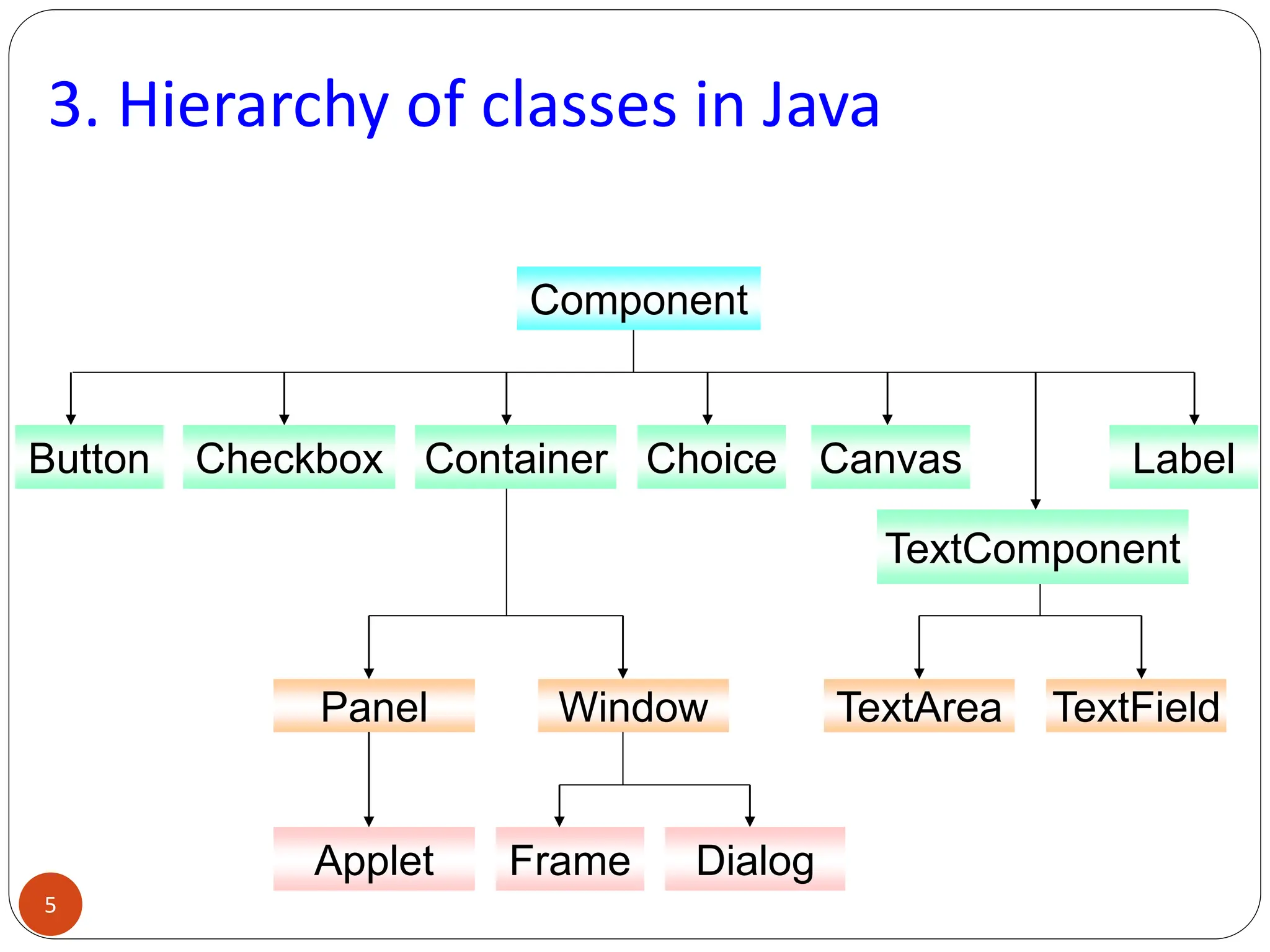
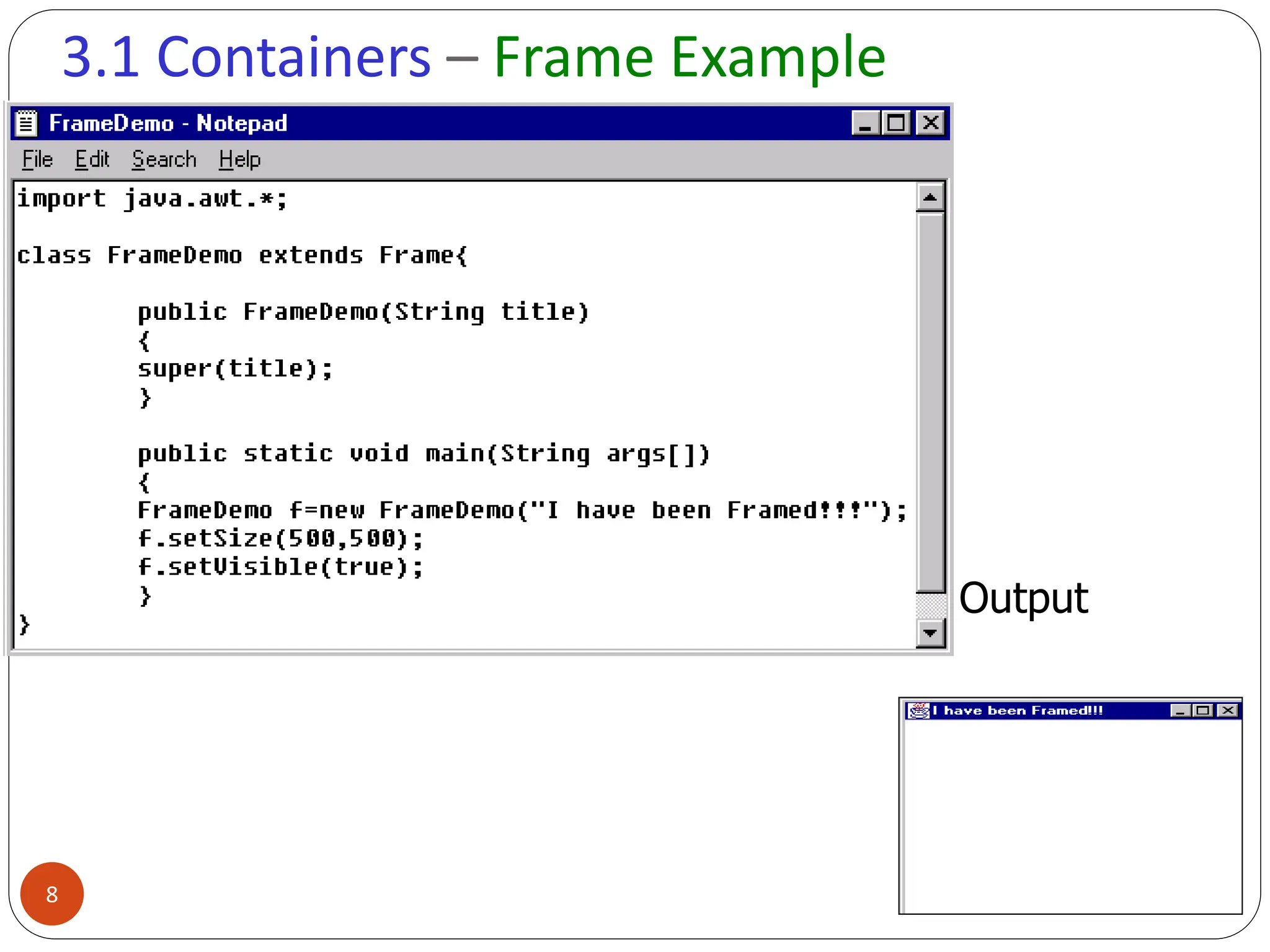
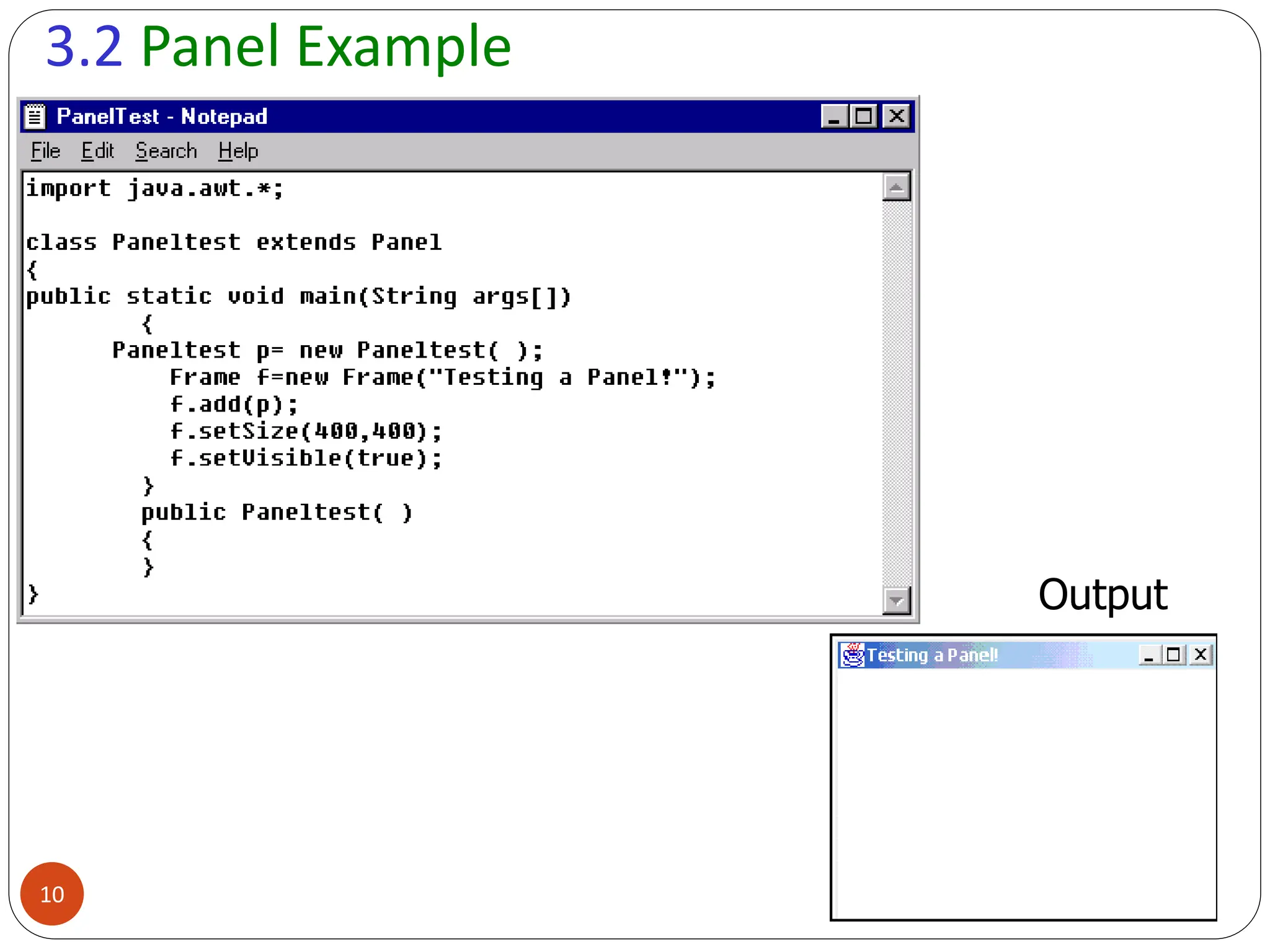
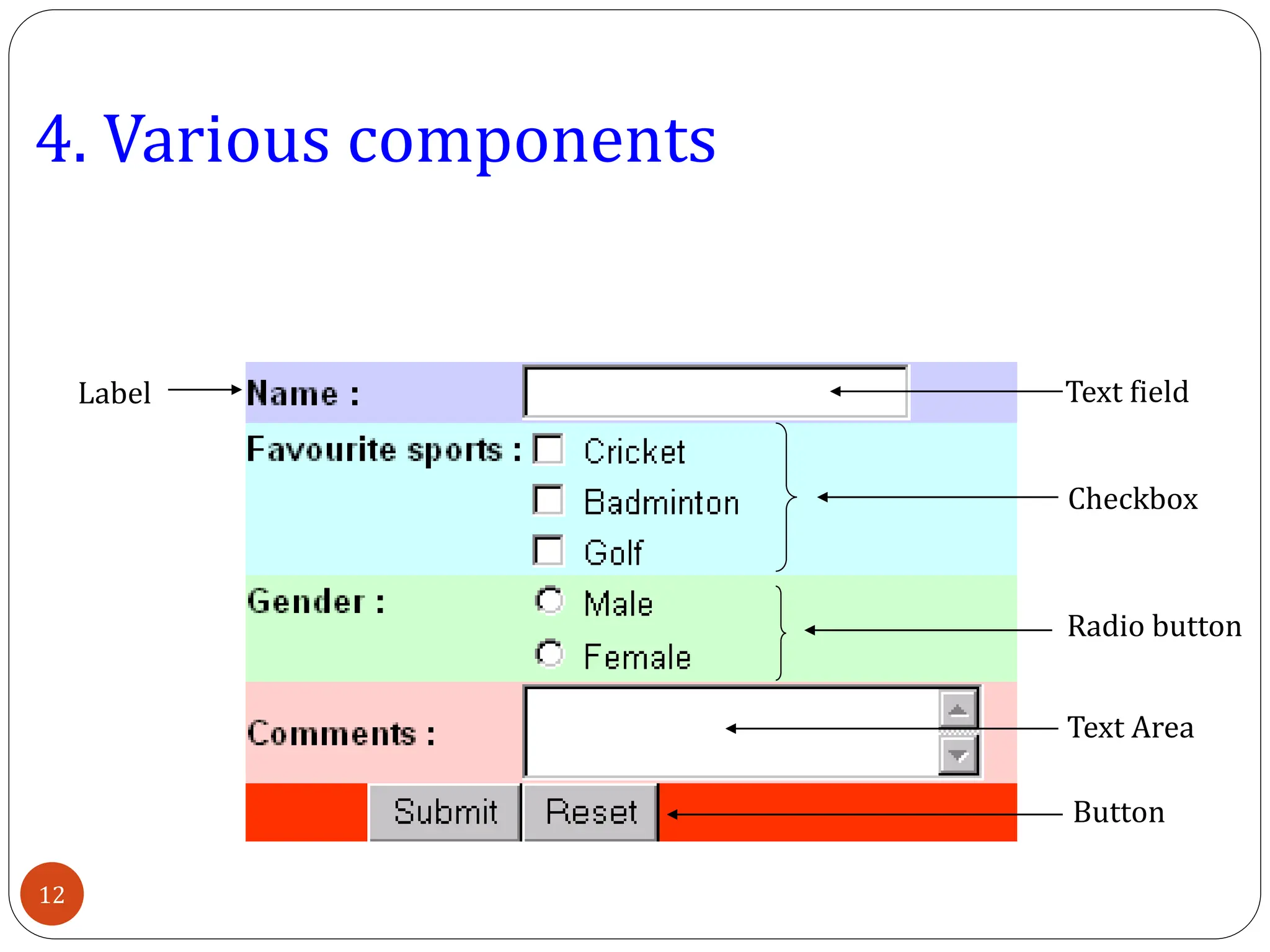
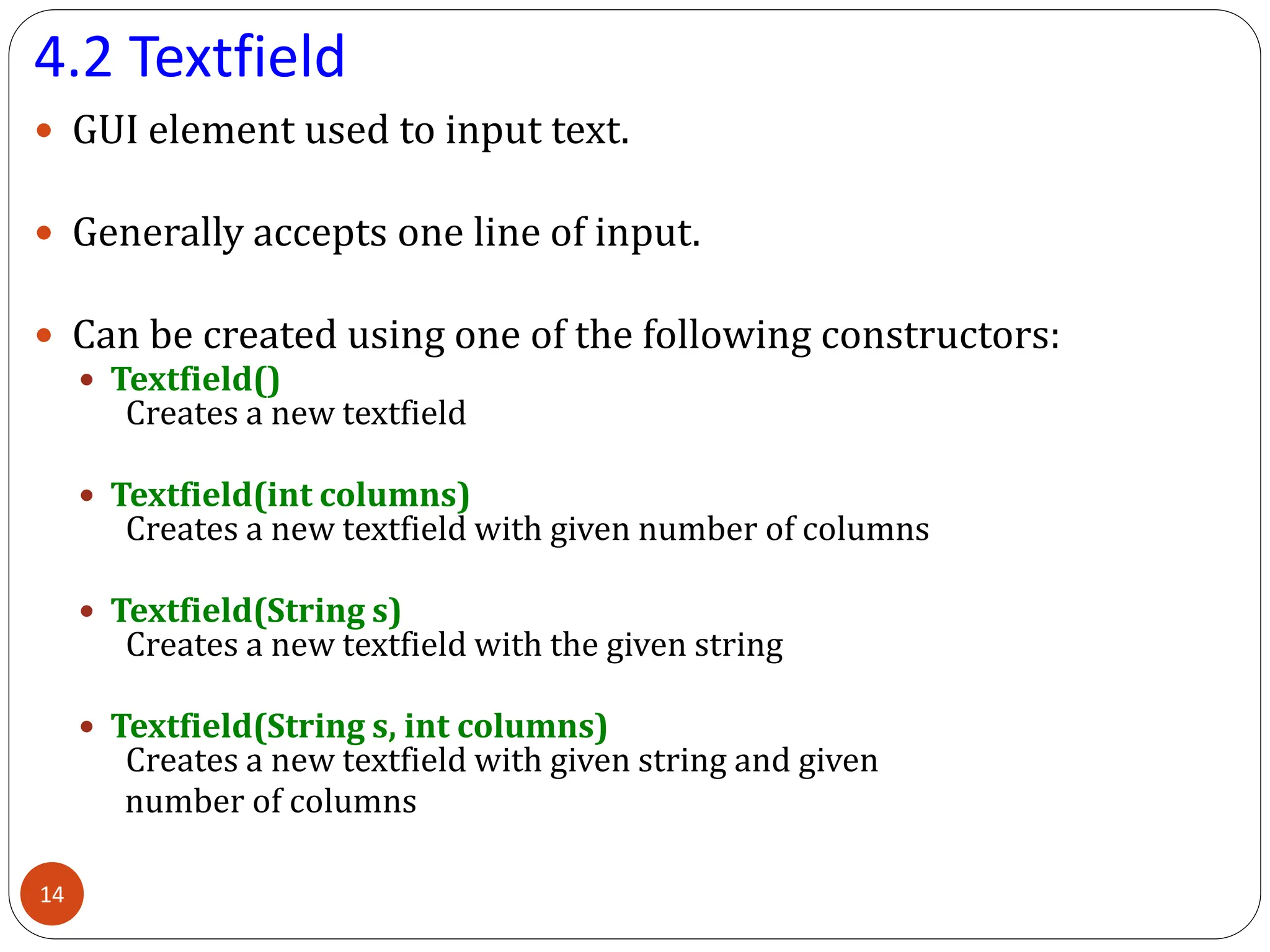
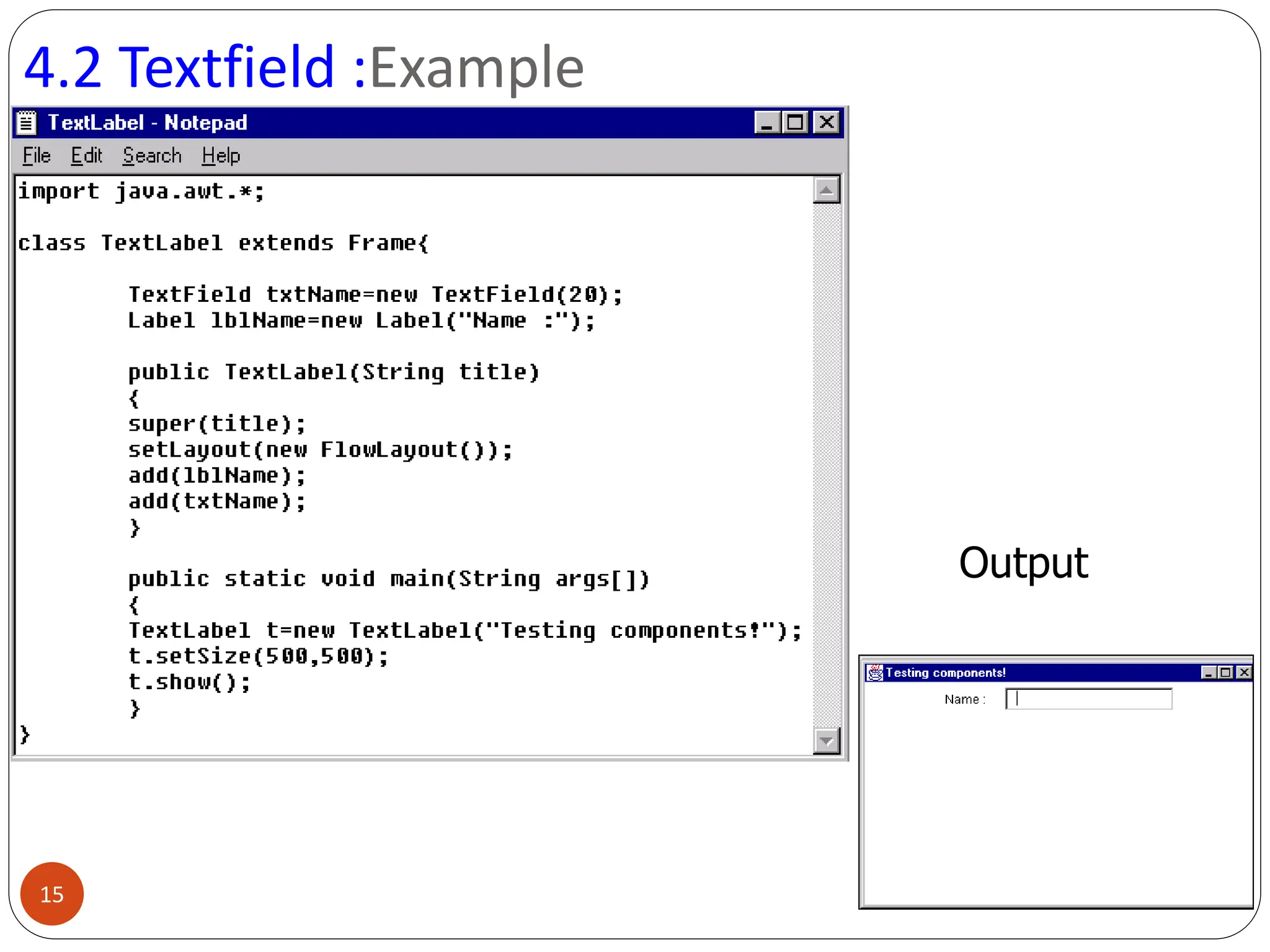
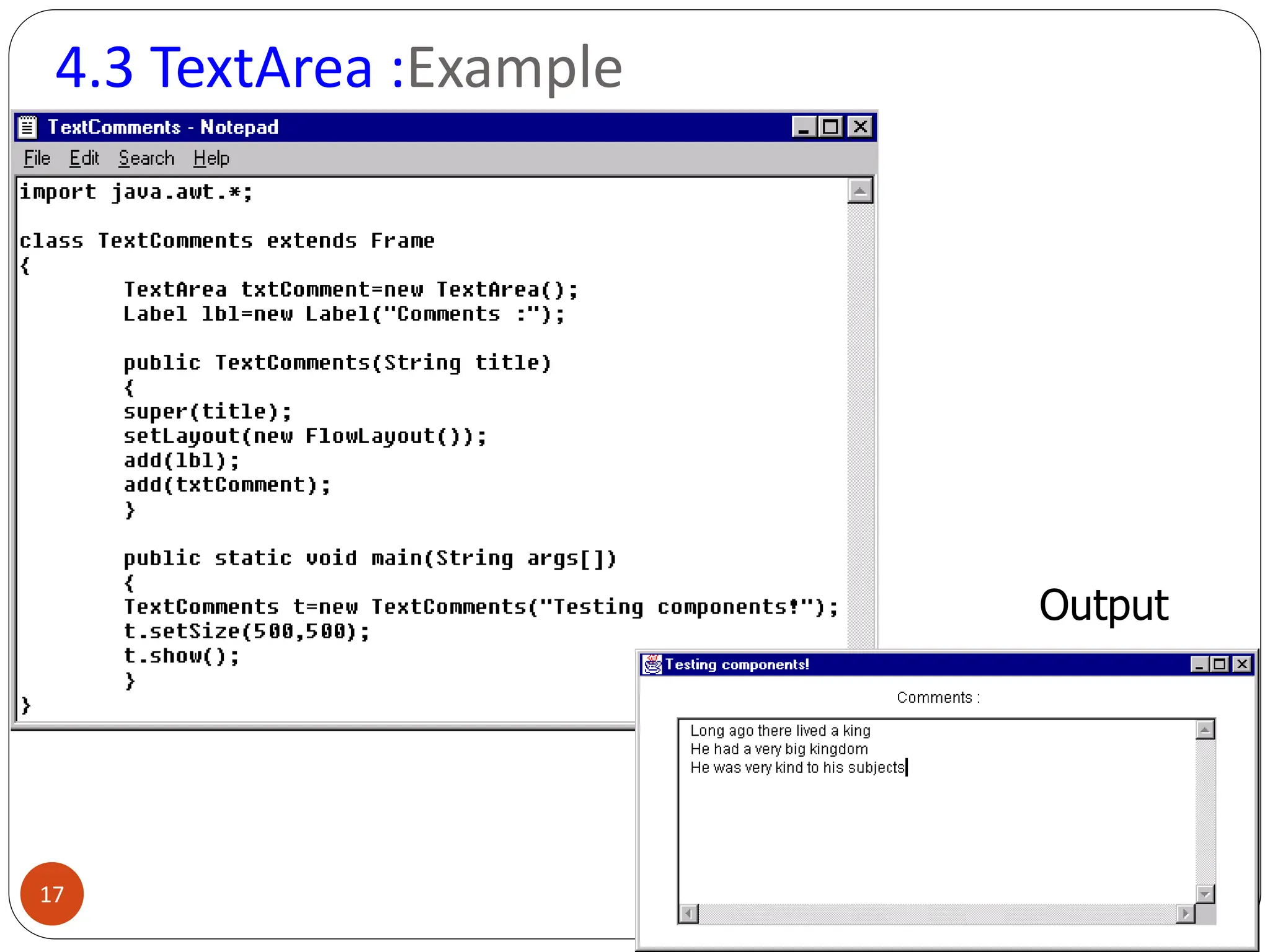
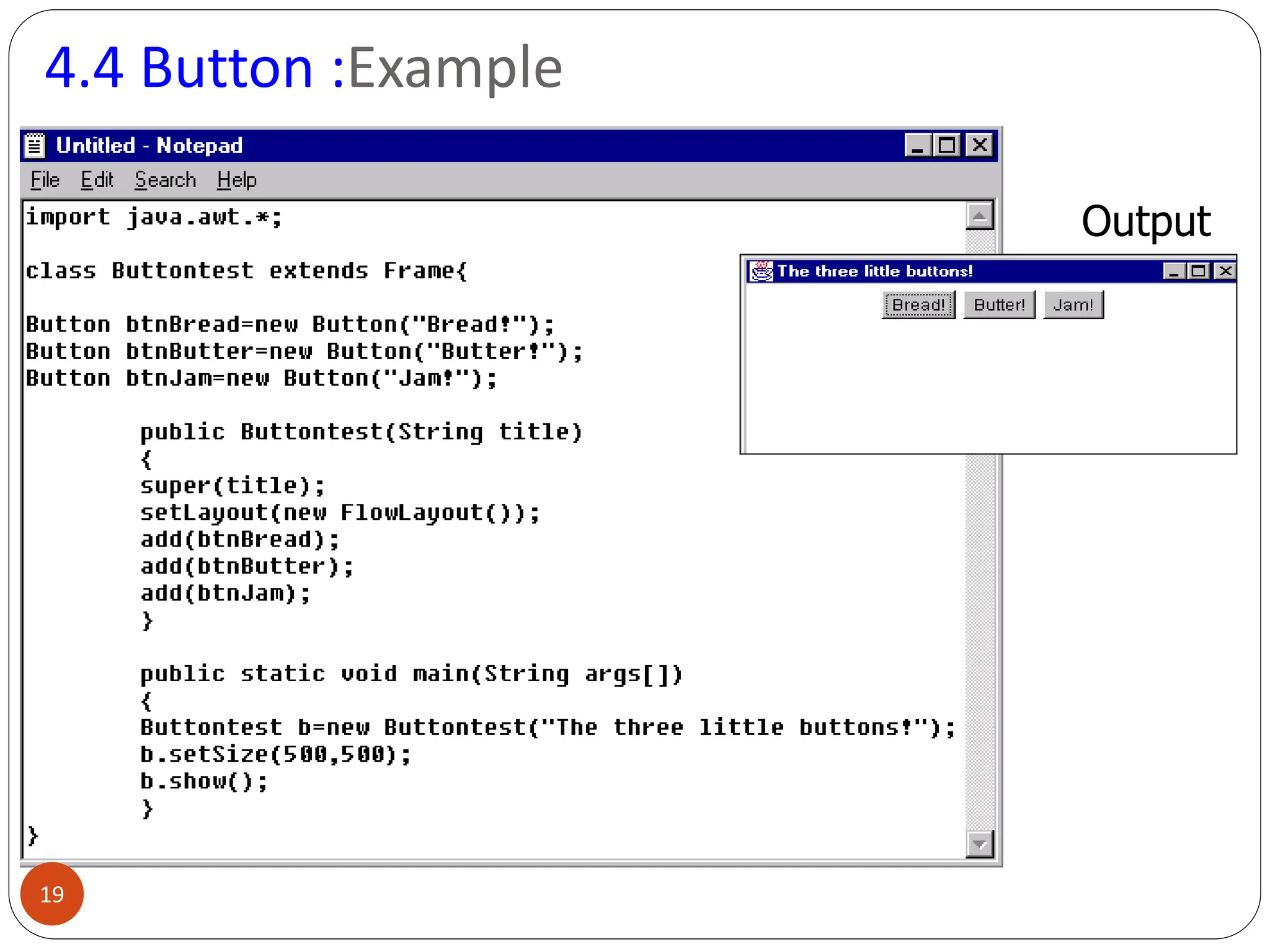
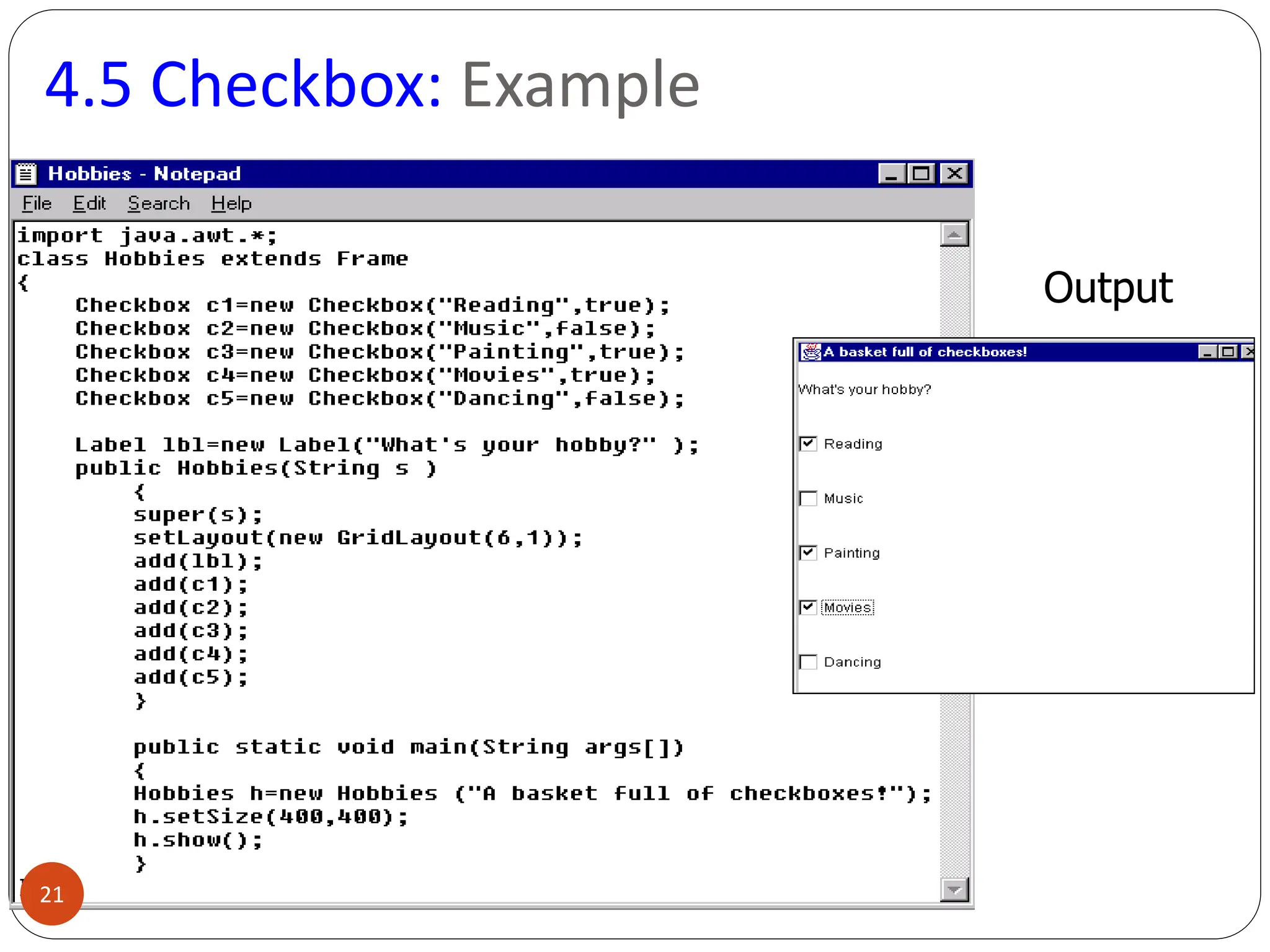
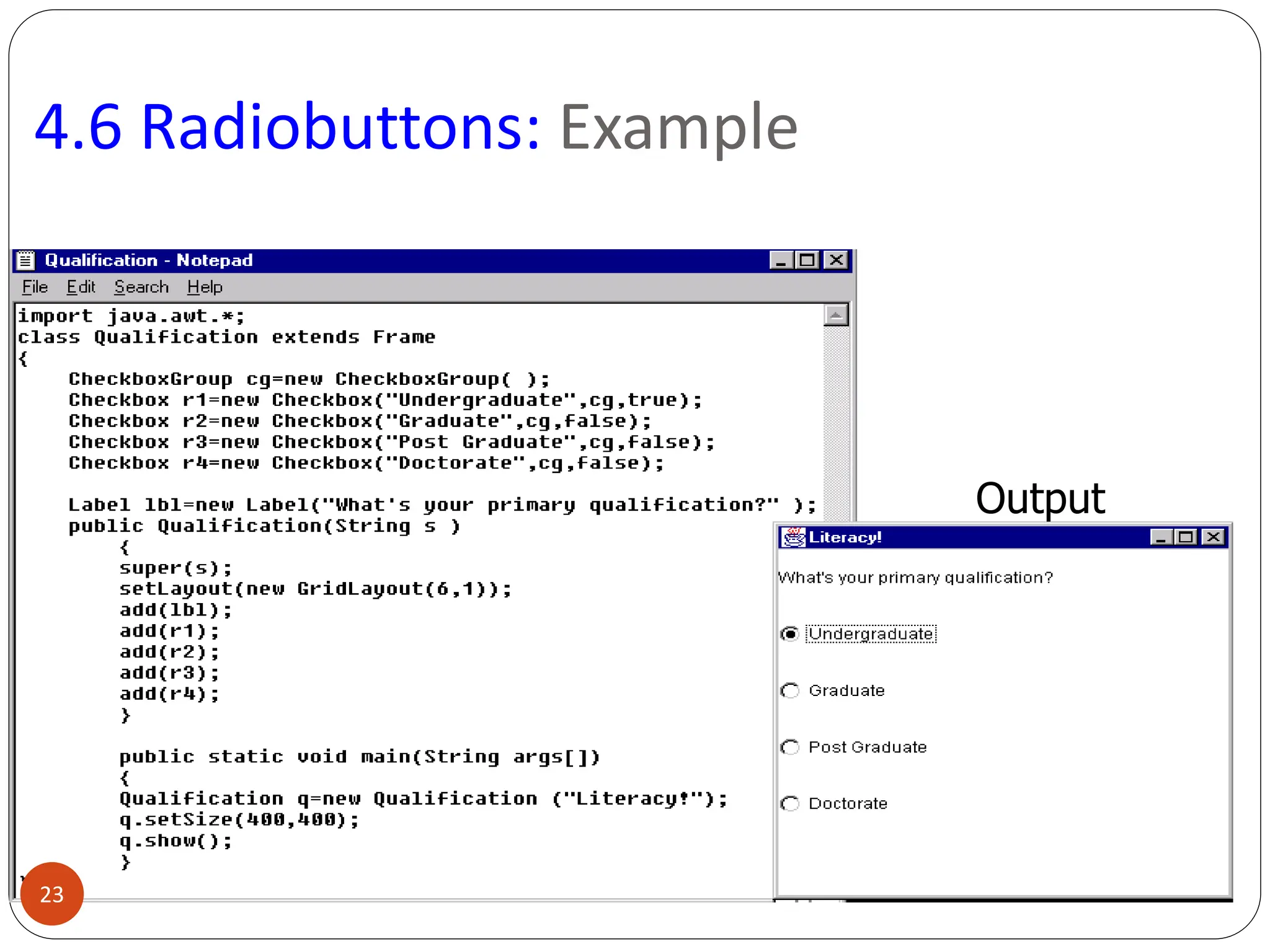
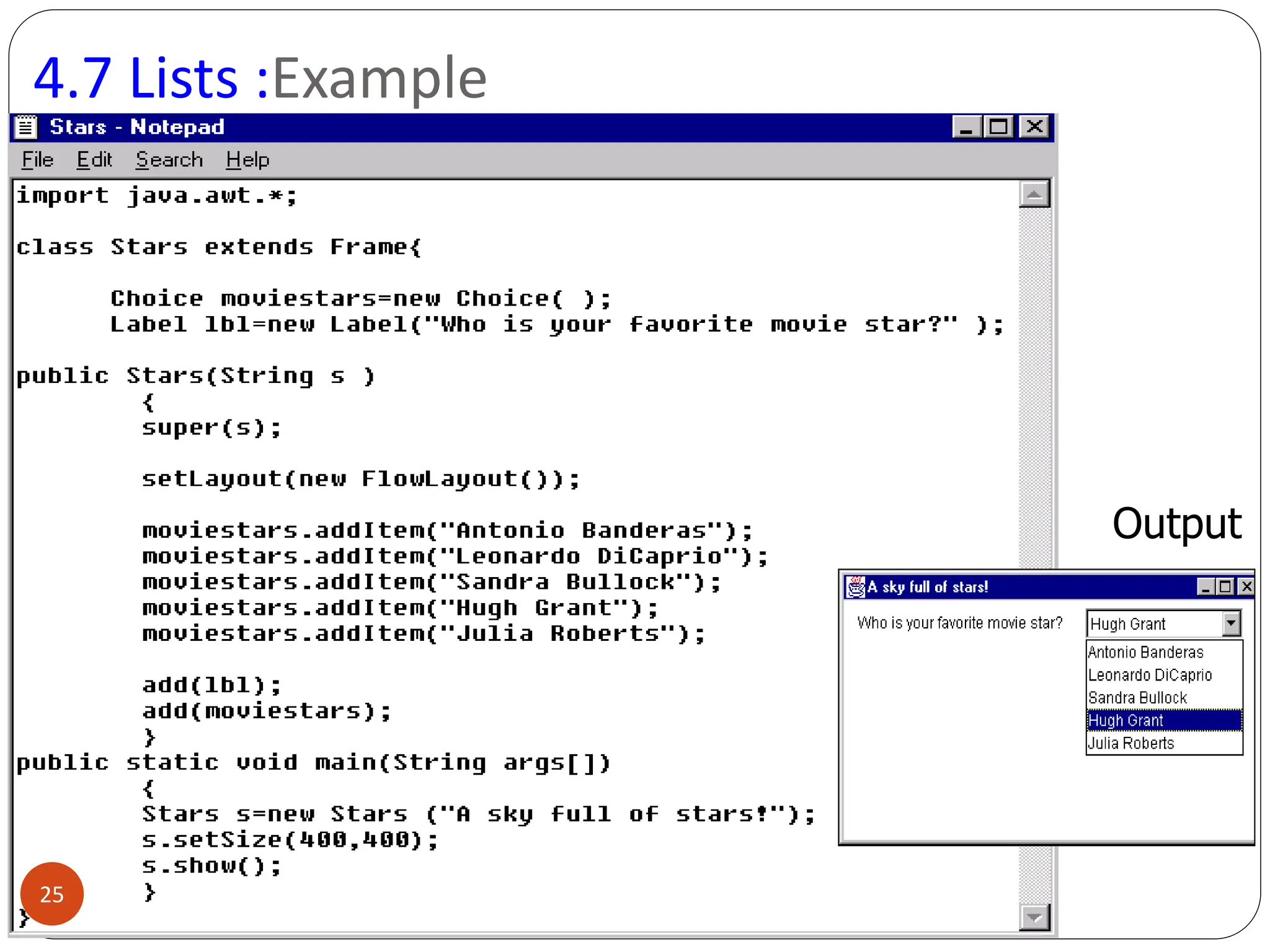
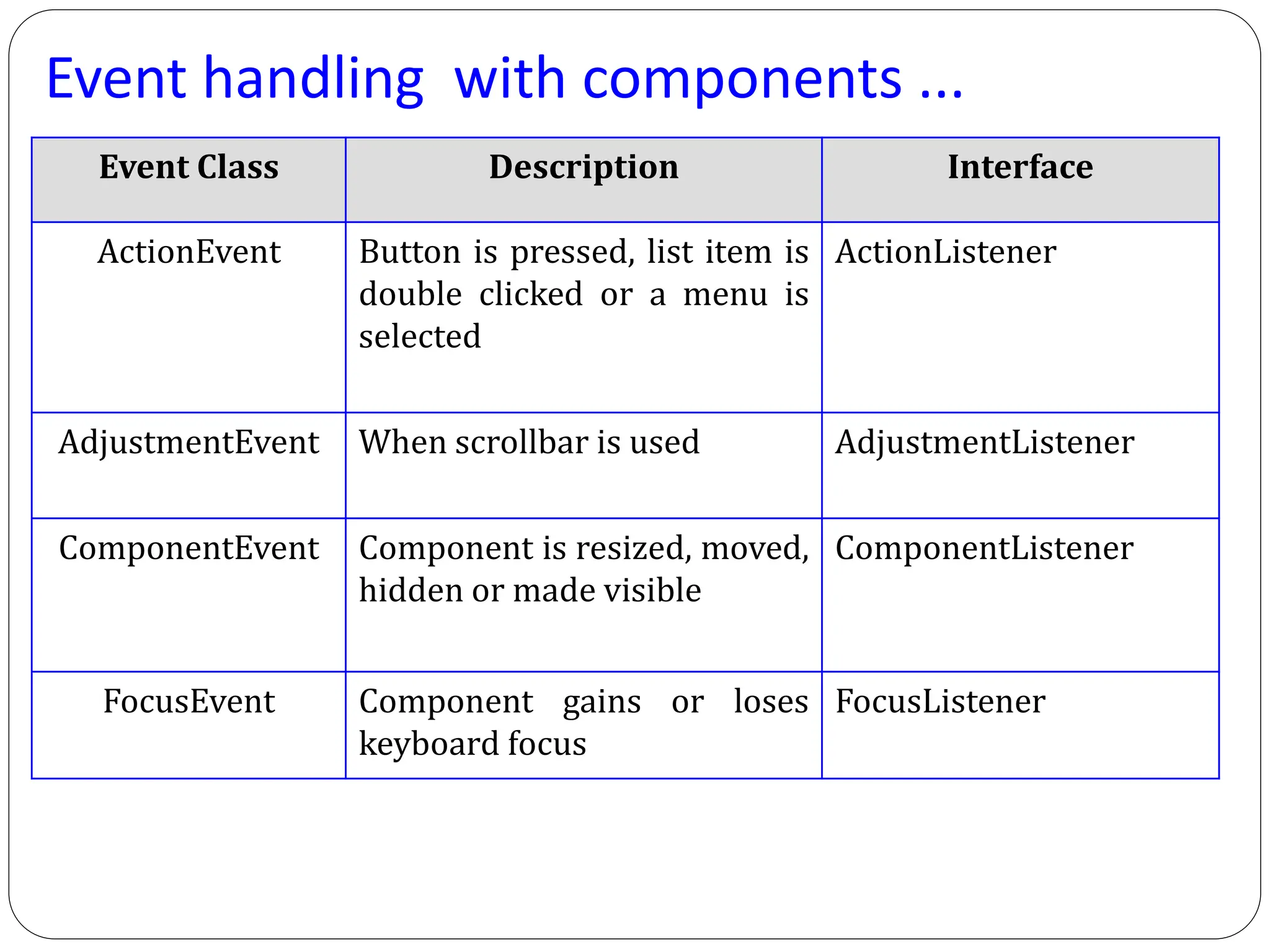
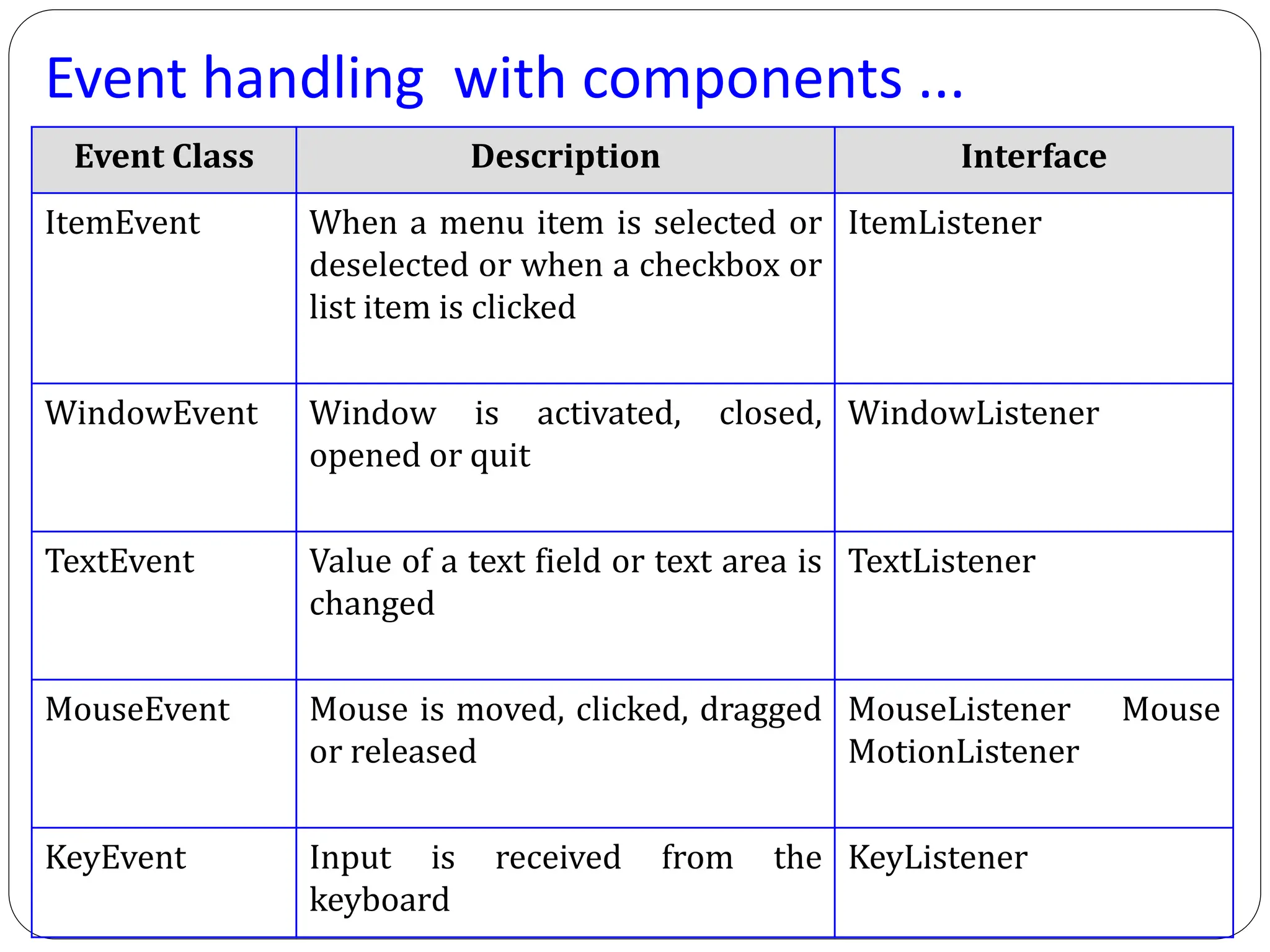
AWT (Abstract Window Toolkit) controls are the user interface elements used in Java to build graphical user interfaces (GUIs). They are part of the java.awt package and provide a way for users to interact with applications through buttons, text fields, labels, and other components.