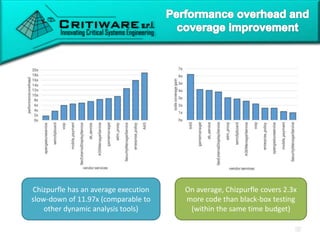
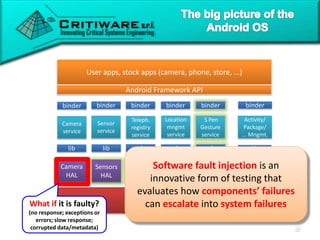
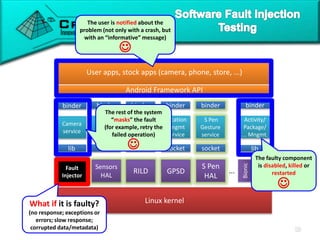
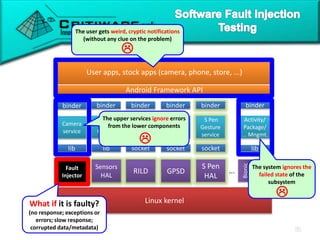
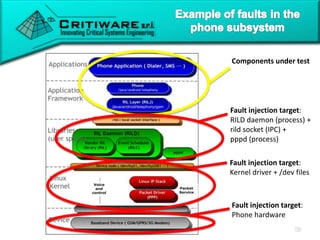
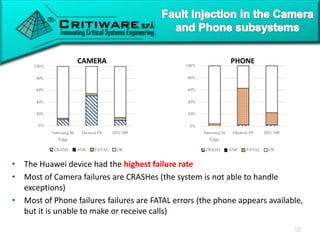
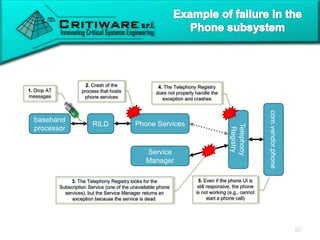
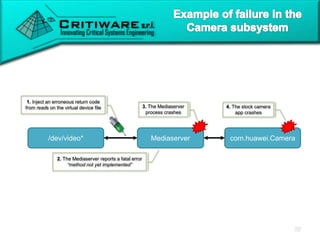
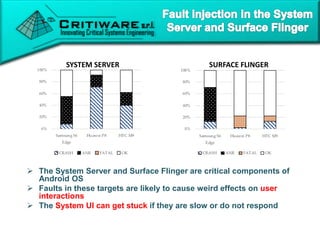
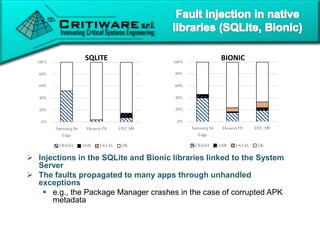
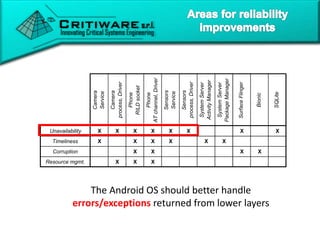
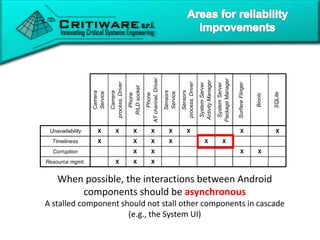
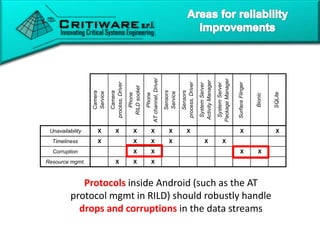
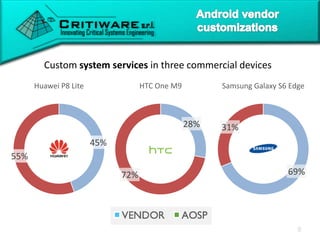
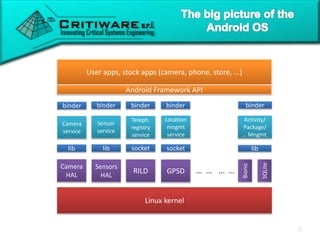
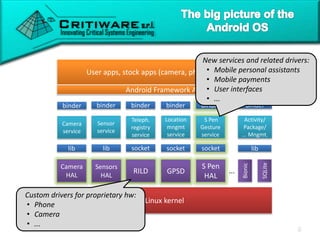
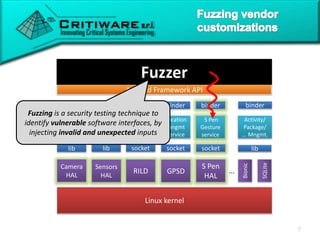
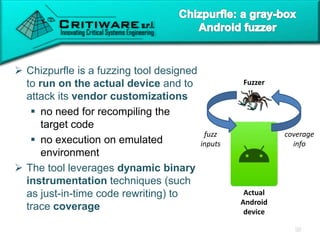
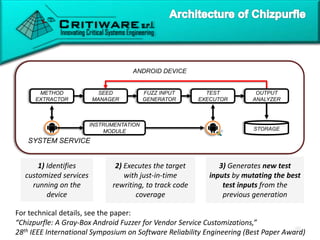
The document discusses attacking proprietary Android vendor customizations through fuzz testing and fault injection testing. It presents Chizpurfle, a gray-box Android fuzzer designed to generate invalid inputs to identify vulnerabilities in vendor customization code without access to source code. Chizpurfle leverages dynamic instrumentation to trace code coverage on actual devices during fuzzing. It detected two bugs from fuzzing Samsung services. The document also discusses a fault injection testing tool that injects faults into Android components to evaluate failure propagation and mitigation. The tool found vendors have varying success in handling faults across components.



![com.samsung.android.cocktailbar.ICocktailBarService
{
"name":"updateCocktail",
"parameters": [
"java.lang.String",
"com.samsung.android.cocktailbar.CocktailInfo",
"int”
]
}
“string” a CocktailInfo object 2
• Random
• Zero
• One
• Add/sub
random eps.
• Max/min value
• ...
• Null
• New obj with
random values
• Fuzz obj fields
• ...
• Random
• Substring
• Truncate
• Replace char
• Very long string
• ...](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/itasec2018-critiware-linkedin-200108120009/85/Attacking-Proprietary-Android-Vendor-Customizations-8-320.jpg)
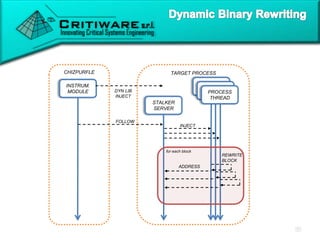
![CHIZPURFLE TARGET PROCESS
INSTRUM.
MODULE
STALKER
SERVER
PROCESS
THREAD
for each block
DYN LIB
NJECT
FOLLOW
INJECT
REWRITE
BLOCK
ADDRESS
mov x29, sp
mov x3, x30
ldp x29,x30,[sp],16
stp x29,x30,[sp-16]!
add x30,x0,#4
save address
stalk (bl f_label)
save address
stalk(ret)
mov x29, sp
mov x3, x30
ldp x29,x30,[sp],16
stp x29,x30,[sp-16]!
add x30,x0,#4
ret
bl f_label
Block
(before rewriting)
Block
(after rewriting)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/itasec2018-critiware-linkedin-200108120009/85/Attacking-Proprietary-Android-Vendor-Customizations-13-320.jpg)

![ Input strings that include
SQL control expressions
(such as single quotes)
trigger an SQL exception
The input crashes the
phone process, and
interrupts any ongoing call
VOIP SERVICE
callInVoIP(String SIPAddress)
SELECT reject_number FROM
reject_num WHERE reject
number=‘[...a random string with
a single quote...]’
CRASH](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/itasec2018-critiware-linkedin-200108120009/85/Attacking-Proprietary-Android-Vendor-Customizations-15-320.jpg)
![ A tricky input to
the S Pen Gesture
service triggers a
fatal error
(NullPointerExc.)
The System Server
process fails,
causing a reboot of
the smartphone
SPENGESTURE SERVICE
injectInput(…, android.view.InputEvent [ ], ...)
android.view.InputEvent array is
non-null and non-empty, and at
least one of its elements is null
REBOOT](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/itasec2018-critiware-linkedin-200108120009/85/Attacking-Proprietary-Android-Vendor-Customizations-16-320.jpg)