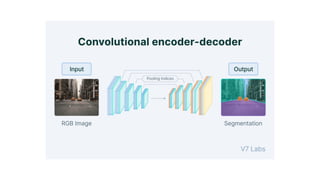
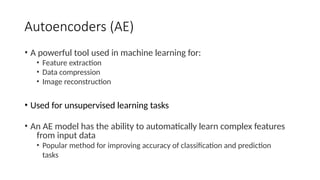
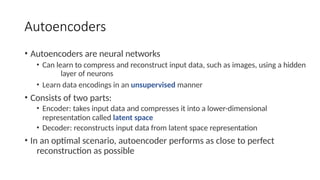
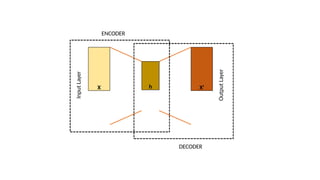
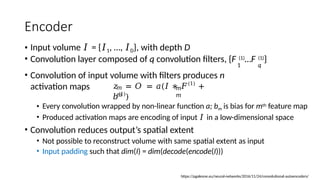
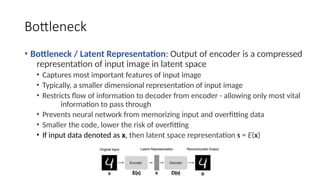
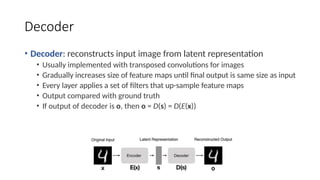
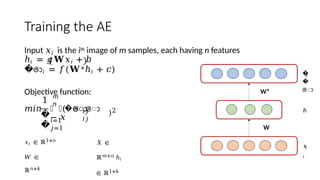
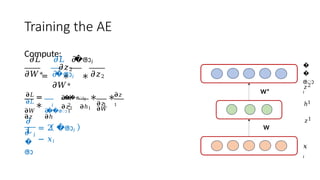
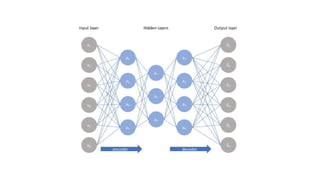
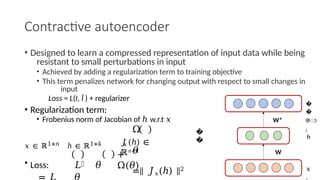
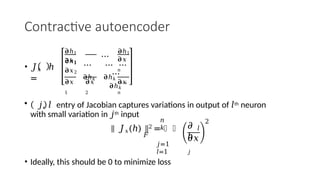
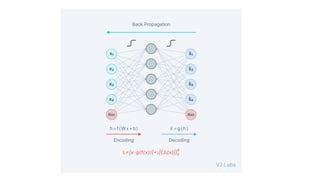
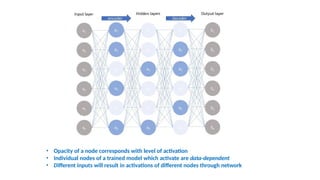
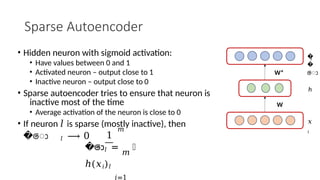
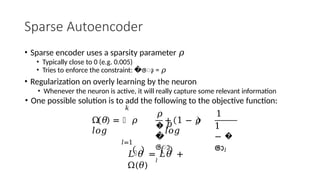
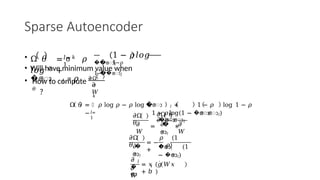
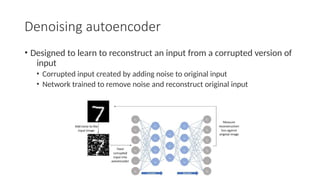
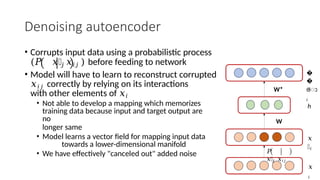
Autoencoders are neural networks used for unsupervised learning, designed to encode input data into a lower-dimensional latent representation and then reconstruct it back with minimal loss. They consist of an encoder that compresses the input and a decoder that reconstructs it. In computer vision, autoencoders are widely used for image denoising, anomaly detection, dimensionality reduction, and feature extraction. Variants like denoising autoencoders (DAEs), variational autoencoders (VAEs), and convolutional autoencoders (CAEs) enhance their capabilities for different tasks.