The document presents a case study of a 21-year-old female patient diagnosed with autoimmune hemolytic anemia. Key findings include low hemoglobin and hematocrit levels, elevated reticulocytes, and positive direct Coombs test. She was treated with prednisolone, folic acid, calcium, vitamin D, risedronate, and levothyroxine. Her bilateral knee pain and weakness improved over the course of her treatment.
![INTRODUCTION
DEFINITION
• Autoimmune hemolytic anemia[AIHA] is characterized by an
abnormal production of auto antibodies[Ig G,M.E,A] that bind
to Antigens on the erythrocyte surface. These antibodies then
lead to destruction of RBC’s thus shortening their life span.
• Red cell lifespan may decrease to 30days.
CLASSIFICATION
• Warm AIHA
• Cold AIHA – Cold Agglutinin Syndrome
Paroxysmal Cold Hemoglobinuria
• Mixed type AIHA
• Drug Induce Immune hemolytic anemia](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pt-3-200708094338/75/autoimmune-hemolytic-anemia-2-2048.jpg)
![WARM AIHA
• In this warm AIHA, the autoantibodies attach to & destroy the
RBC at temperature ≥ to 37 degrees celcius.
• More common among women.
• MECHANISM OF DESTRUCTION: Due to Extravascular
hemolysis
• Associated with development of Ig G
• May be due to primary or secondary etiology
Primary – idiopathic
Secondary –due to underlying disease[eg: lymphoproliferative
or autoimmune disorders]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pt-3-200708094338/75/autoimmune-hemolytic-anemia-3-2048.jpg)


![MIXED TYPE AIHA
• Features similar to WAIHA & CAS
• Both IgG & C3d[activated by IgM cold Ab] are detected
DRUG INDUCED AIHA
• Antibodies directed against or one of its metabolites
• All may involve IgG &C3
• Eg: Pencillin , Cephalosporins , Quinidine , Methyldopa](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pt-3-200708094338/75/autoimmune-hemolytic-anemia-6-2048.jpg)





![TREATMENT
WARM AHIA
• Folic acid supplements
• Corticosteriods like
prednisolone[1-
1.5mg/kg/day]
• Immunoglobulins like
rituximab, azathioprine
etc..
• If ineffective splenectomy
considered
• Blood transfusion
• Splenectomy
COLD AIHA
• Removal of underlying
disease.
• Use antibiotics like pencillin
in case of infections
• Rituximab is given majorly
• Avoid cold weather an cold
drinks
• Blood transfusion
• Splenectomy](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pt-3-200708094338/75/autoimmune-hemolytic-anemia-12-2048.jpg)


![DEMOGRAPHIC DETAILS
• Patient name: XYZ
• Age: 21 Years
• Gender: Female
• Height:165cm
• Weight: 85kg
• BMI: 31.2Kg/sqmm[over weight]
• IP No:472890
• Dept: General medicine-554
• DOA:11/NOV/19
• DOD:14/NOV/19](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pt-3-200708094338/75/autoimmune-hemolytic-anemia-15-2048.jpg)



![Day 2
• B/L Knee pain
• Weakness reduced
• No other issues
• T.GEMFOS[Risedronate]-35mg/week on empty stomach with 1full
glass of water, Don’t EAT, LIE DOWN, BEND for 2hrs, can walk and sit
Day -3
• B/L Knee pain reduced
No weakness
No headache
• Can be discharged tomorrow](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pt-3-200708094338/75/autoimmune-hemolytic-anemia-19-2048.jpg)




![IMMUNOSEROLOGY
• Rheumatoid factor assay : <8.6 IU/L [ normal : <121 IU/L]
PERIPHERAL SMEAR
• RBC Morphology : Microcytic Hypochromic with Anisocytosis,
spherocytes
• WBC : normal in count & disturbances
• PLATELET : Adequate
BIOCHEMISTRY
LUPUS ANTICOAGULANT
• DIL RUSSEL VIPER VEN TIME : 58.00 sec
• DRVVT CONTROL : 49.00 sec
• DRVVT:DRVVTC Ratio – 1.18 sec
• REFERENCE VALUE [ <1.30sec]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pt-3-200708094338/75/autoimmune-hemolytic-anemia-24-2048.jpg)
![URINE
• Total Input- 1300ml
• Total Output – 1200ml
MRI OF KNEE JOINTS
• Findings : few irregular areas of altered signal intensity with T1
isointense &peripheral hyperintense rim, hyperintense on T2
weighed fat
• Marrow edema noted in femoral condyle with ill defined
margins of sub-chondral altered signal area
• Findings suggestive of medullary infracts in distal femur with
sub-chondral osteonecrosis in medial femoral condyle
• Mildly reduced fibro femoral joint space with reduced articular
cartilage thickness[grade-2]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pt-3-200708094338/75/autoimmune-hemolytic-anemia-25-2048.jpg)



![OBJECTIVE EVIDENCE
• Haemoglobin- 10.10gms% [low]
• Hematocrit -12%[low]
• Reticulocytes - 3.76%[ high]
• Bc Unconjugated -1.67mg/dl [high]
• RBC Morphology – microcytic hypochromic with anisocytosis,
spherocytes
• Direct Coombs test - positive](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pt-3-200708094338/75/autoimmune-hemolytic-anemia-29-2048.jpg)





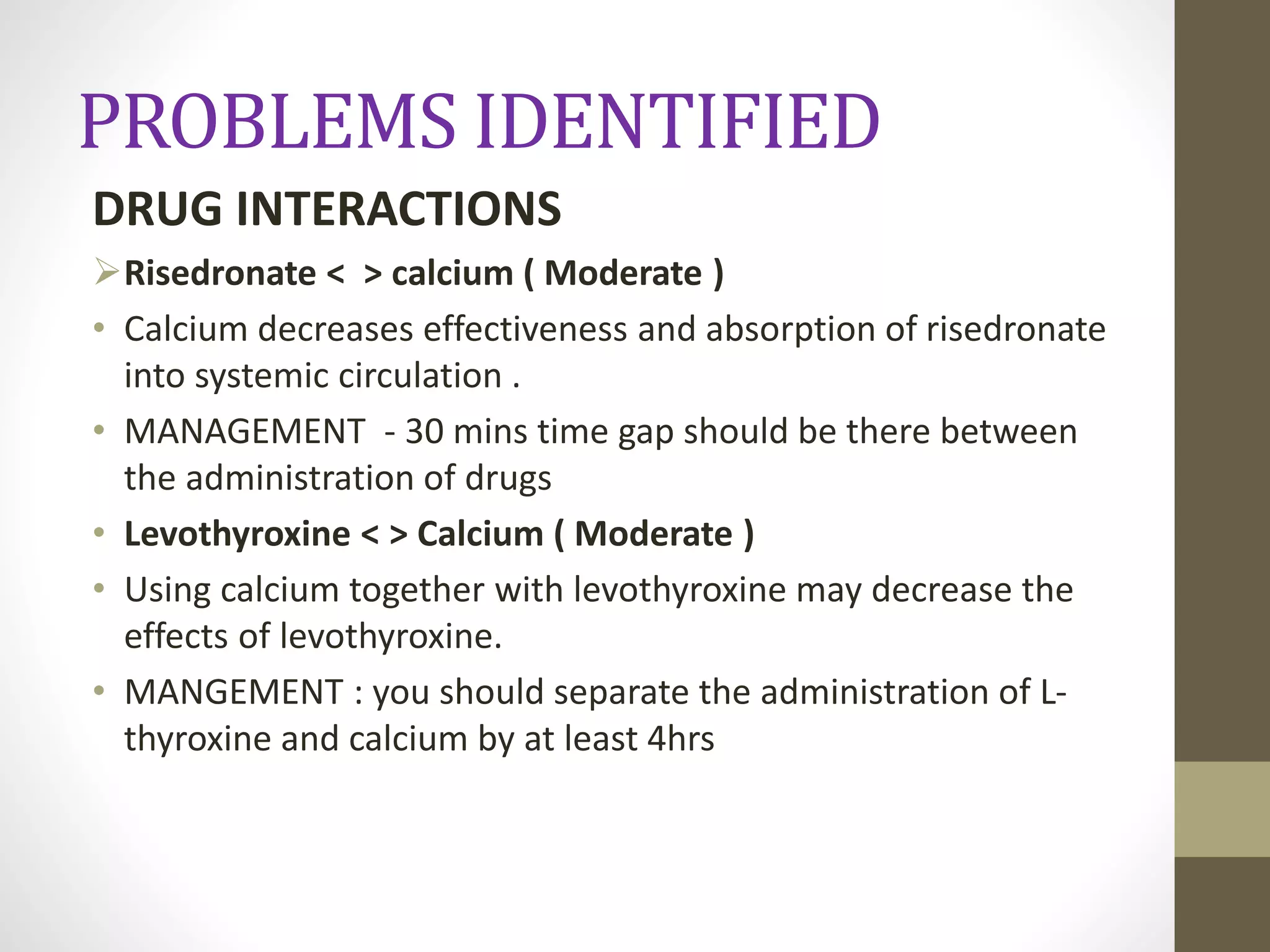



![PATIENT COUNSELLING
ABOUT THE DISEASE
• The patient must be counselled about
the disease i.e., AUTOIMMUNE
HEMOLYTIC ANEMIA which is a condition
that causes your RBCs to die sooner than
normal. And your bone marrow cannot
make new RBCs fast enough to replace
the ones that have died.
• Further the disease complications
[jaundice, hemogobinuria, arrhythmias
or cardiomyopathy ] also have to be
explained.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pt-3-200708094338/75/autoimmune-hemolytic-anemia-39-2048.jpg)


![DIET
FOODS TO BE TAKEN
• Leafy greens – [spinach, kale, broccoli] – Helps to prevent
relapse of anemia
• Meats- [chicken, beef ,ham] –useful in treating anemia
• Honey, amla juice, jack fruit & custard apple increases Hb
content in body.
• Beetroot is good remedy for treating anemia
• Banana and figs helps to stimulate production of RBC
• Enriched cereals or pastas helps to treat anemia
• Spices- including mustard seeds and ginger](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pt-3-200708094338/75/autoimmune-hemolytic-anemia-42-2048.jpg)




