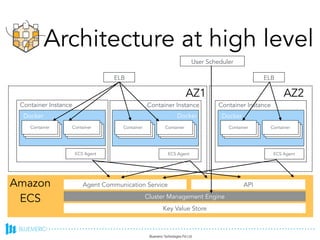
- ECS provides a way to run Docker containers on a cluster of Amazon EC2 instances. It consists of container instances, tasks, services, and a scheduler.
- A task definition specifies the details of a task/container such as name, image, memory requirements, and port mappings.
- A service keeps desired number of tasks running and provides load balancing using an ELB. It ensures tasks are rescheduled if they fail health checks.
- The launch process involves setting up security, IAM roles, container instances, task definitions, services, and pushing Docker images to ECR.


![Task Definition
• Family (version controlled name)
• Container Definitions
• basic
• name *
• image *
• memory *
• portMappings [hostPort, containerPort, protocol tcp/udp]
• advanced
• Volumes](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ecs-dockermeetup-160118102441/85/AWS-ECS-Quick-Introduction-4-320.jpg)


![Launch Process
STEP 1 : Security Group
STEP 2 : IAM User + Permissions : Amazon ECS First Run Wizard
[permissions]
STEP 3: Launch your container instances in a VPC
STEP 4: Create container cluster / ECR
STEP 5: Create task definition
STEP 6: Create service instance
STEP 7: Configure repository and Build, tag, and push Docker image](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ecs-dockermeetup-160118102441/85/AWS-ECS-Quick-Introduction-8-320.jpg)