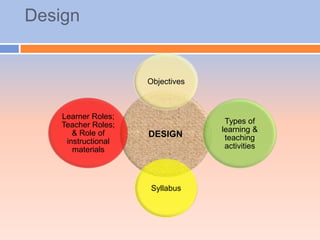
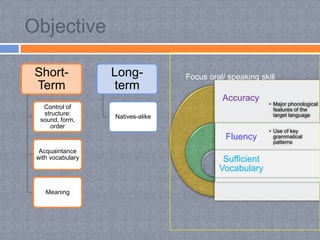
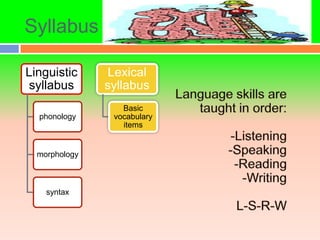
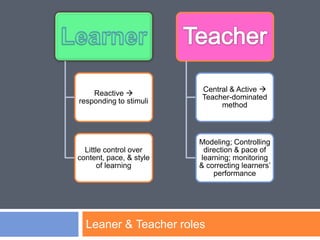
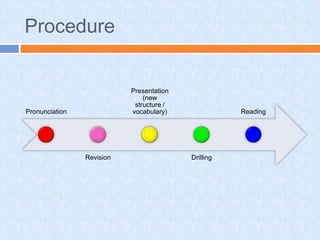
The audiolingual method was developed in the 1940s in response to the need for foreign language education during World War II. It was based on behaviorist theories of language learning that emphasized oral skills through repetition and mimicry. Under this method, learners played a passive role while teachers tightly controlled lessons focusing on drilling pronunciation, grammar patterns, and vocabulary through repetitive question-and-answer exchanges. By the 1960s, the audiolingual method declined as its limitations became apparent, including its inability to develop learners' communicative competence and the lack of transfer of skills to real-world settings.