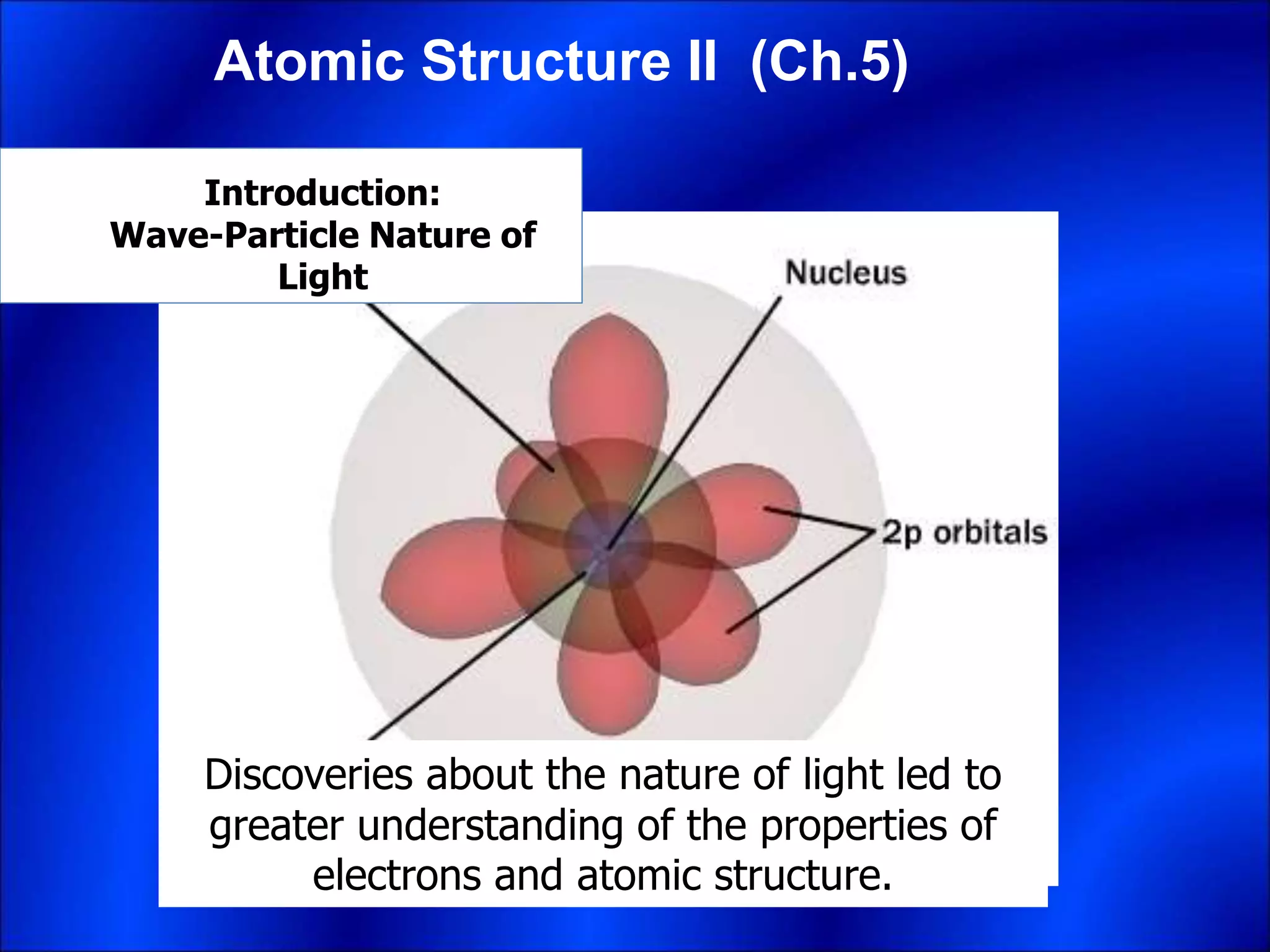
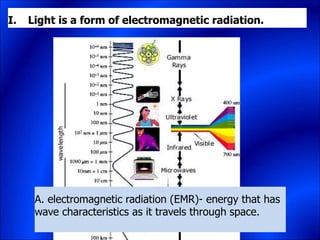
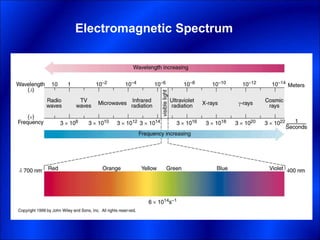
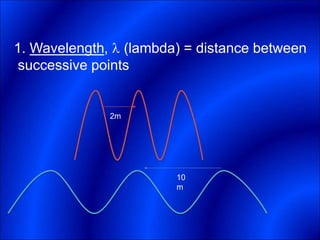
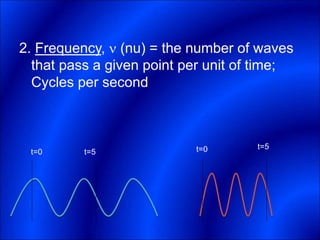
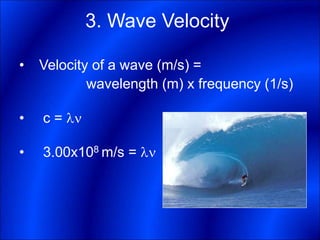
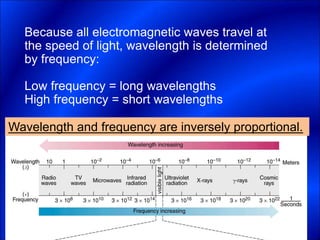
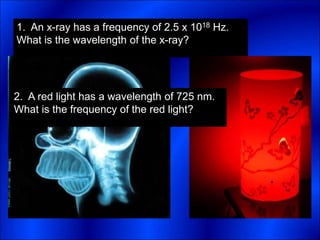
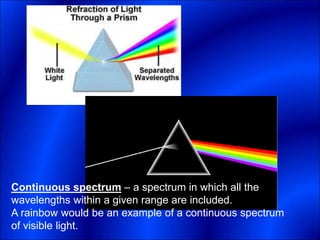
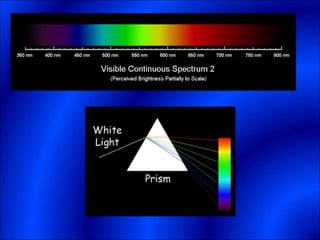
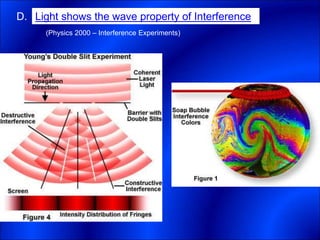
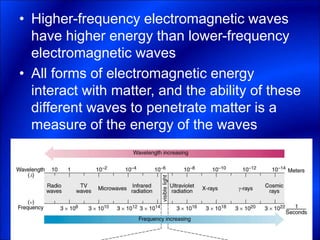
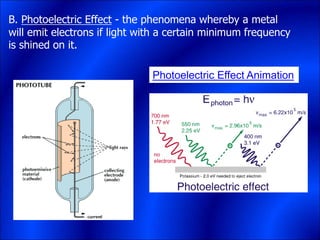
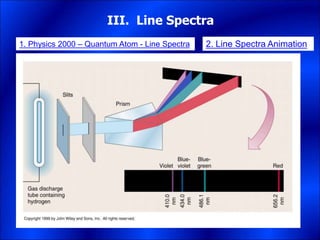
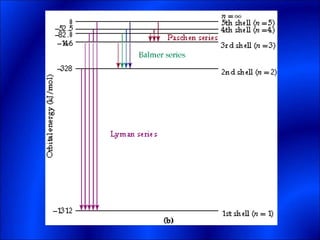
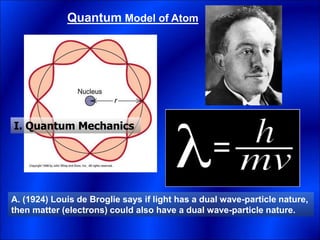
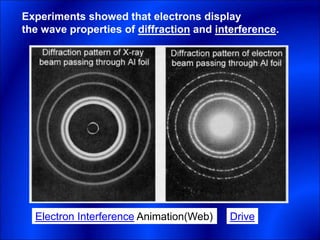
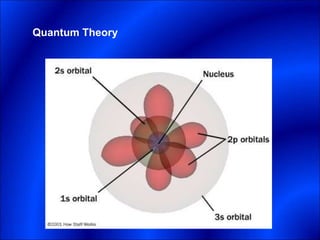
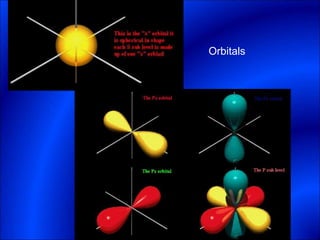
Electrons and light have both wave-like and particle-like properties. Experiments in the early 1900s showed that electrons can behave like waves and light can behave like particles. This led to the development of quantum physics and models of atomic structure. The quantum model of the atom describes electrons as existing in orbitals or probability clouds around the nucleus rather than defined orbits. Electrons can only occupy certain allowed orbitals and jump between these orbitals, emitting or absorbing photons of light. The energy and wavelength of these photons correspond to the spacing between orbitals and make up the characteristic line spectra of elements.