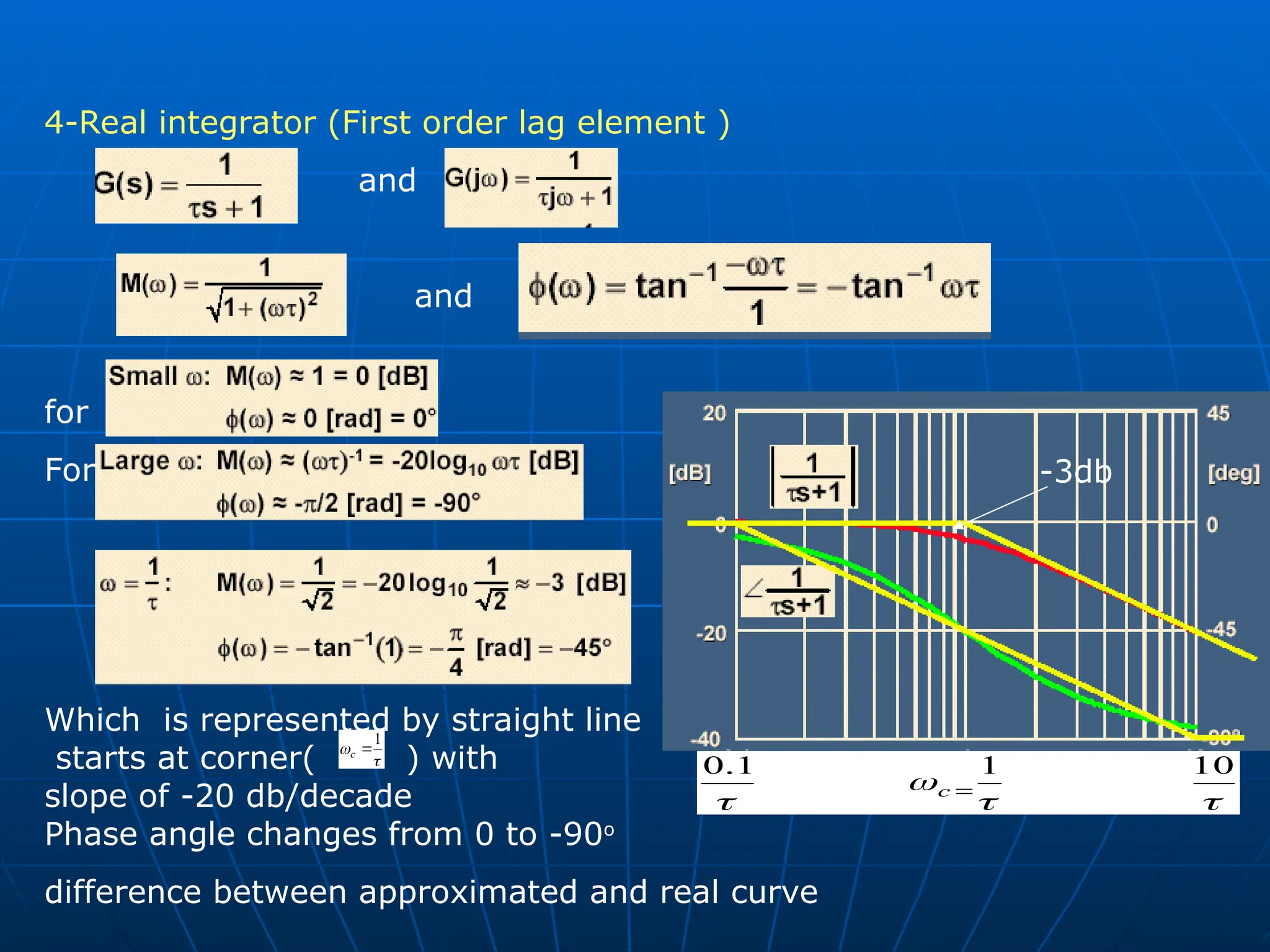
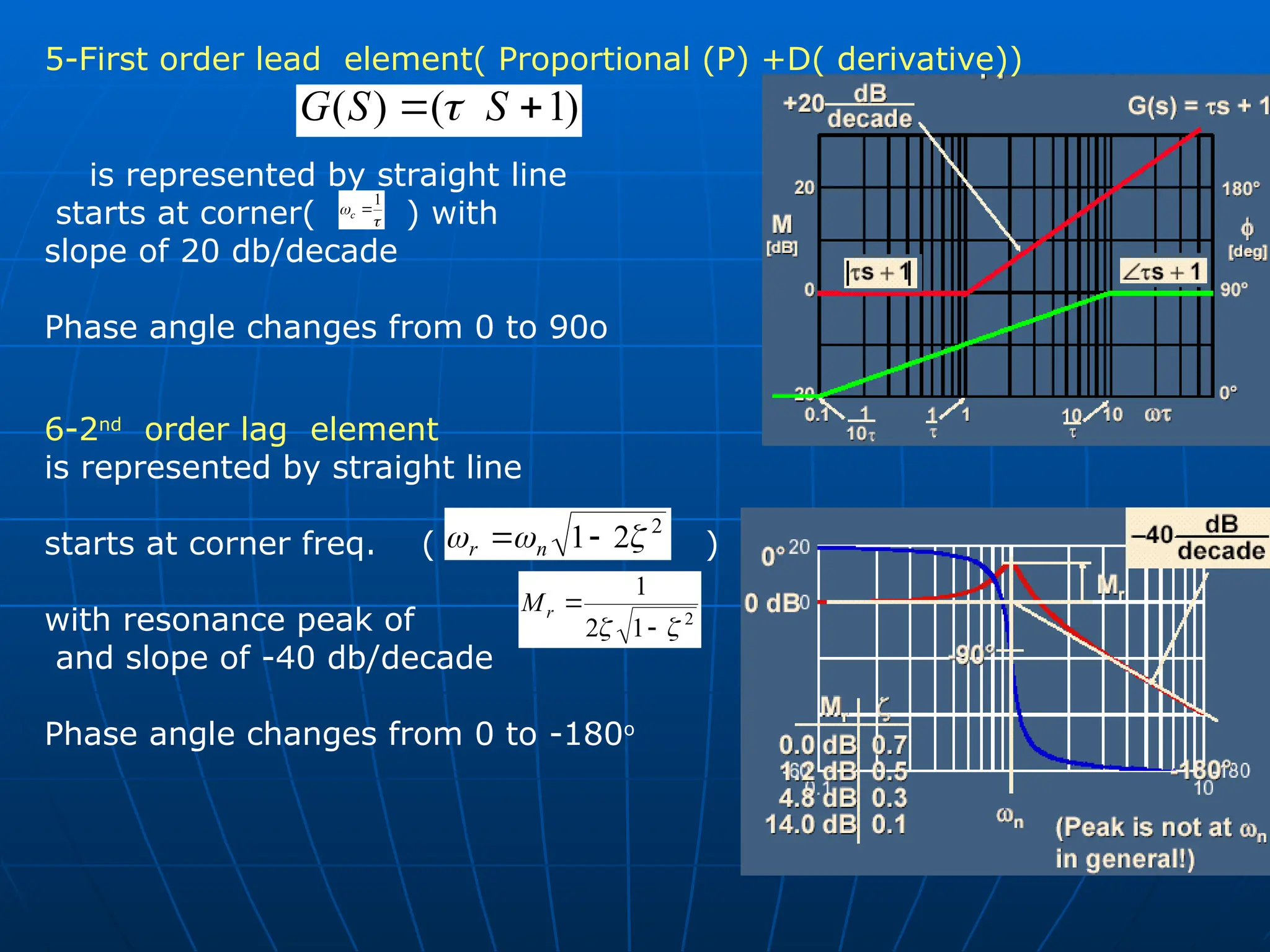
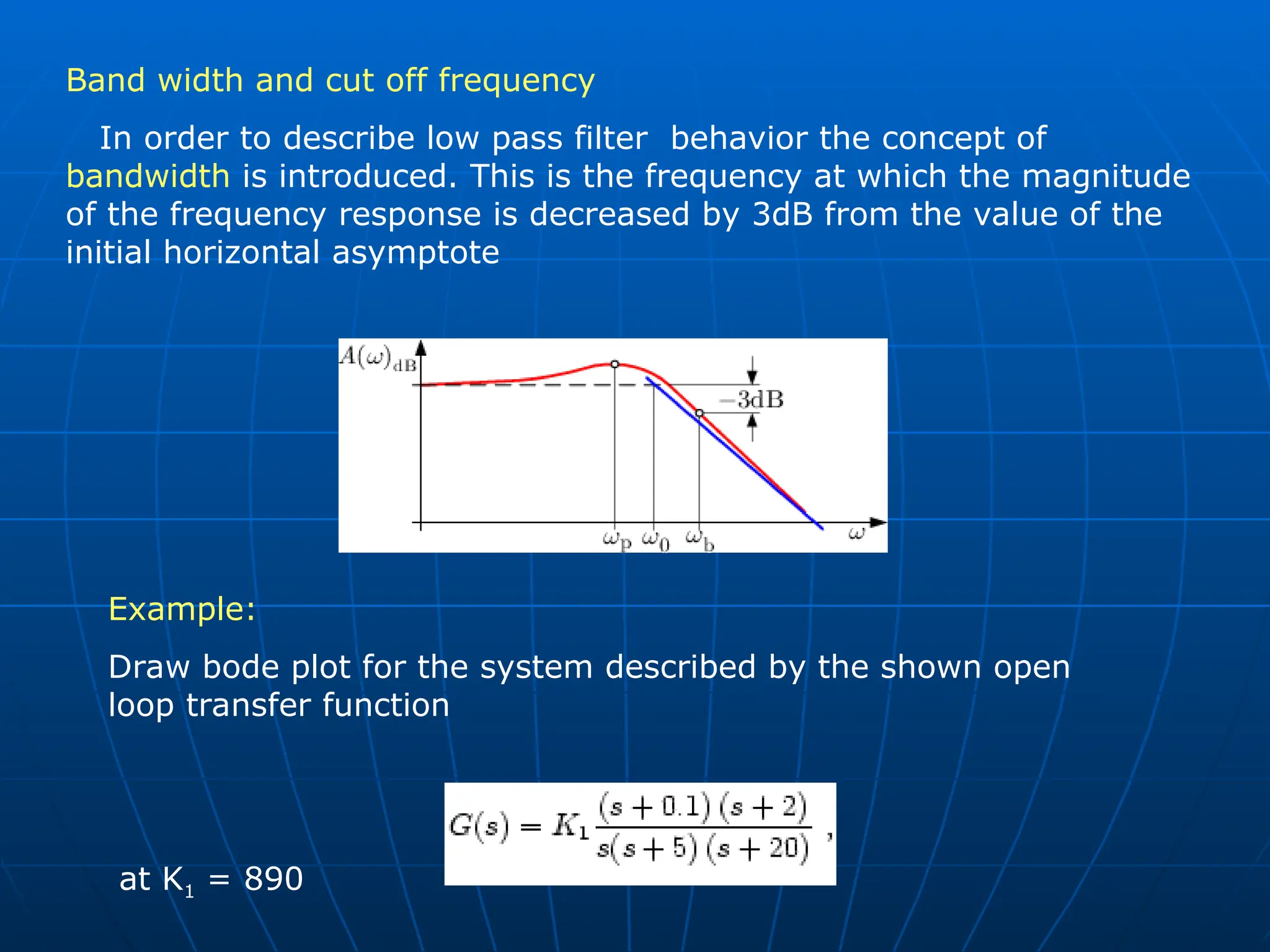
The document discusses stability analysis of control systems using Bode plots, including phase and gain margins, as well as relevant MATLAB applications. It explains how to create Bode diagrams, determine bandwidth, and analyze various system elements such as integrators and derivatives. The document also provides MATLAB code for plotting and assessing system stability.

![If the absolute value and the phase of the frequency response are separately
plotted over the frequency on semi log paper . This representation is called a
Bode diagram or Bode plot. Usually will be specified in decibels [dB] By
definition this is
Bode plot
Decade
General form of transfer
)
(
)
(
)
(
1
1
j
n
j
v
i
m
i
p
s
s
z
s
K
s
G
1-Gain element (K)
S j
0
)
0
(
tan
)
( 1
K
and
t
cons
db
K
K
db
M tan
log
20
)
( 10
M](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/64stabilityanalysis-241109175813-d9ff906b/75/automatic-control-systems-stability-analysis-ppt-3-2048.jpg)
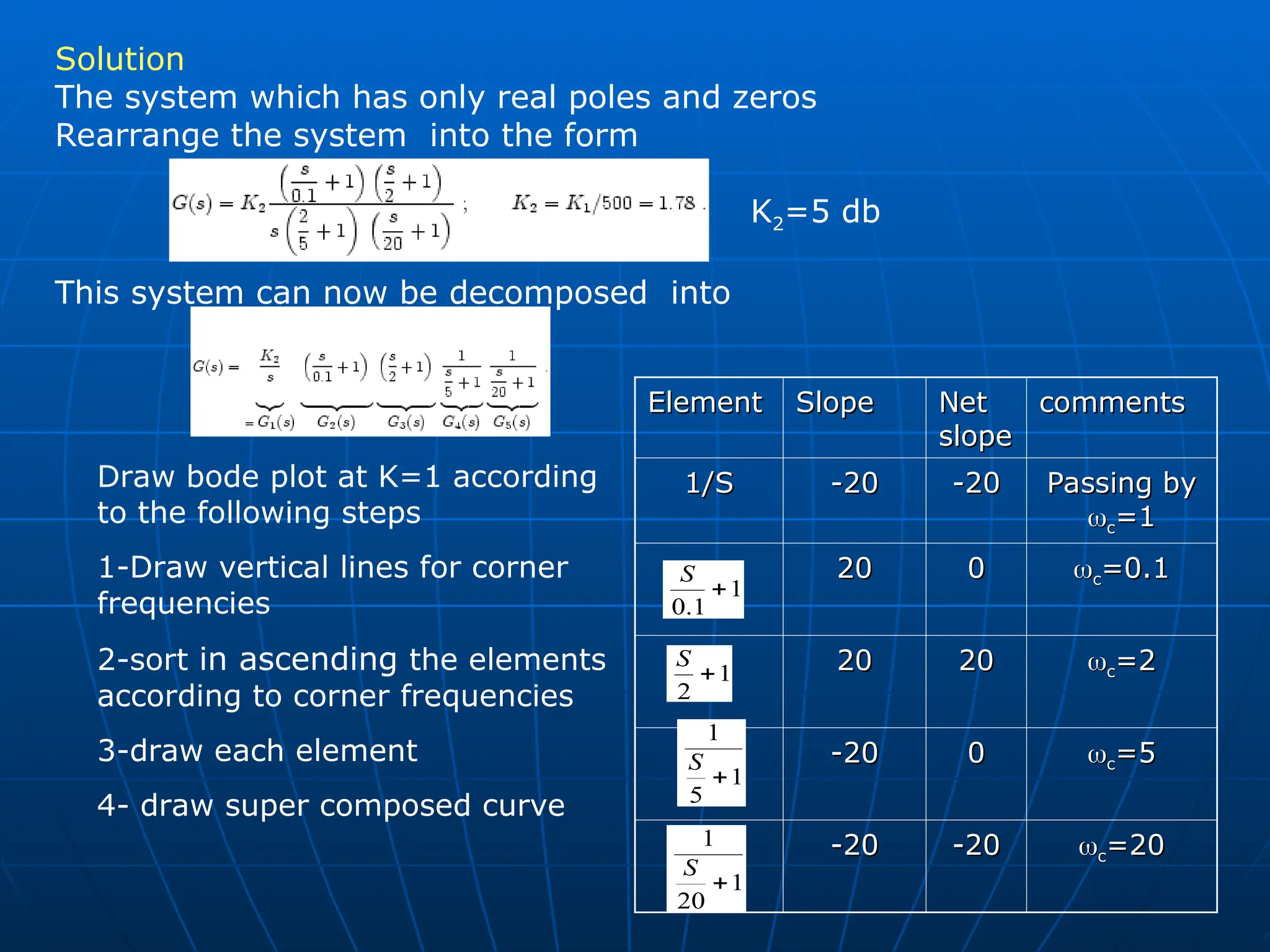
![K=1
K=1.78
5 db
5-Shift bode plot at k=1 by 5 db
6-Draw the relation between phase
and frequencies according to the
following phase equation
20
tan
tan
2
tan
1
.
0
tan
90
)
( 1
5
1
1
1
Following MATLAB code can be
written to draw the bode plot
for previous problem
Num=[8.9 18.69 1.78];
Den=[ 0.01 0.25 1 0];
sys=tf(num,den);
Bode(sys)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/64stabilityanalysis-241109175813-d9ff906b/75/automatic-control-systems-stability-analysis-ppt-10-2048.jpg)
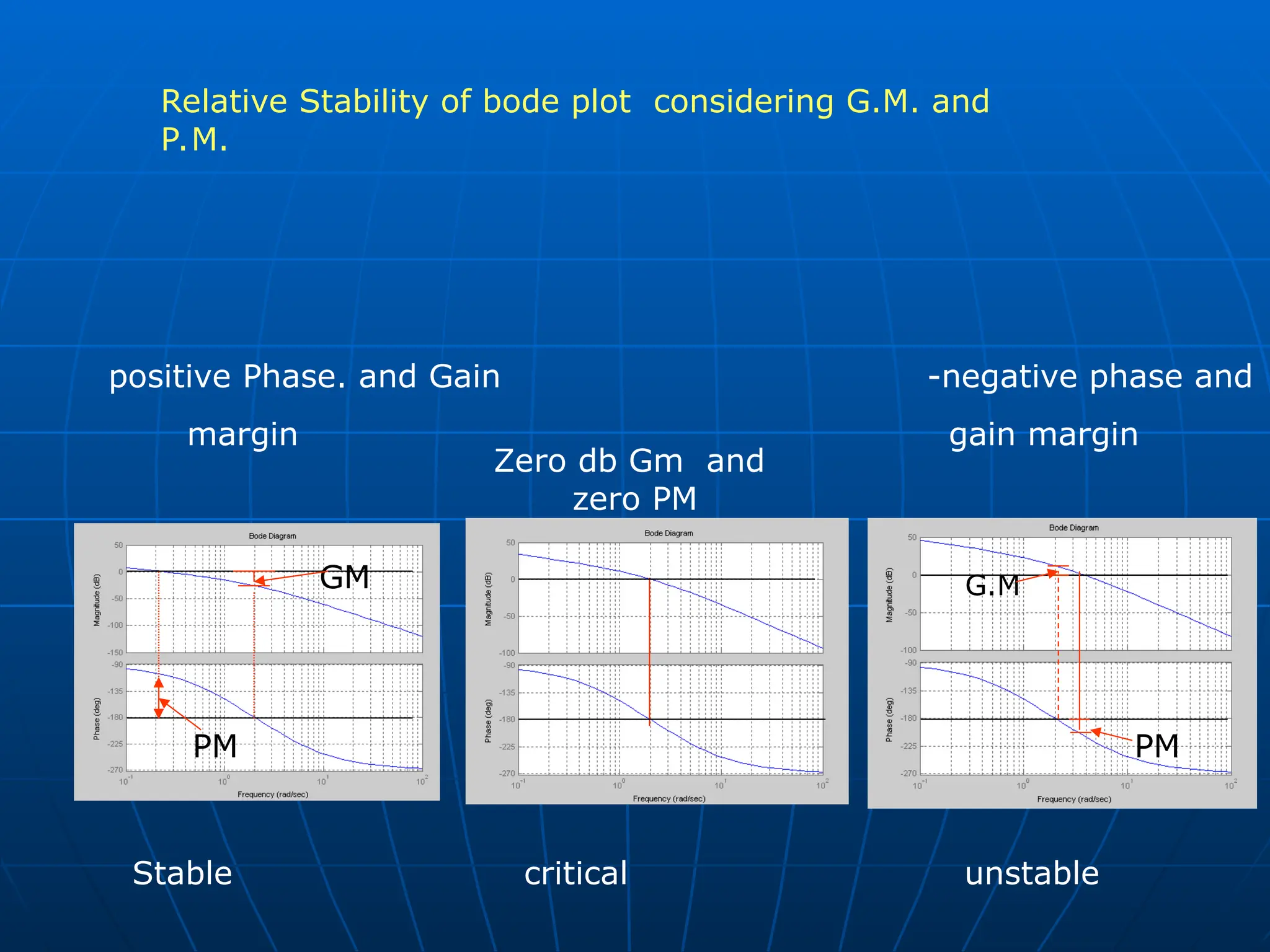
![Gain and phase margin
Phase cross over
Gain cross over
gc
gain margin (GM) is defined as the
change in open loop gain required to
make the system unstable.
GM=-20log Ap at phase =-180o
phase margin (PM) is defined as the
change in open loop phase shift required
to make a closed loop system unstable.
at unity amplitude
180
)
( 1
P
A
PM
MATLAB Commands
Num=[ ];
Den=[ ];
Sys=tf(num,den);
[ gm pm gc pc]=Margin(sys)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/64stabilityanalysis-241109175813-d9ff906b/75/automatic-control-systems-stability-analysis-ppt-11-2048.jpg)