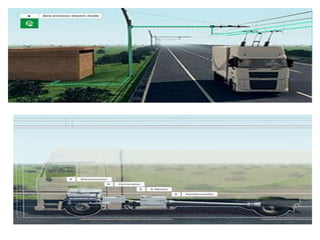
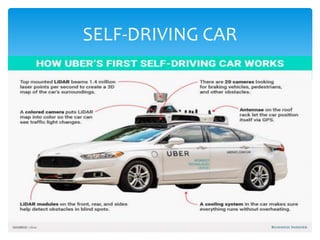
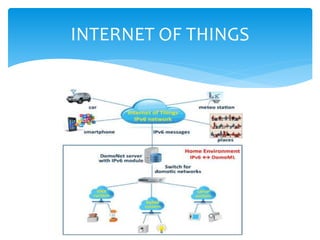
The document discusses automation and provides definitions, tools, applications, advantages, limitations, and emerging technologies related to automation. Automation is defined as the use of control systems to operate equipment, which can be achieved through mechanical, hydraulic, pneumatic, electrical/electronic, and computer systems. Some automation tools discussed include artificial neural networks, distributed control systems, HMIs, SCADA, PLCs, instrumentation, motion control, and robotics. Applications of automation span various industries like food/drink, retail, mining, surveillance, transportation, waste management, homes, and laboratories. The advantages of automation include replacing dangerous/repetitive work, faster production at lower costs, improved quality and consistency, and capabilities beyond humans.