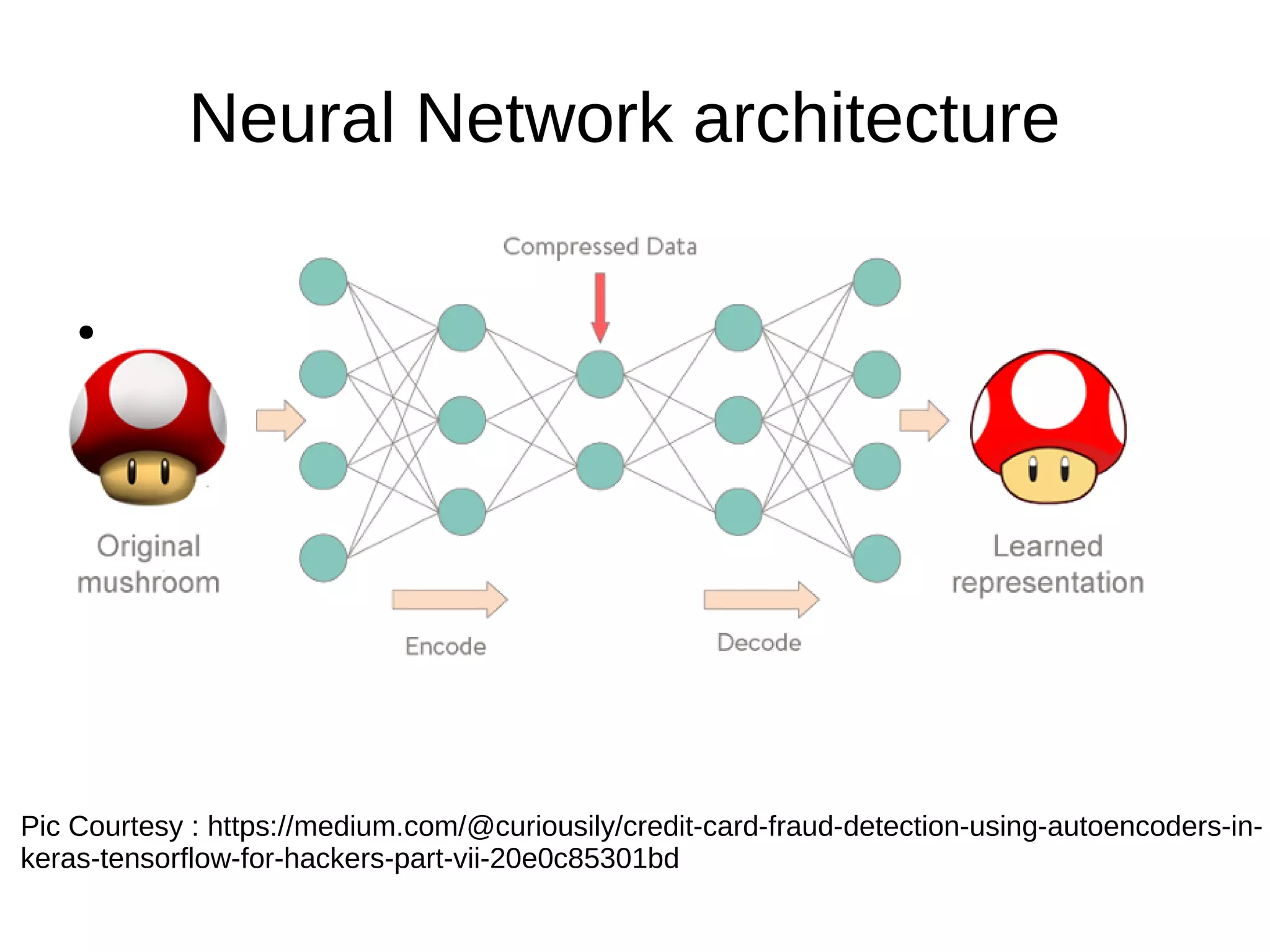
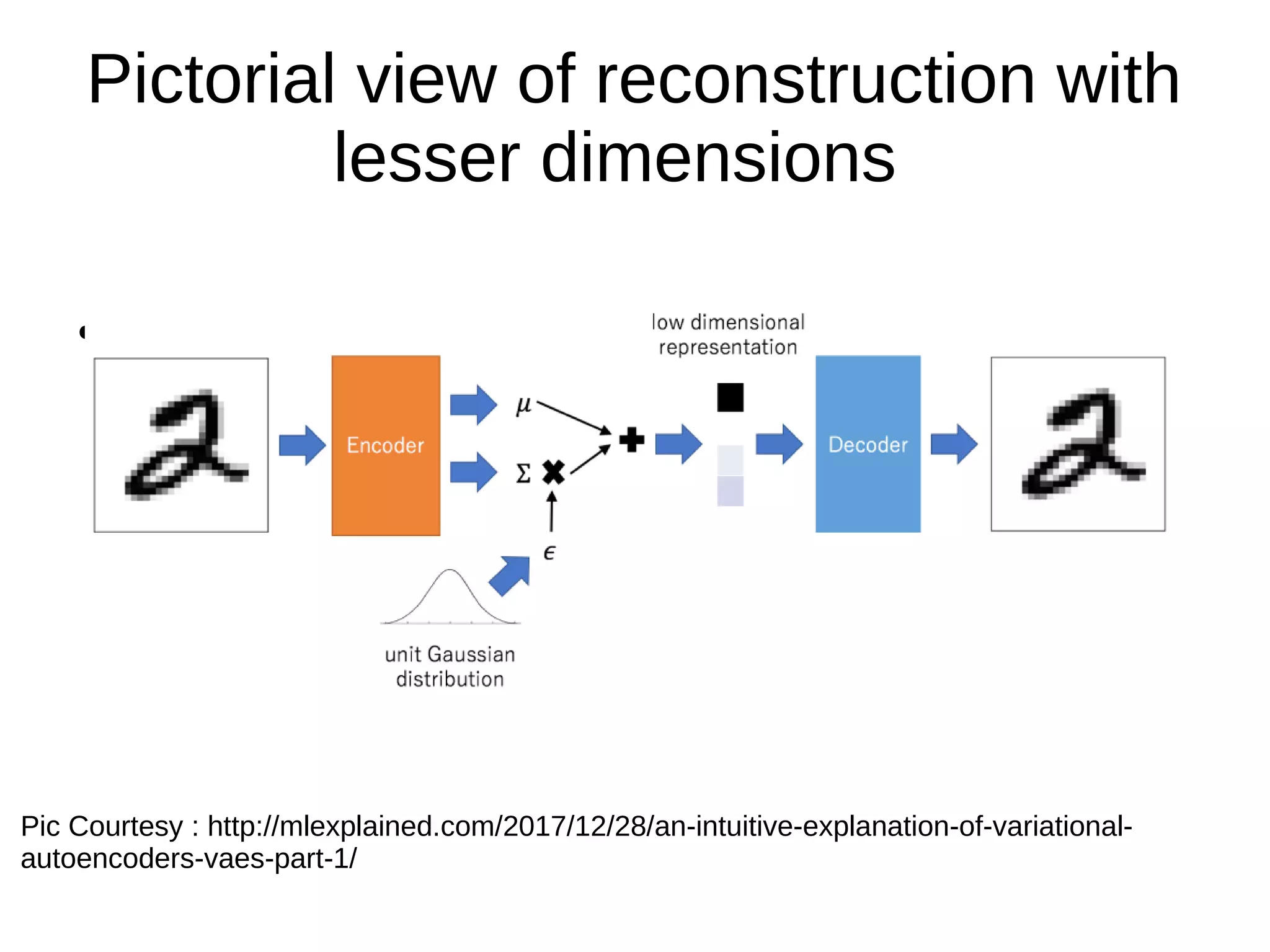
- Autoencoders are a type of neural network used for unsupervised learning tasks like dimensionality reduction and denoising. They work by encoding the input into a lower-dimensional representation and then decoding to reconstruct the original input.
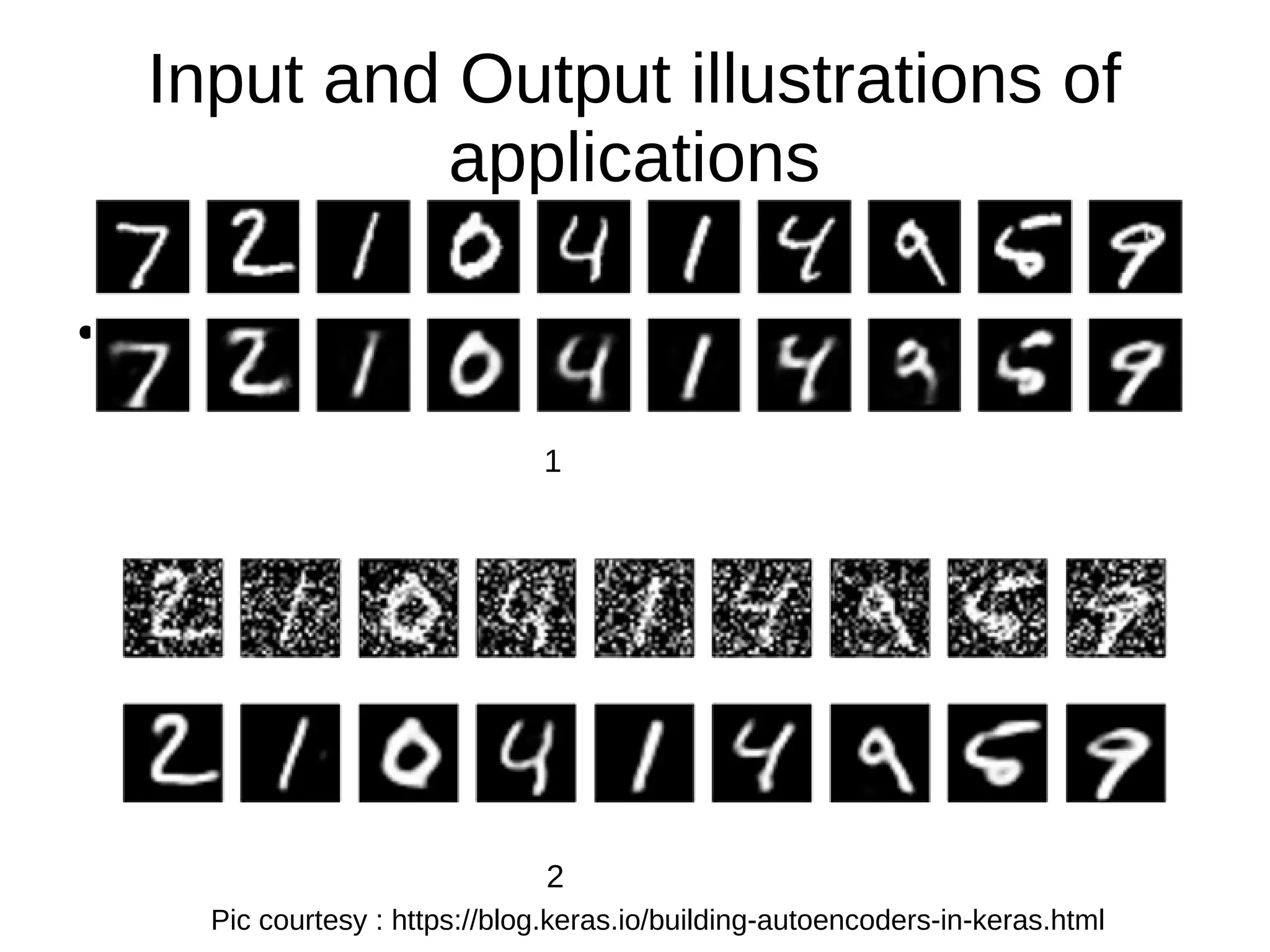
- The document discusses applications of autoencoders like reconstruction with reduced dimensions and image denoising. It provides illustrations of these applications and sample Python code for implementing autoencoder reconstruction.
- In conclusion, the document provides an overview of autoencoders and their framework for moving from hand-engineered algorithms to inference-based learning, with references provided for further reading.