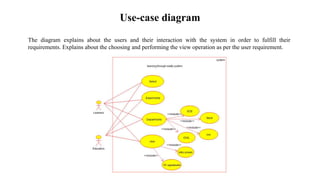
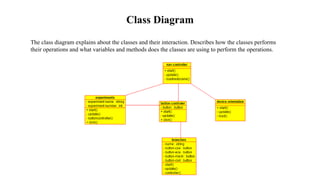
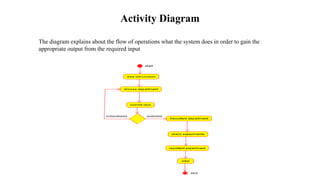
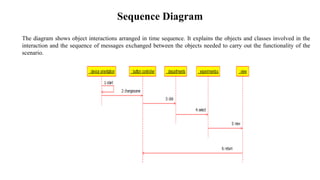
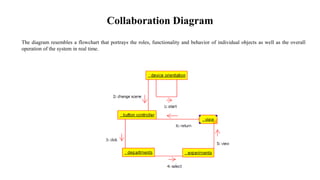
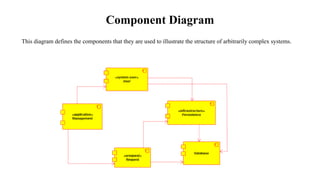
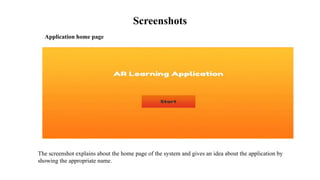
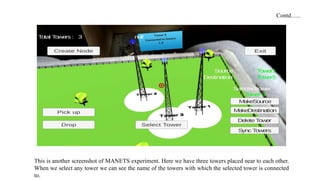
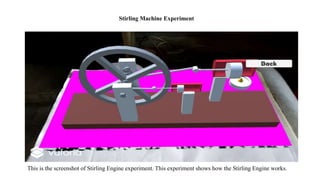
The document presents the development of an educational technology tool based on animation concepts, aiming to enhance learning through augmented reality by providing interactive, multi-dimensional access to educational materials. It identifies the limitations of existing educational systems, proposes a new system that incorporates augmented reality for improved visualization and interaction with educational content, and outlines requirements, design diagrams, and future enhancements. Ultimately, the project meets organizational needs by ensuring efficient resource utilization and user-friendly operations.