The document describes the key components of an axiomatic system for geometry:
- Undefined terms like point, line, and plane that can only be described, not defined.
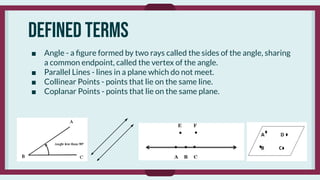
- Defined terms with precise definitions like angle, parallel lines, and midpoint.
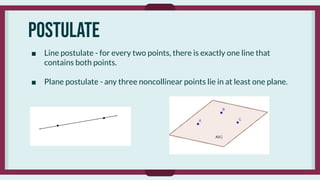
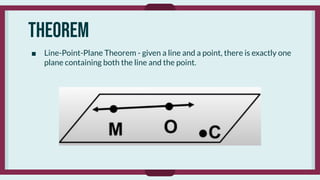
- Axioms/postulates that are accepted as true without proof, such as lines determined by points and planes containing points.
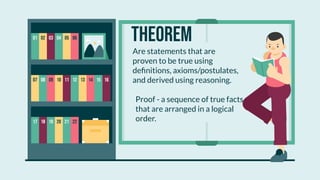
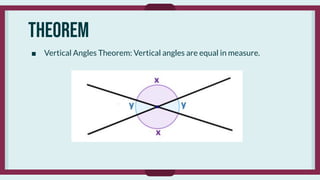
- Theorems that are proven true using definitions, axioms, and logical reasoning, such as the Vertical Angles Theorem.