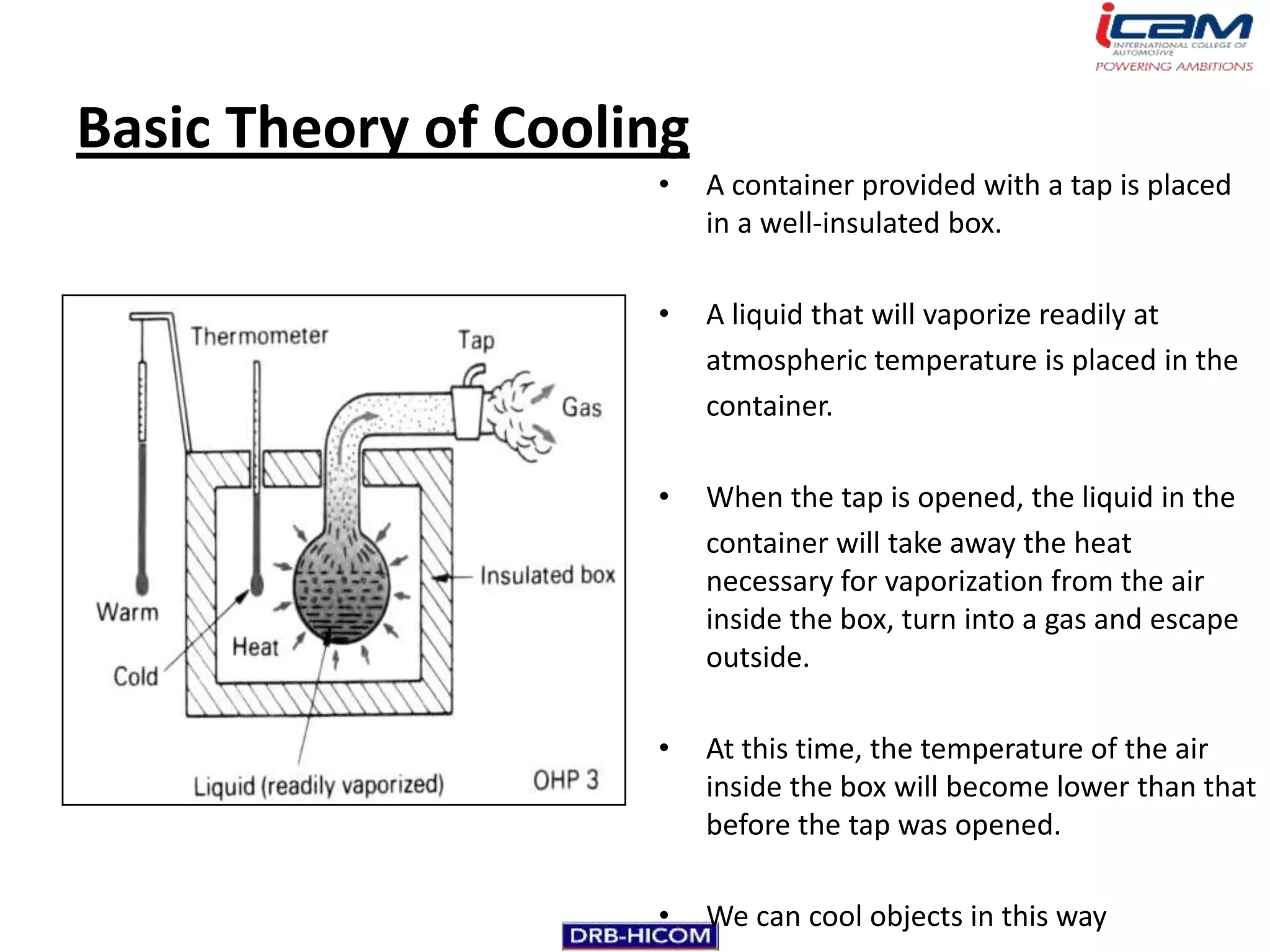
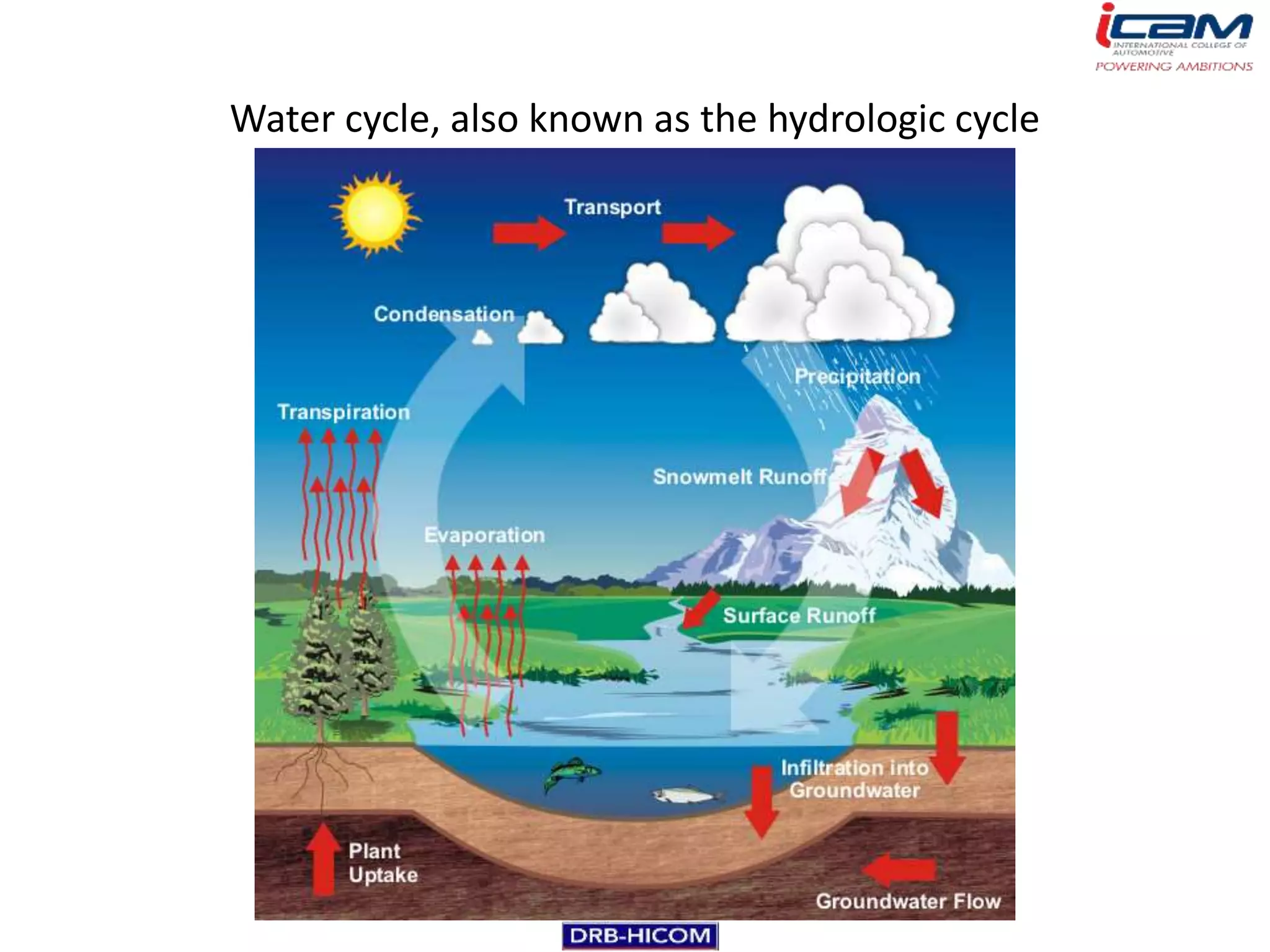
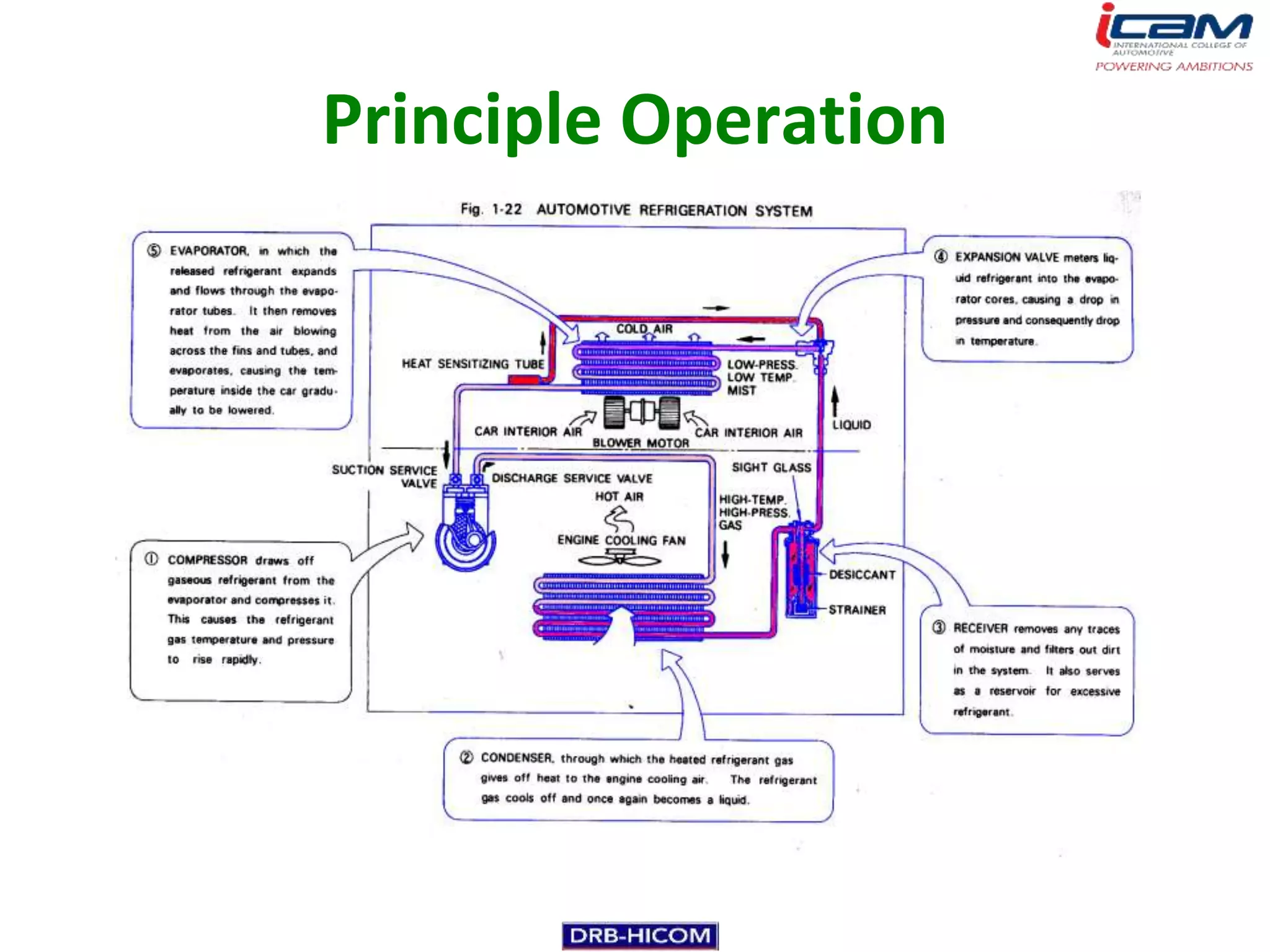
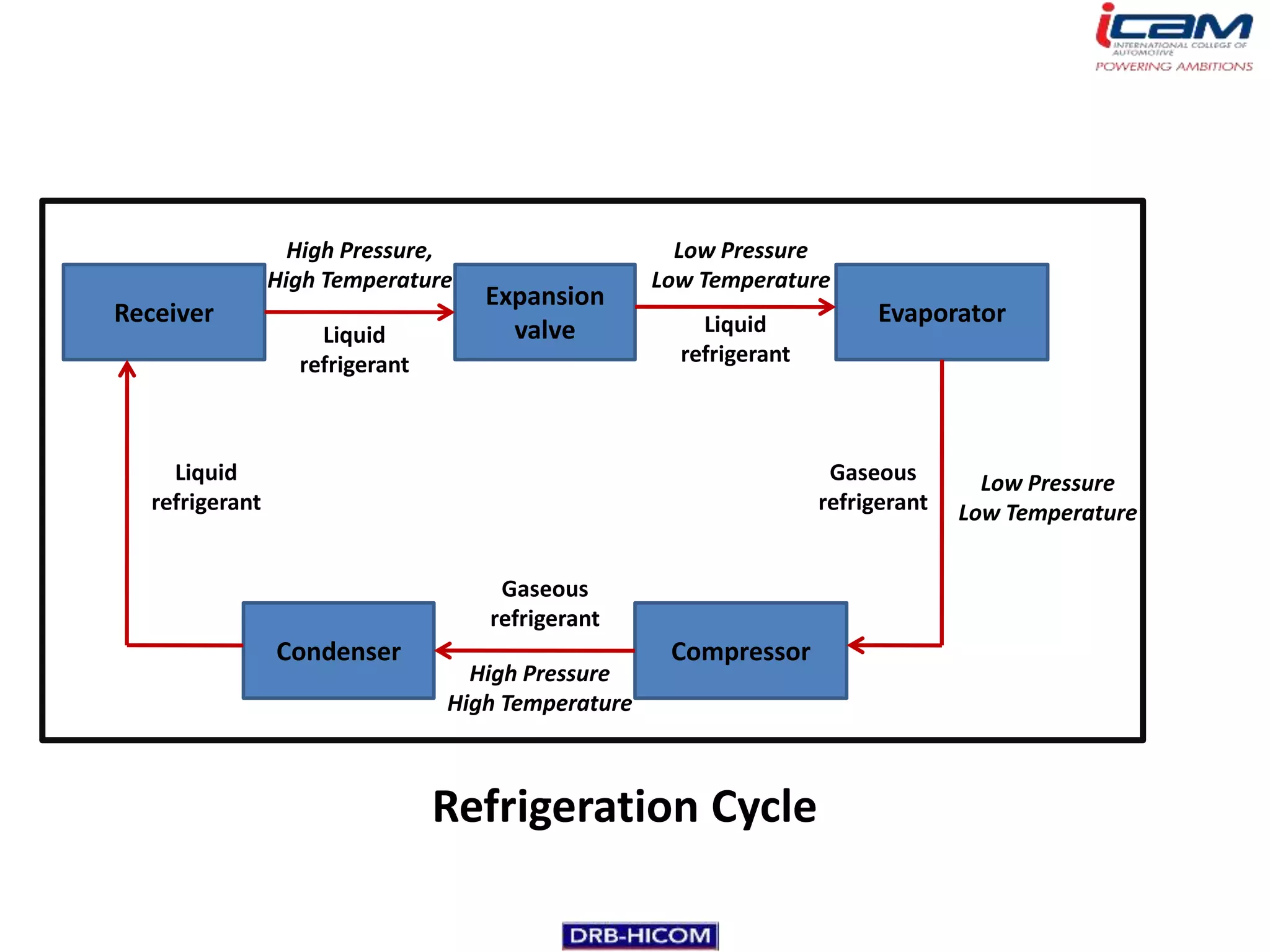
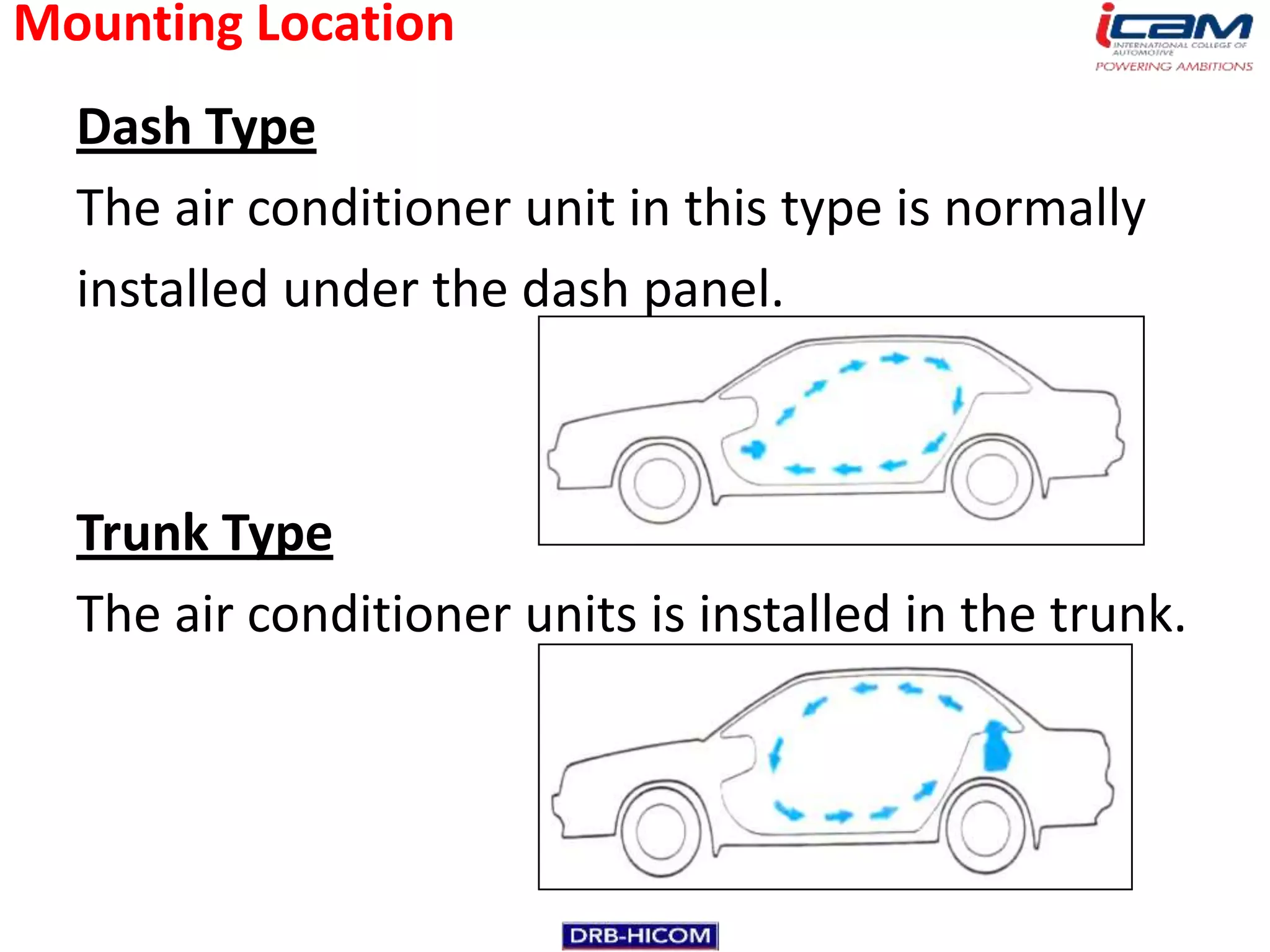
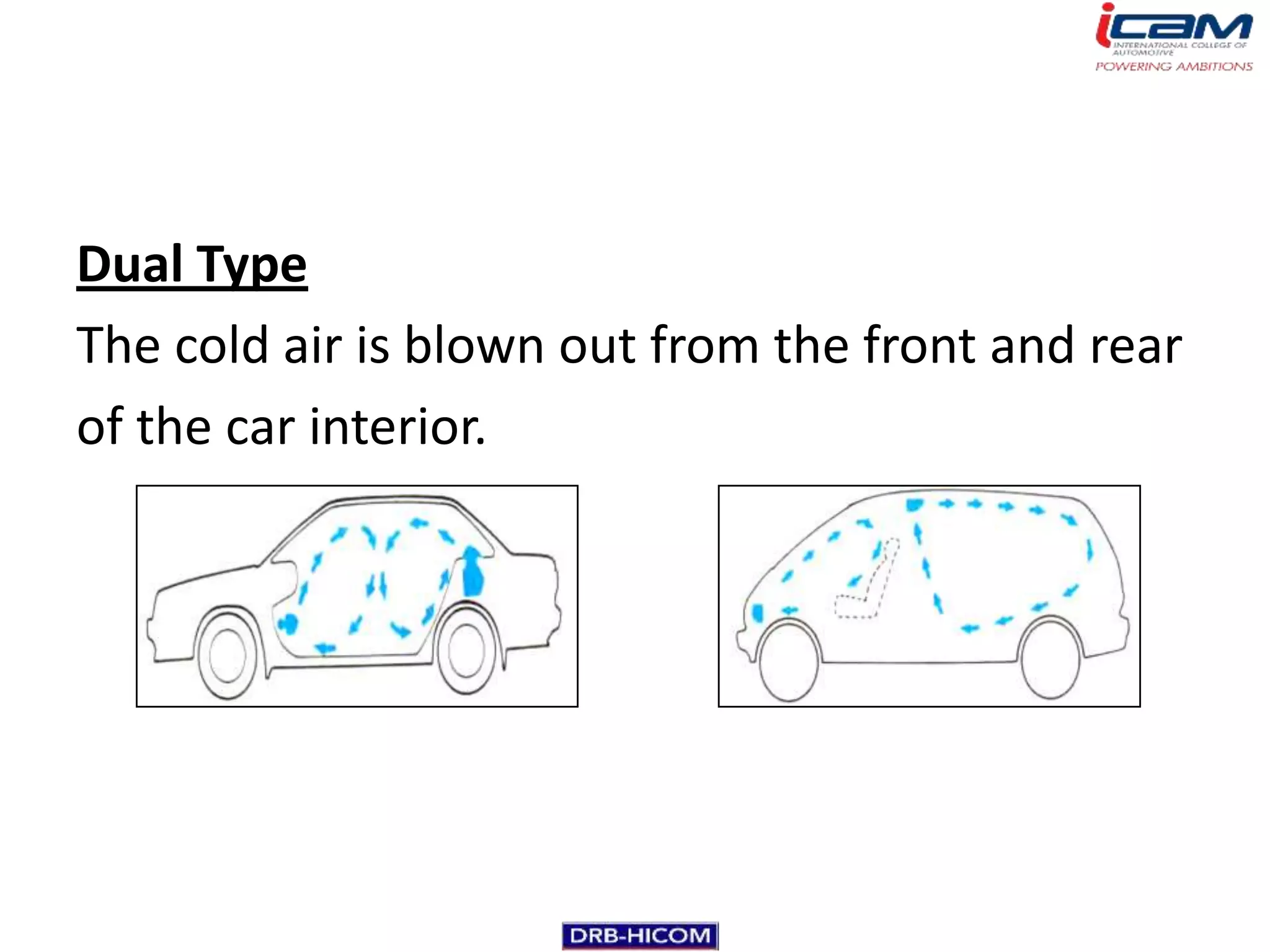
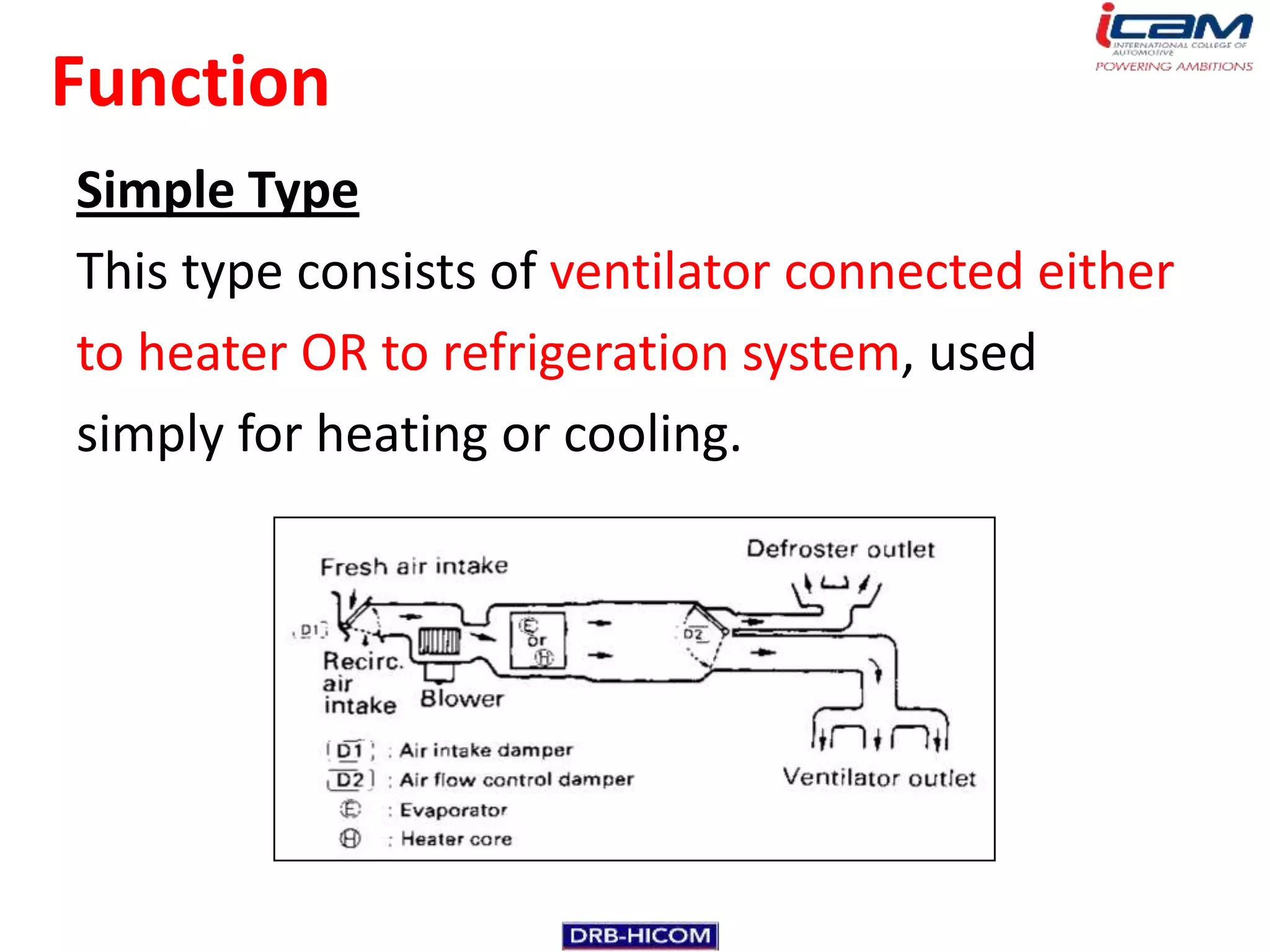
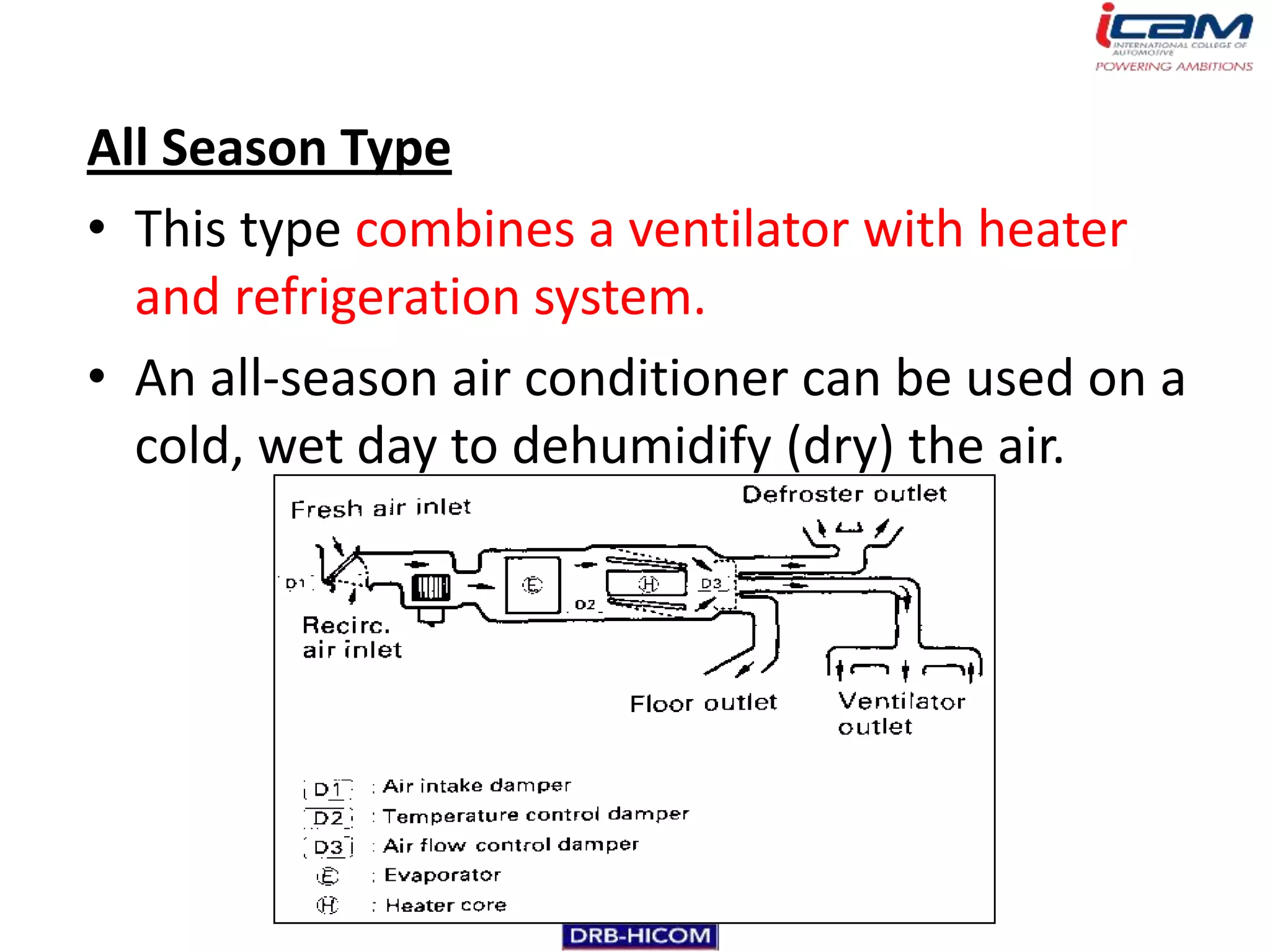
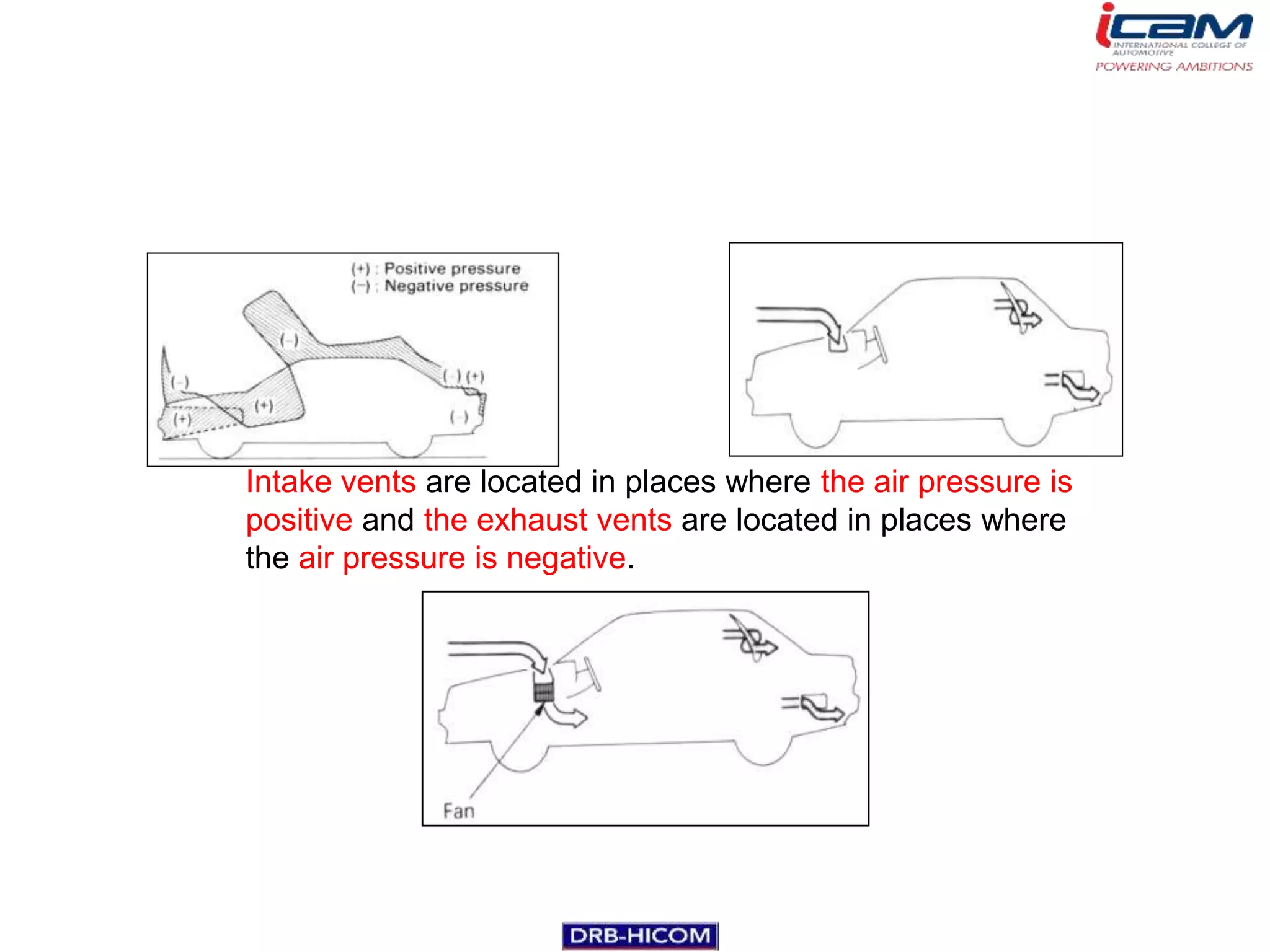
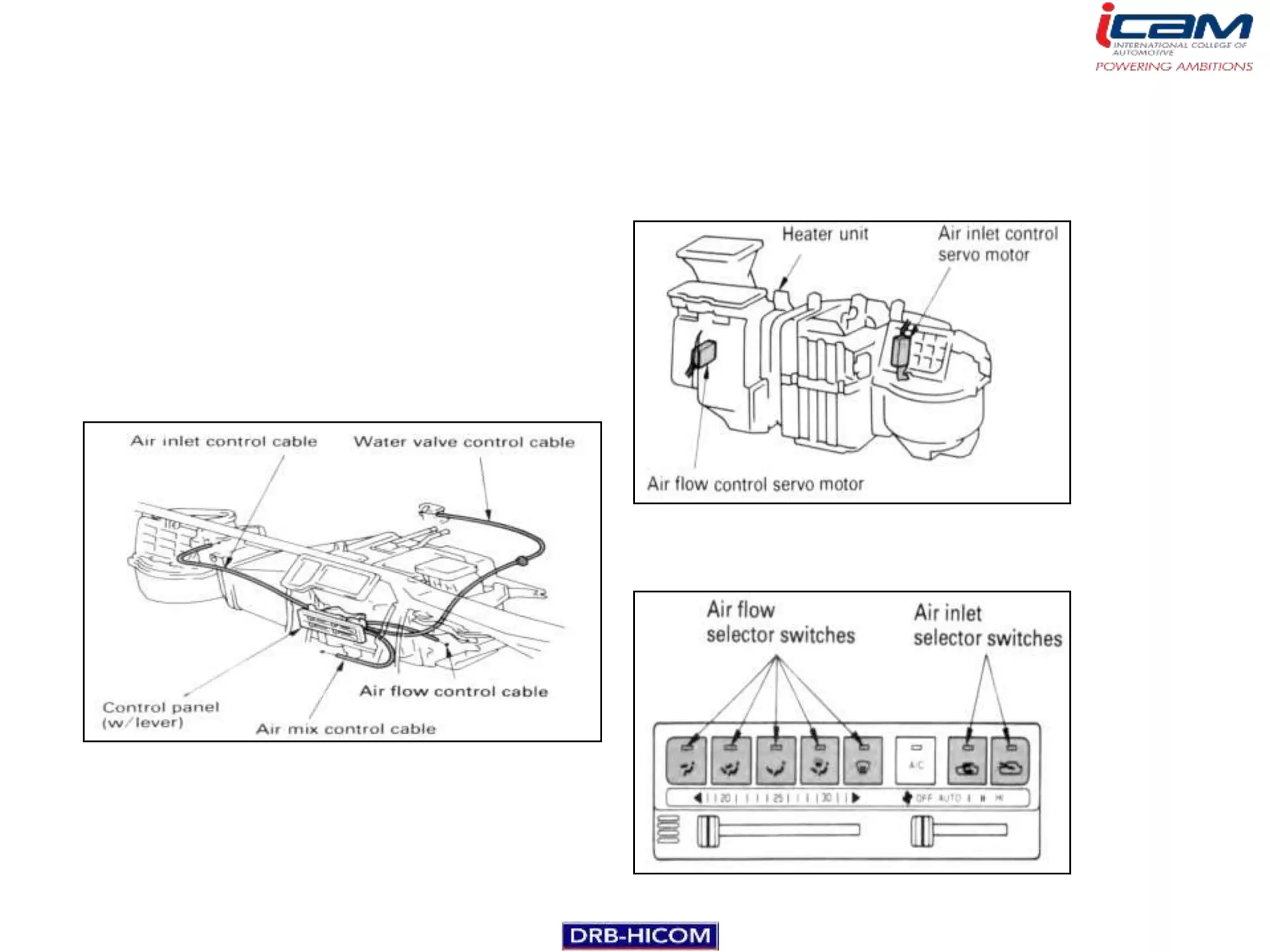
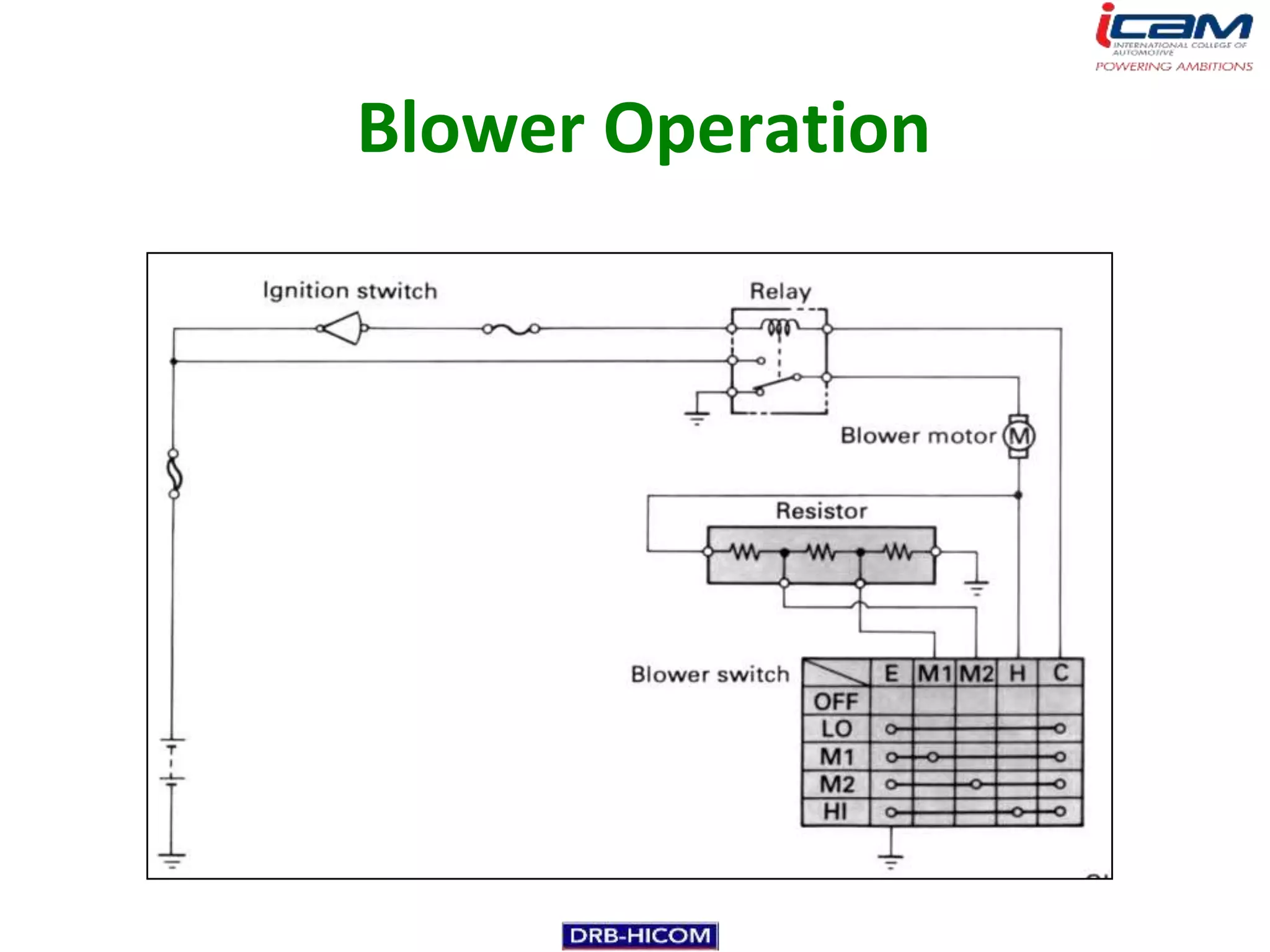
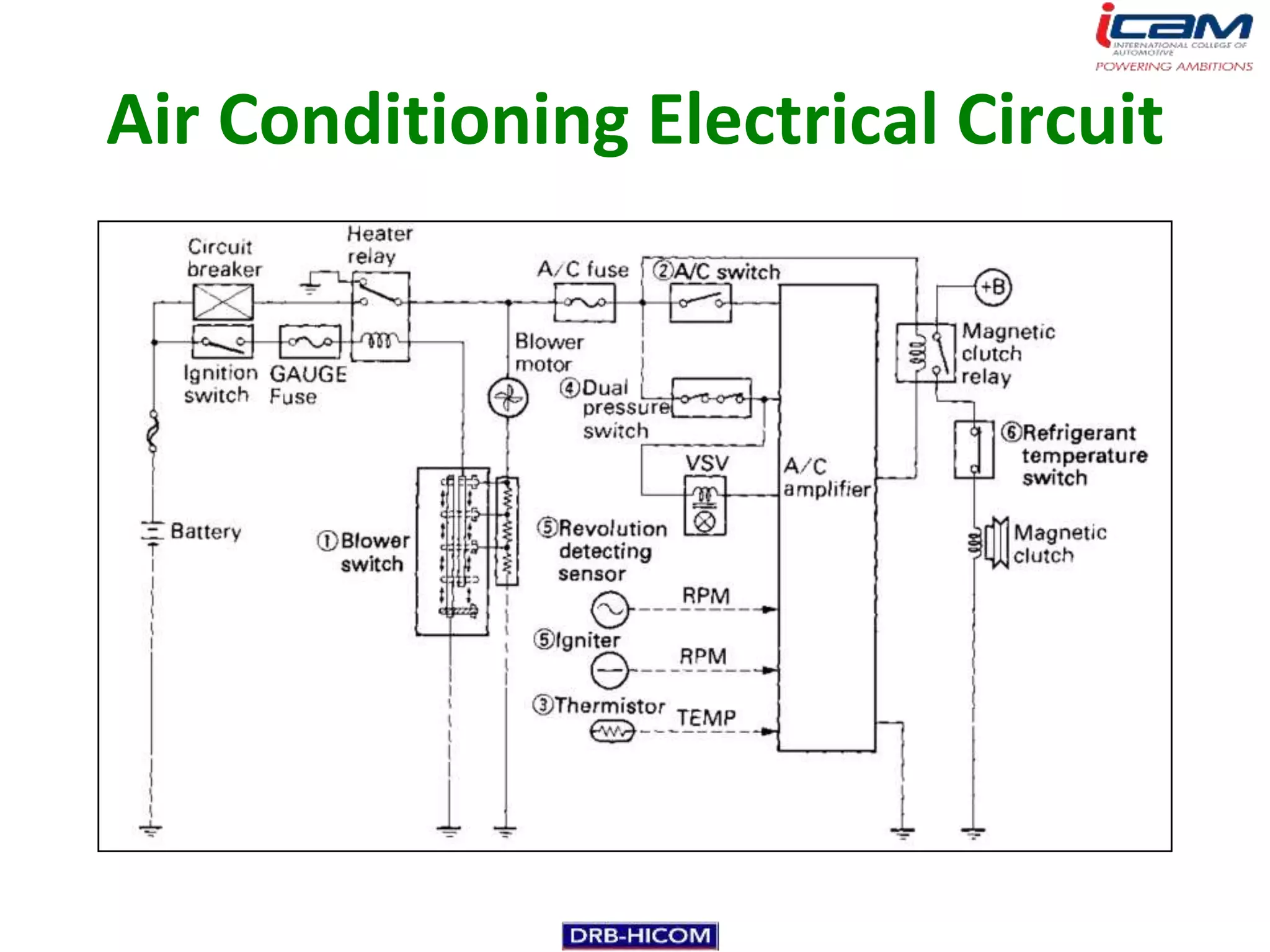
The document summarizes the basic components and operation of an automobile air conditioning system. It describes how refrigerants like R-12 and R-134a are used in the refrigeration cycle to absorb heat from the air and cool the interior. The cooling system involves a compressor, condenser, expansion valve, and evaporator to circulate the refrigerant and lower the air temperature. Air conditioners also include a blower, vents, dampers, and controls to circulate and distribute the cooled air throughout the vehicle cabin.