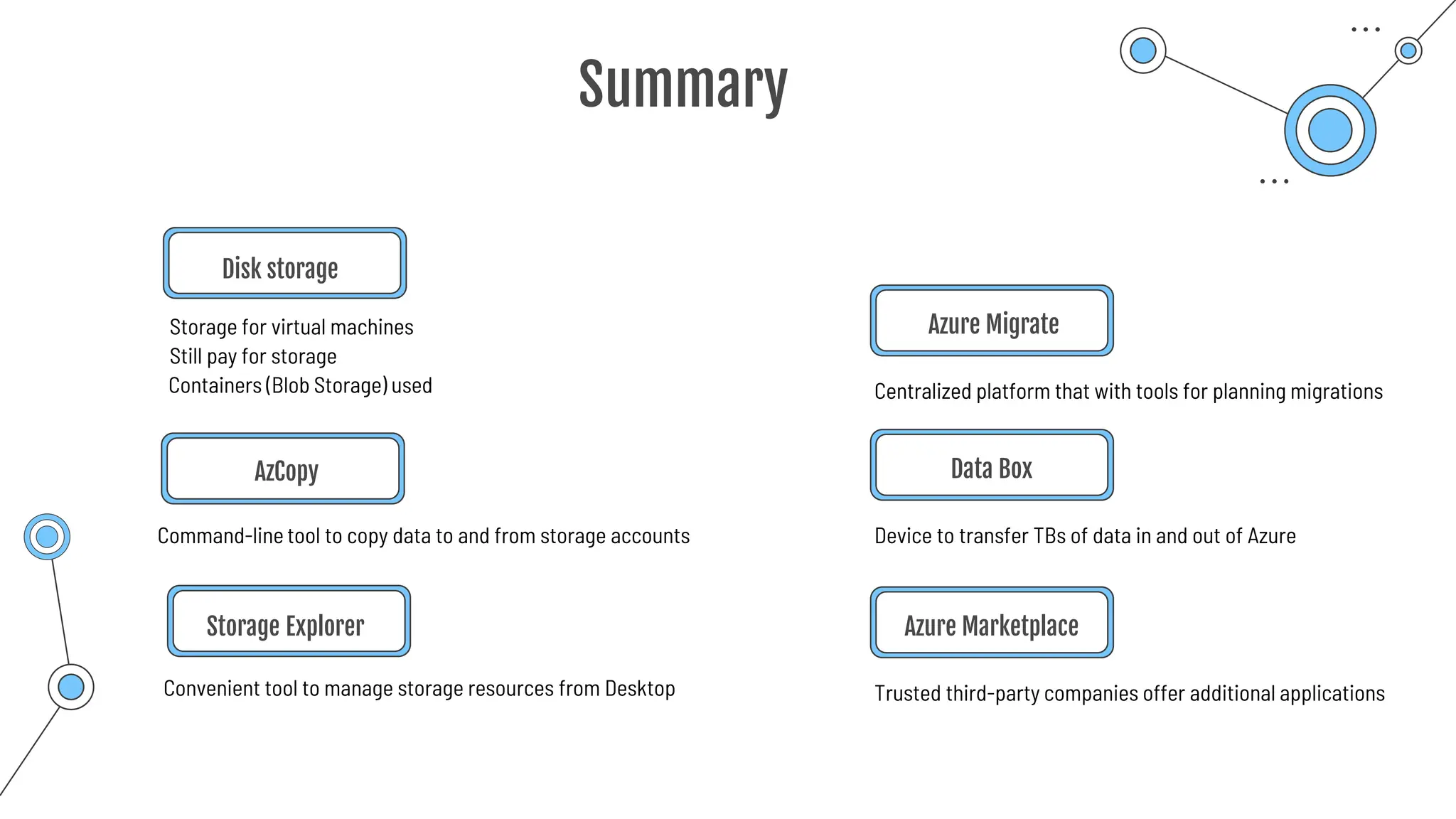
![AzCopy
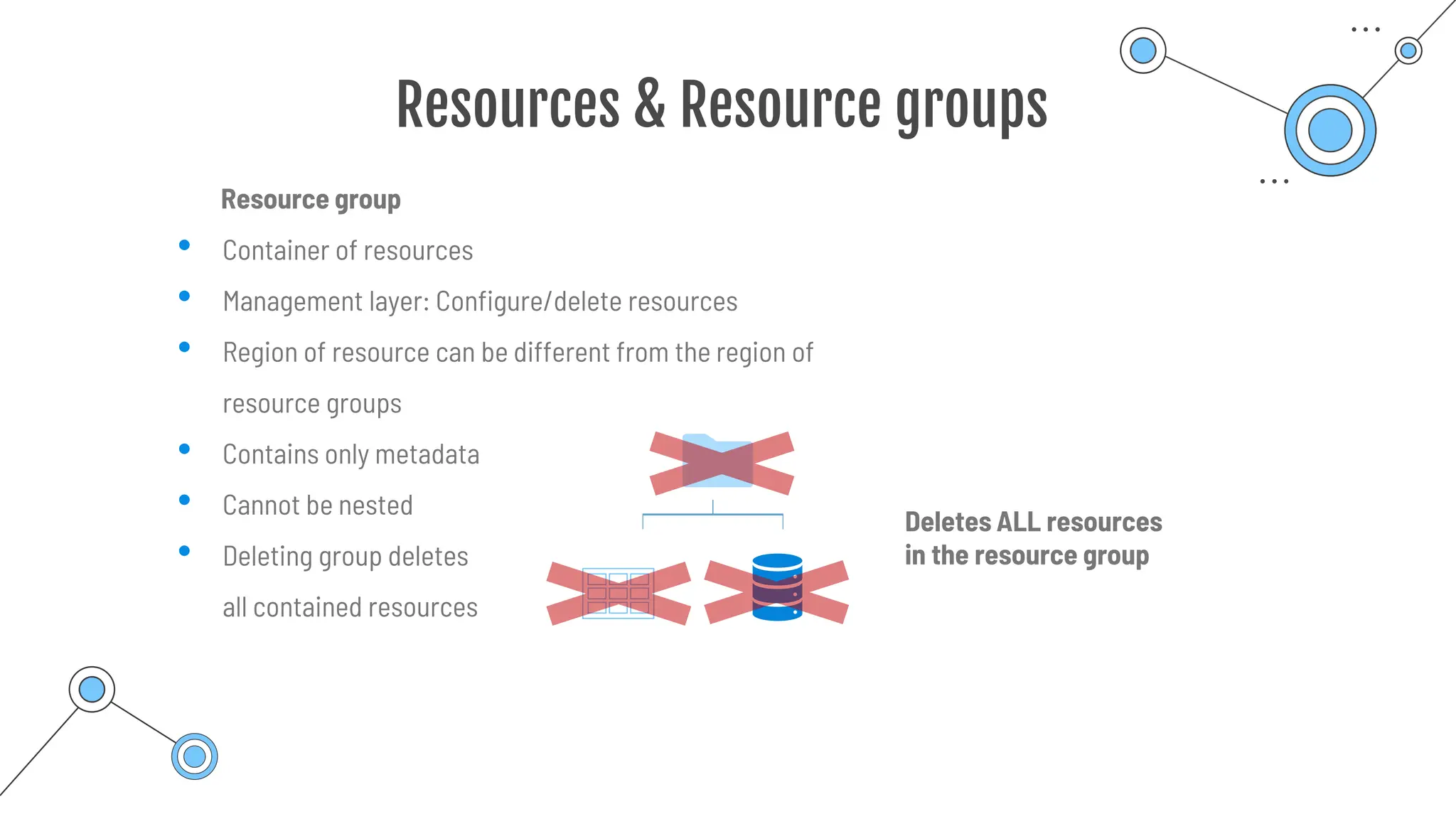
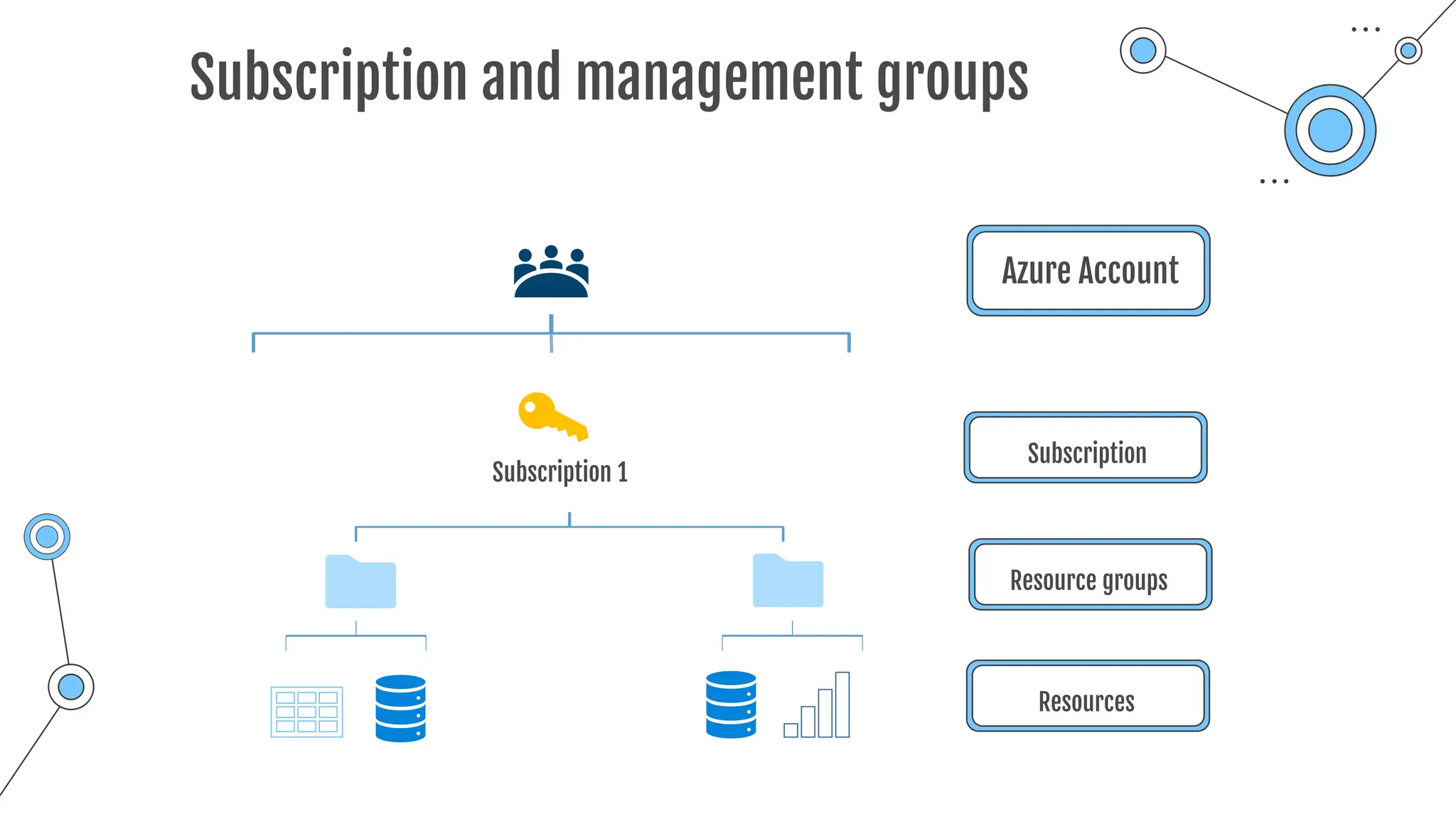
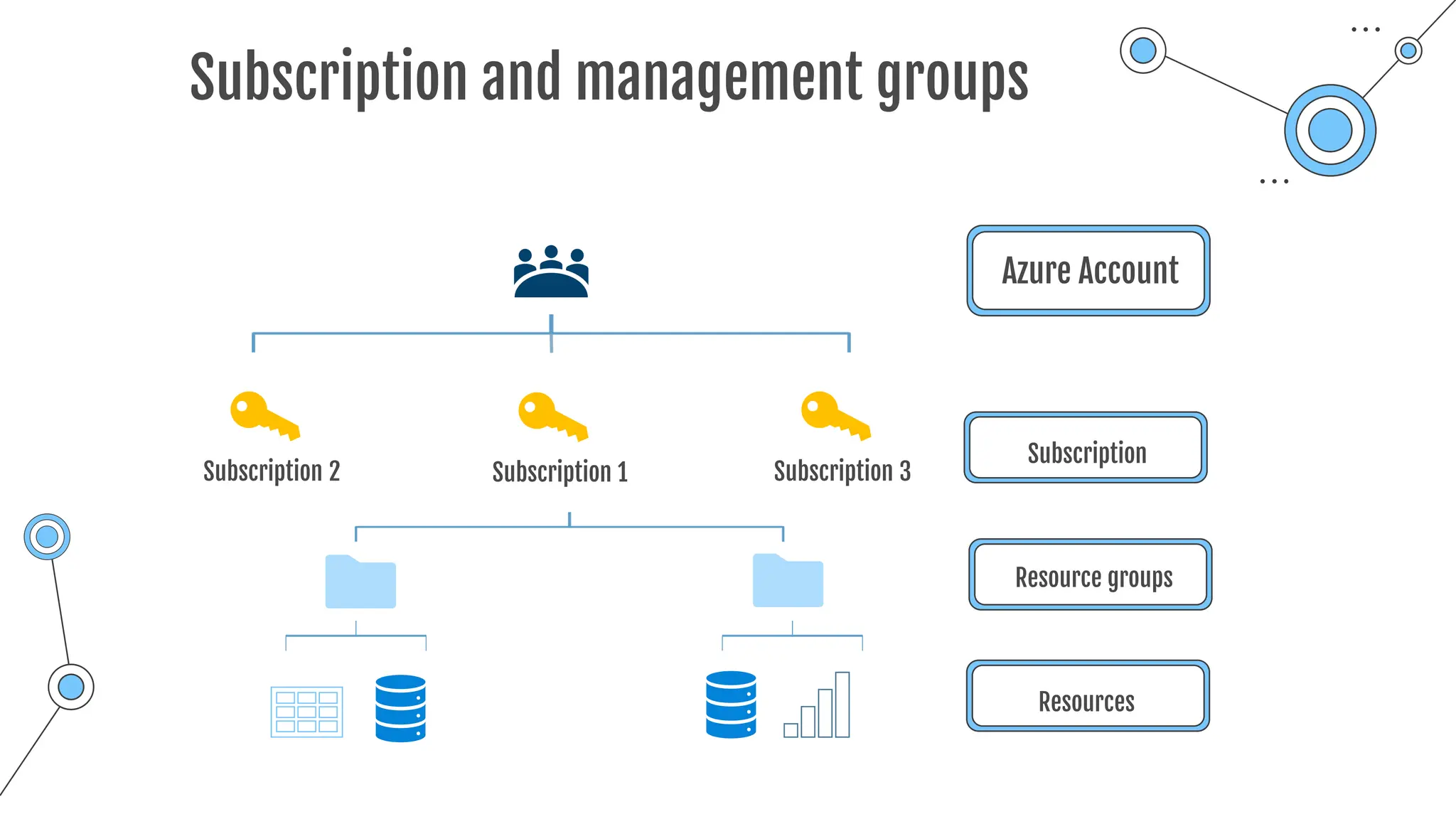
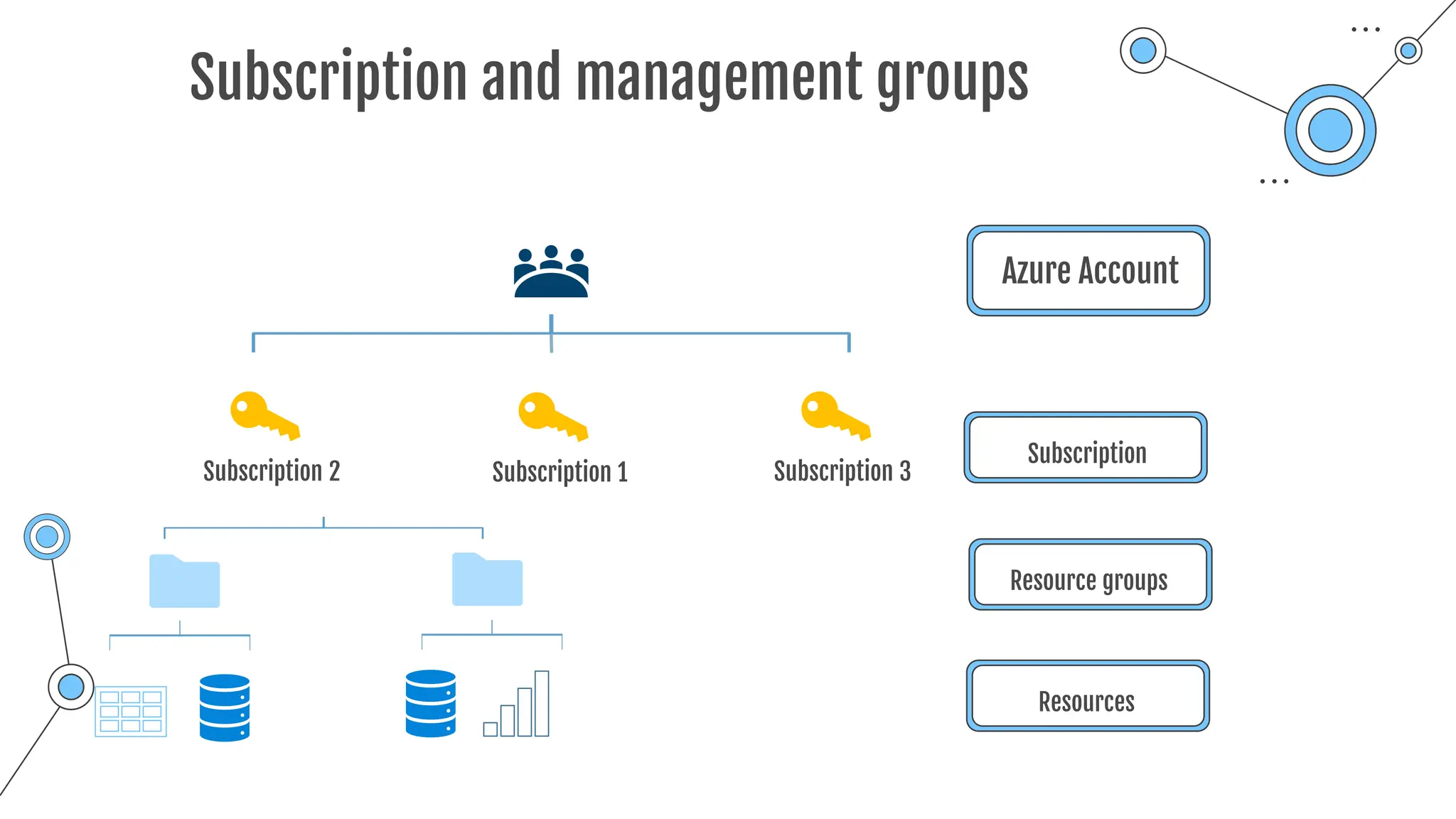
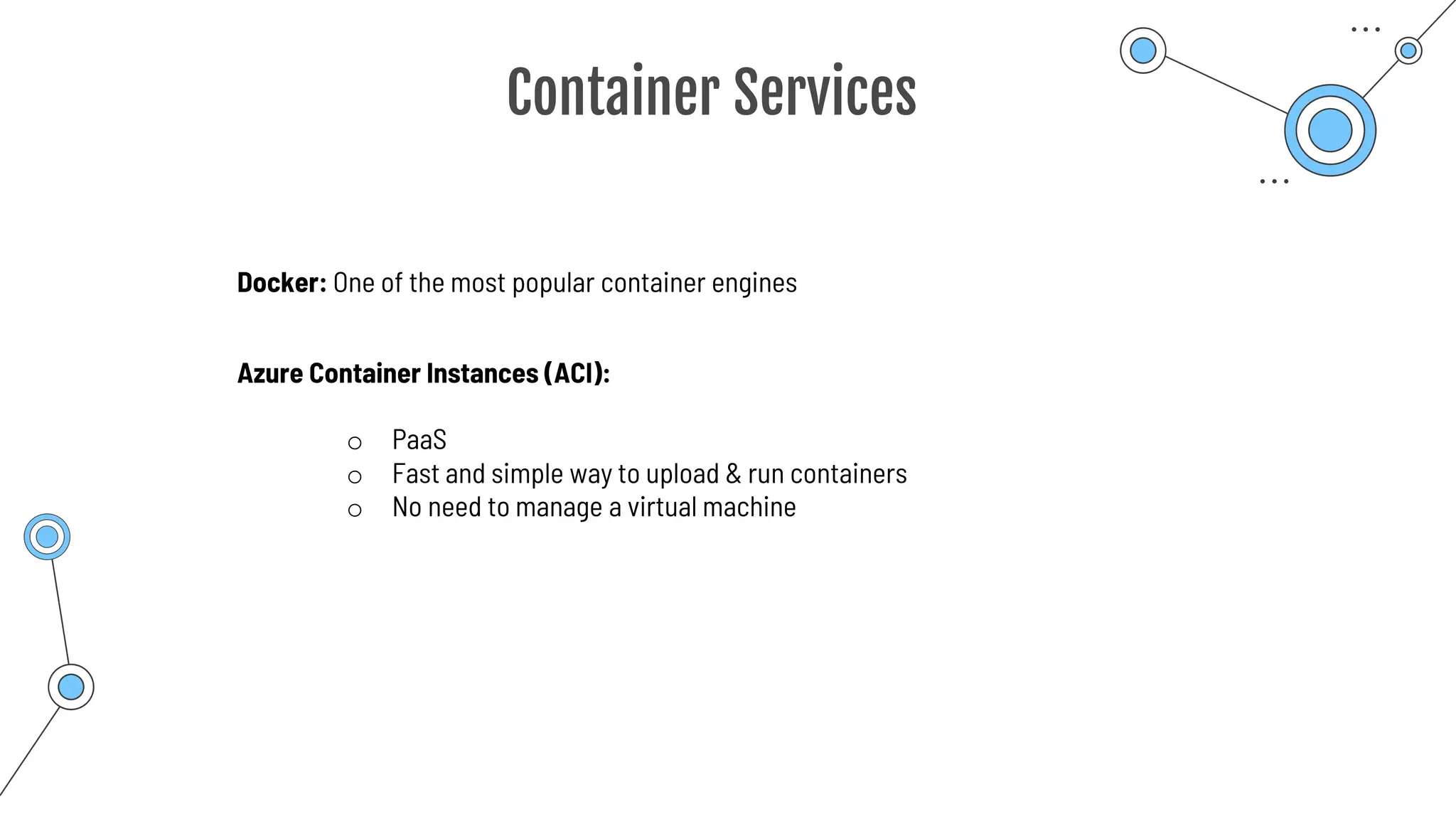
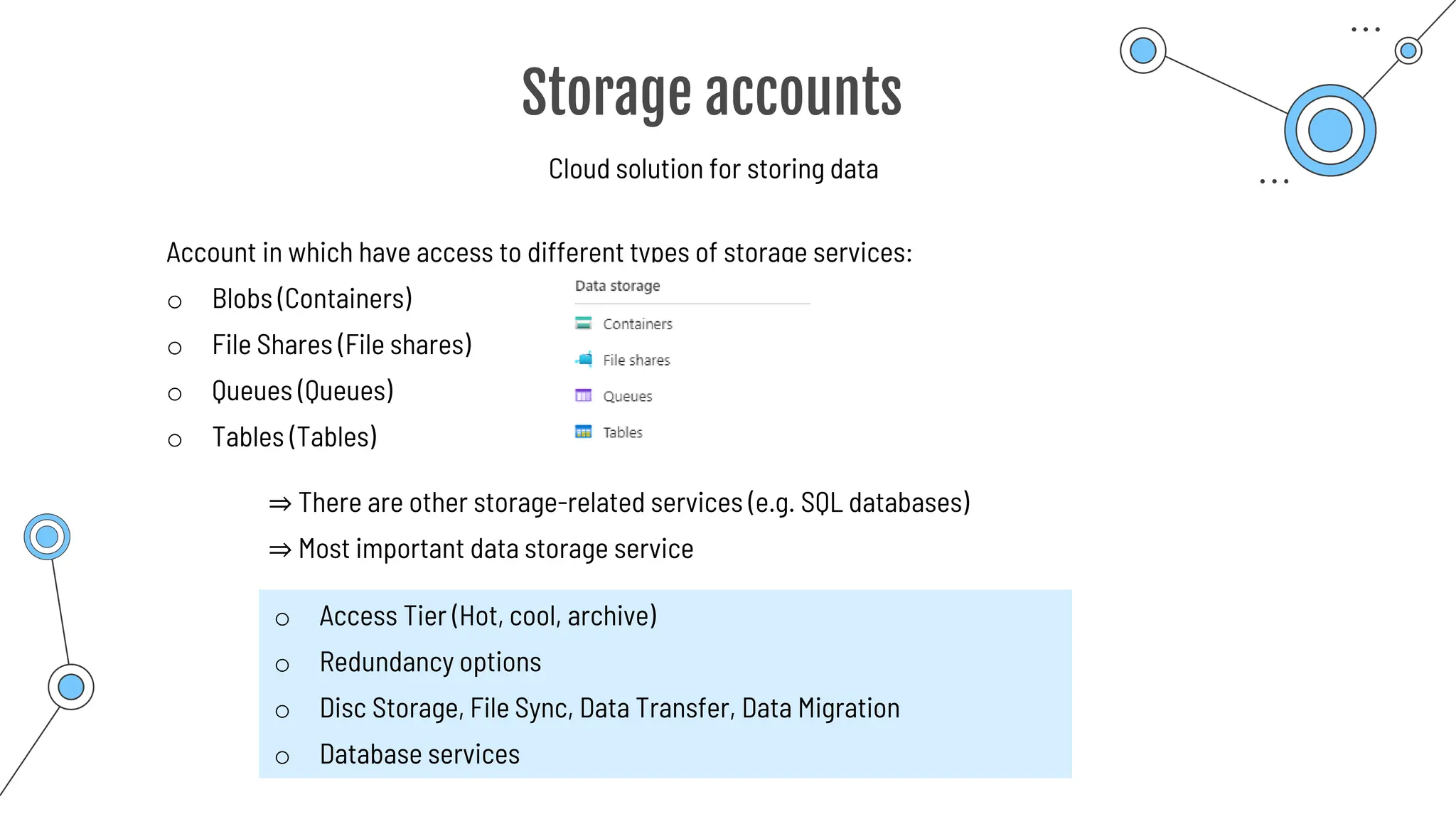
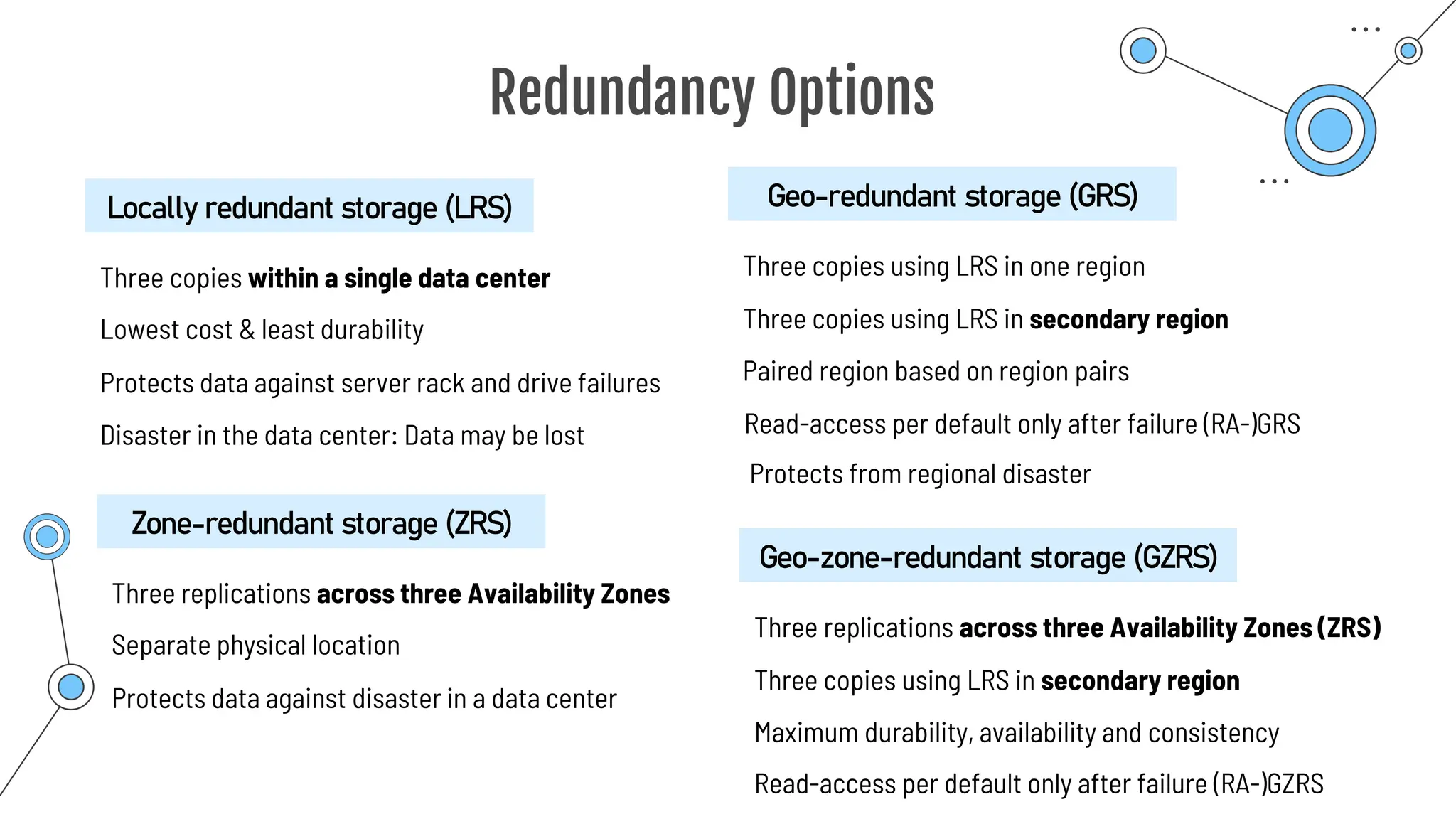
Command-line tool to copy data to and from storage accounts
o Can be downloaded to Windows or Linux
o Used within Azure Cloud Shell
o Upload, download, sync or transfer files and blobs
Command Description
azcopy copy Copies source data to a destination location
azcopy list Lists the entities in a given resource.
azcopy remove Delete blobs or files from an Azure storage account.
azcopy make Creates a container or file share.
azcopy [command] [arguments] --[flag-name]=[flag-value]
azcopy copy 'file-link-with-sas-key''container-link-with-sas-key'](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/allslides1-240501210005-f8375ca2/75/AZ-900-preparation-slides-for-microsoft-certification-157-2048.jpg)





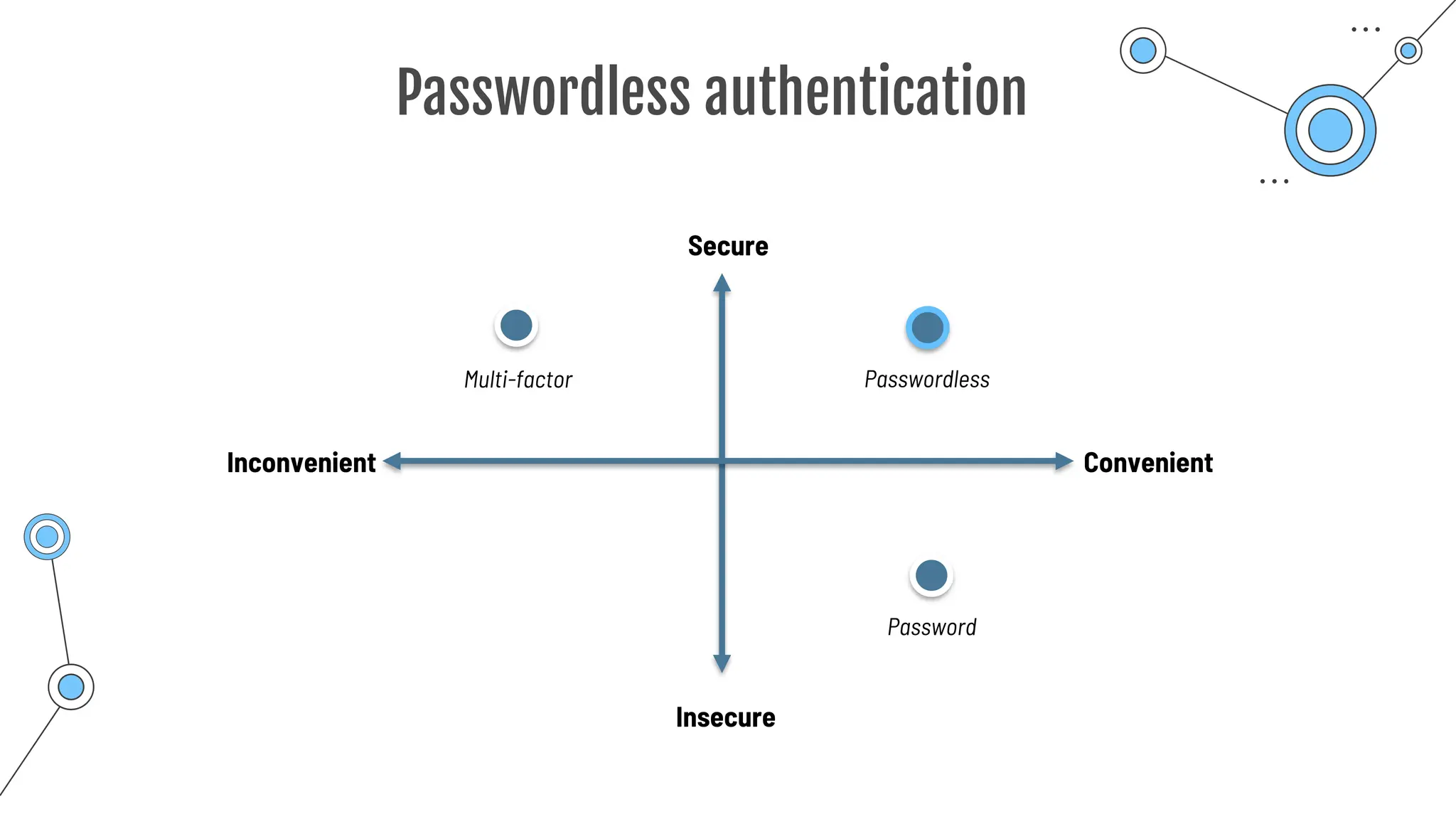
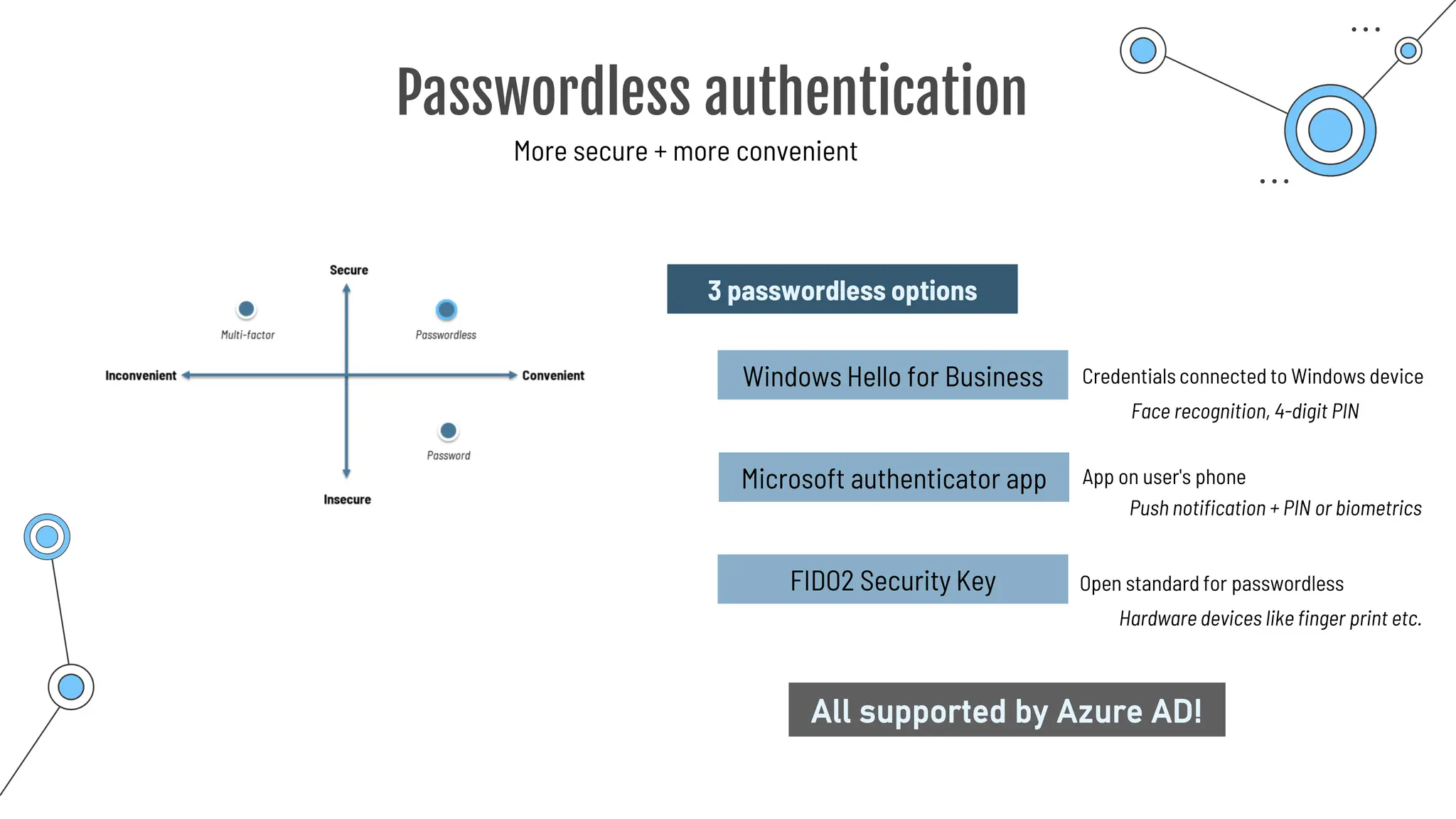
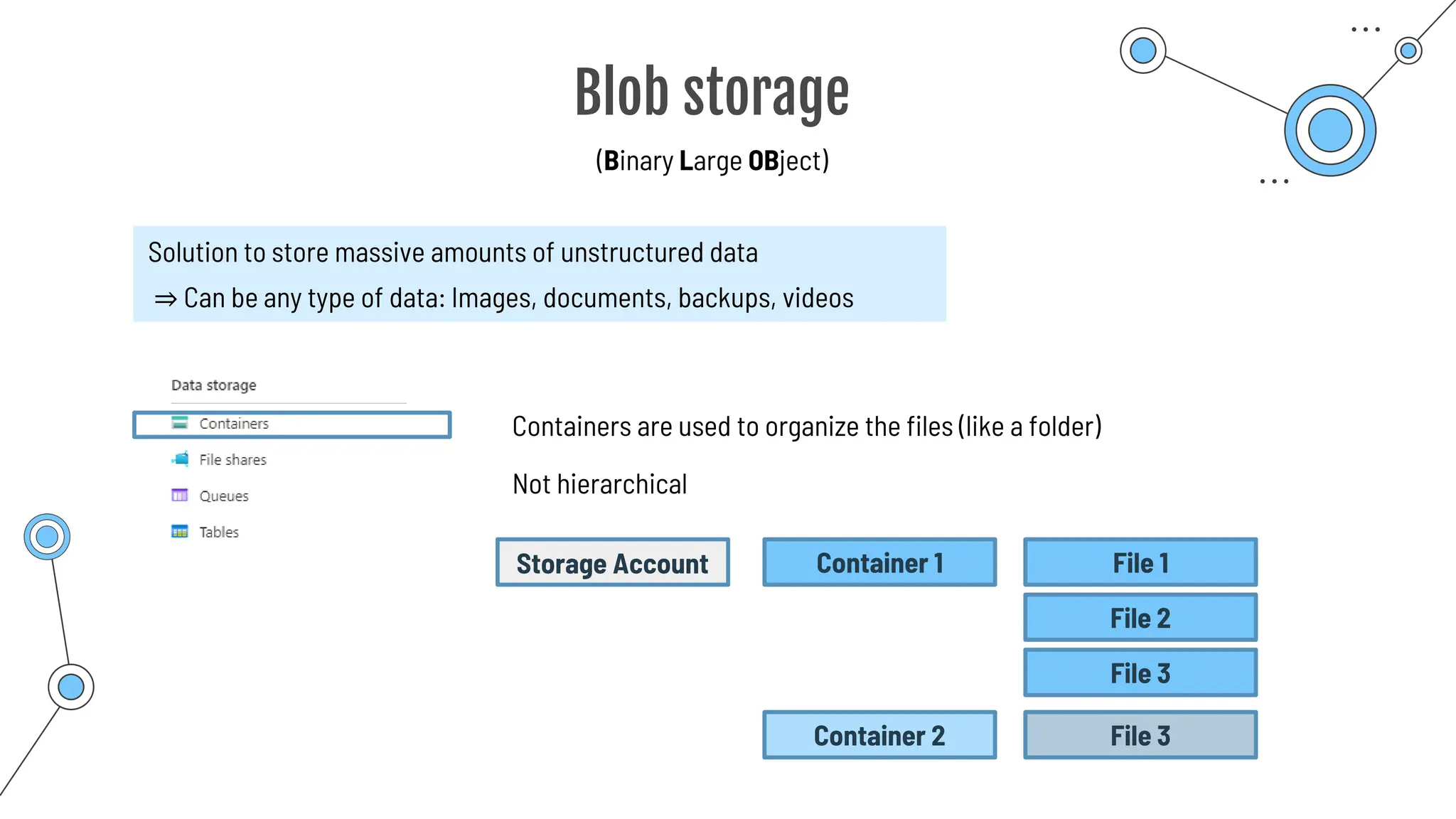
![Multi-Factor Authentication
Additional method of authentication
nikolai.schuler@[...].com
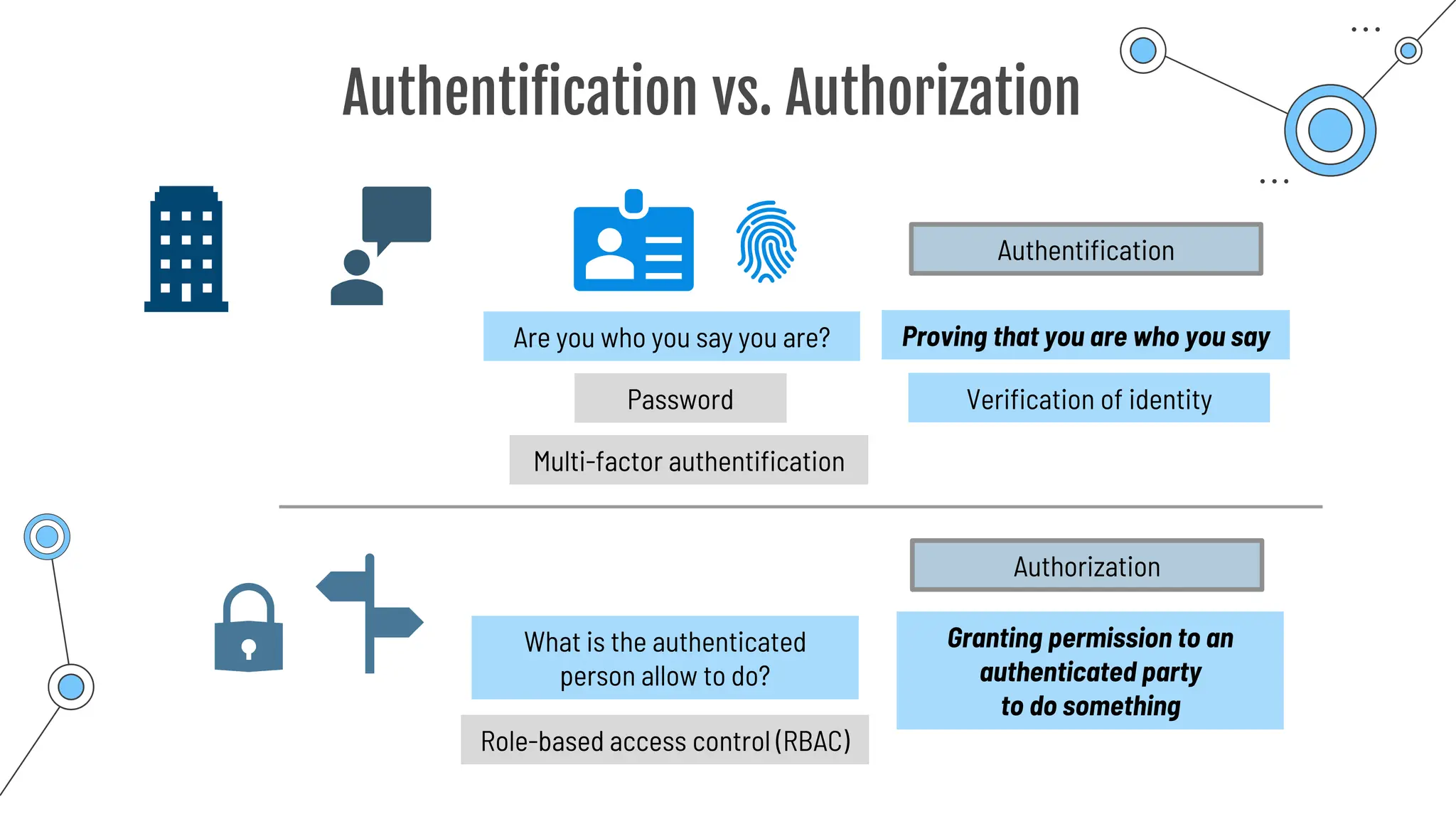
Authentication
**********
Password can get found out!
Username:
Password:
2nd authentication factor
… Know
… Have
**********
Password:
… Are
Something you …
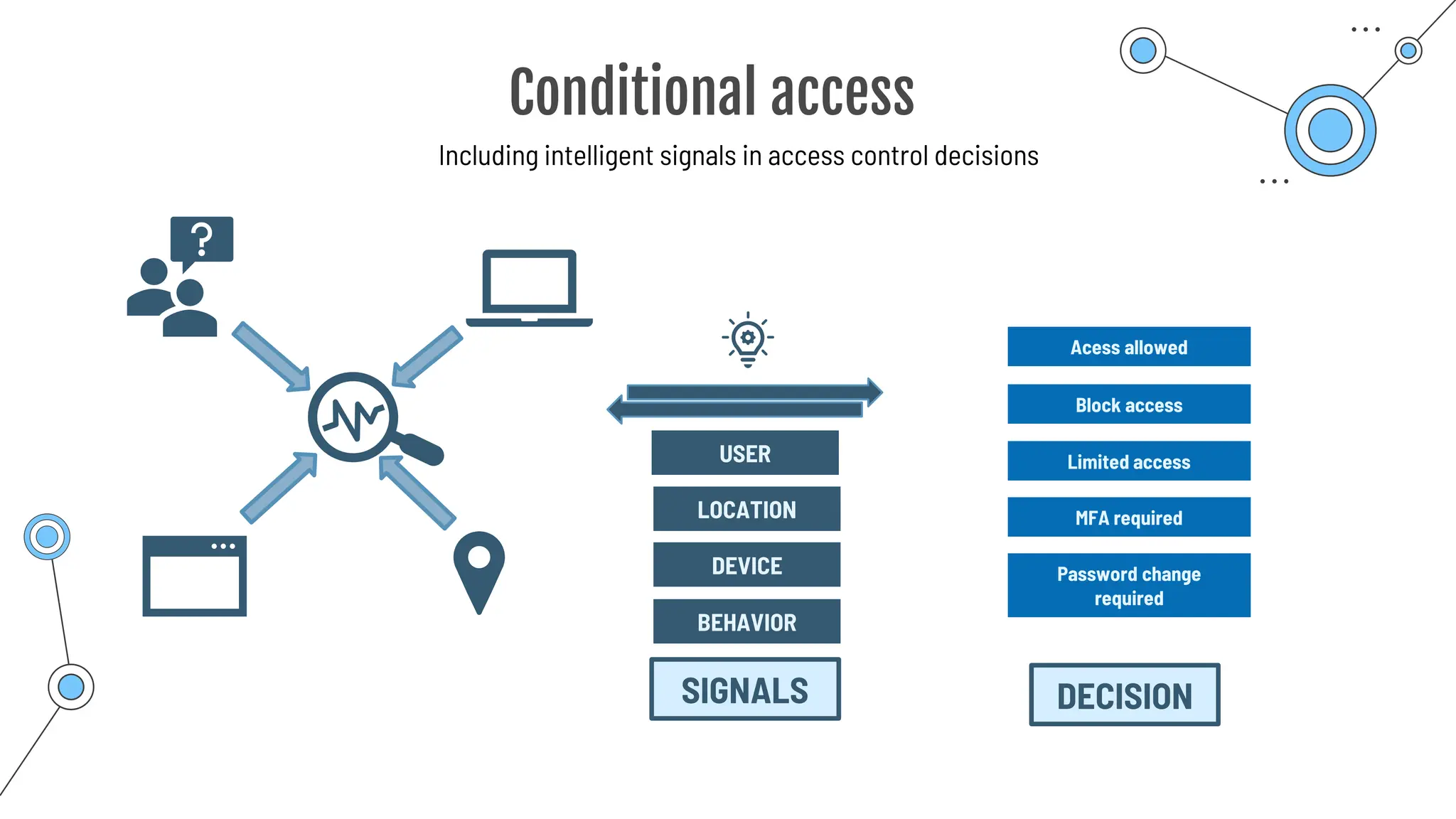
One way:
Conditional Access](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/allslides1-240501210005-f8375ca2/75/AZ-900-preparation-slides-for-microsoft-certification-177-2048.jpg)