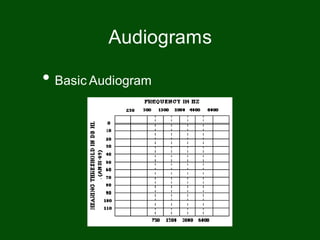
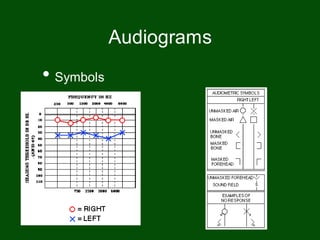
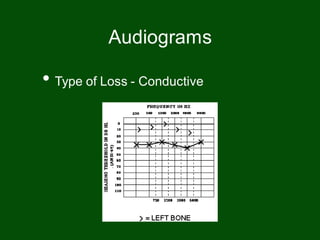
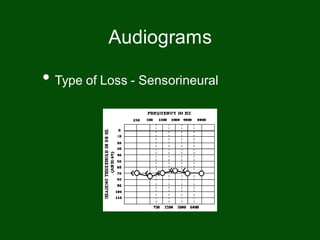
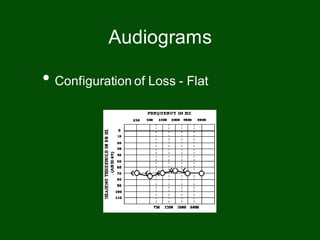
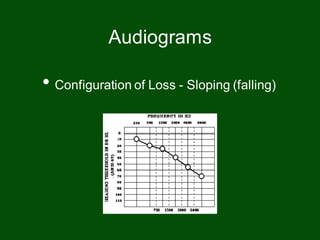
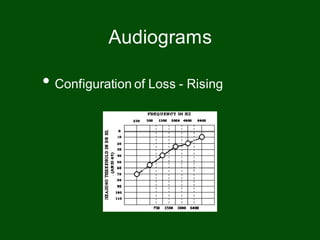
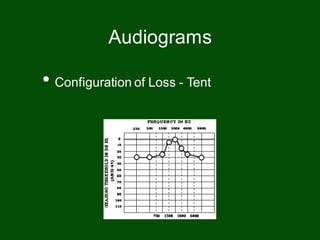
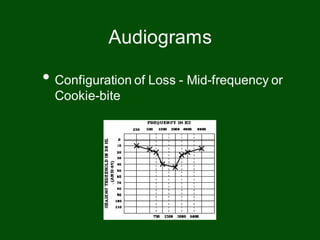
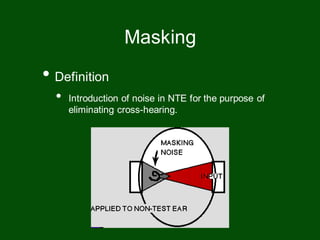
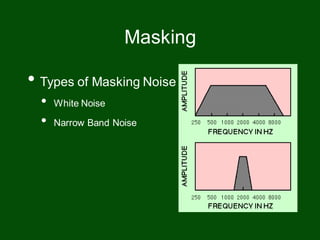
This document provides information on pure tone audiometry testing procedures including: the roles of both the patient and clinician in testing; how to conduct air and bone conduction tests; how to interpret audiograms including different types and configurations of hearing loss; definitions of terms like frequency, intensity, and masking; and descriptions of common equipment used like audiometers and inserts.