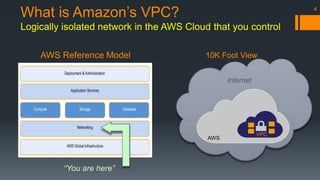
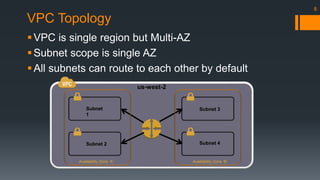
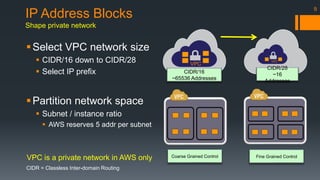
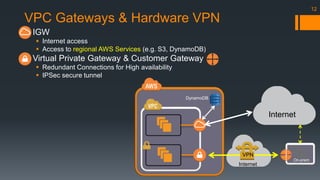
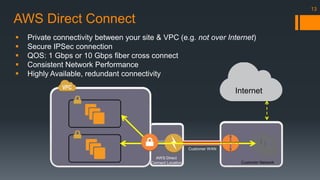
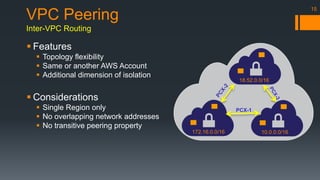
The document is an introduction to AWS VPC presented by Gary Silverman, outlining its benefits, building blocks, and best practices. It details how VPC allows control over network architecture, security measures, and integration with on-premises networks. The presentation also emphasizes considerations for design, segregation of environments, and essential network management strategies.










![Reference Architecture: HA Web App with VPN
19
Availability Zone ‘B’
DB Tier
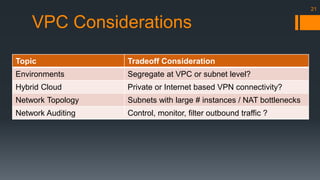
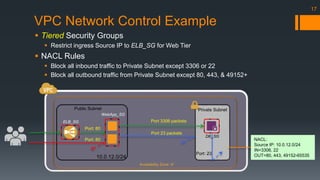
NACL:
Source IP: 10.0.[2|12].0/24
IN=3306, 22
OUT=80, 443, 3306, 49152-65535
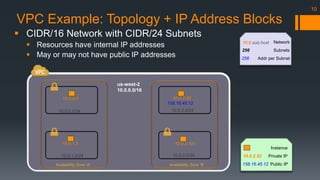
us-west-2 10.0.0.0/16
10.0.12.0/24
Web/App Tier
10.0.13.0/24
NAT
ELB Tier
10.0.11.0/24
Availability Zone ‘A’
DB Tier
10.0.2.0/24
Web/App Tier
10.0.3.0/24
NAT
ELB Tier
10.0.1.0/24
On-prem](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/awschicagomeetupintrovpcpublish-140923174130-phpapp01/85/Introduction-to-AWS-VPC-Guidelines-and-Best-Practices-19-320.jpg)