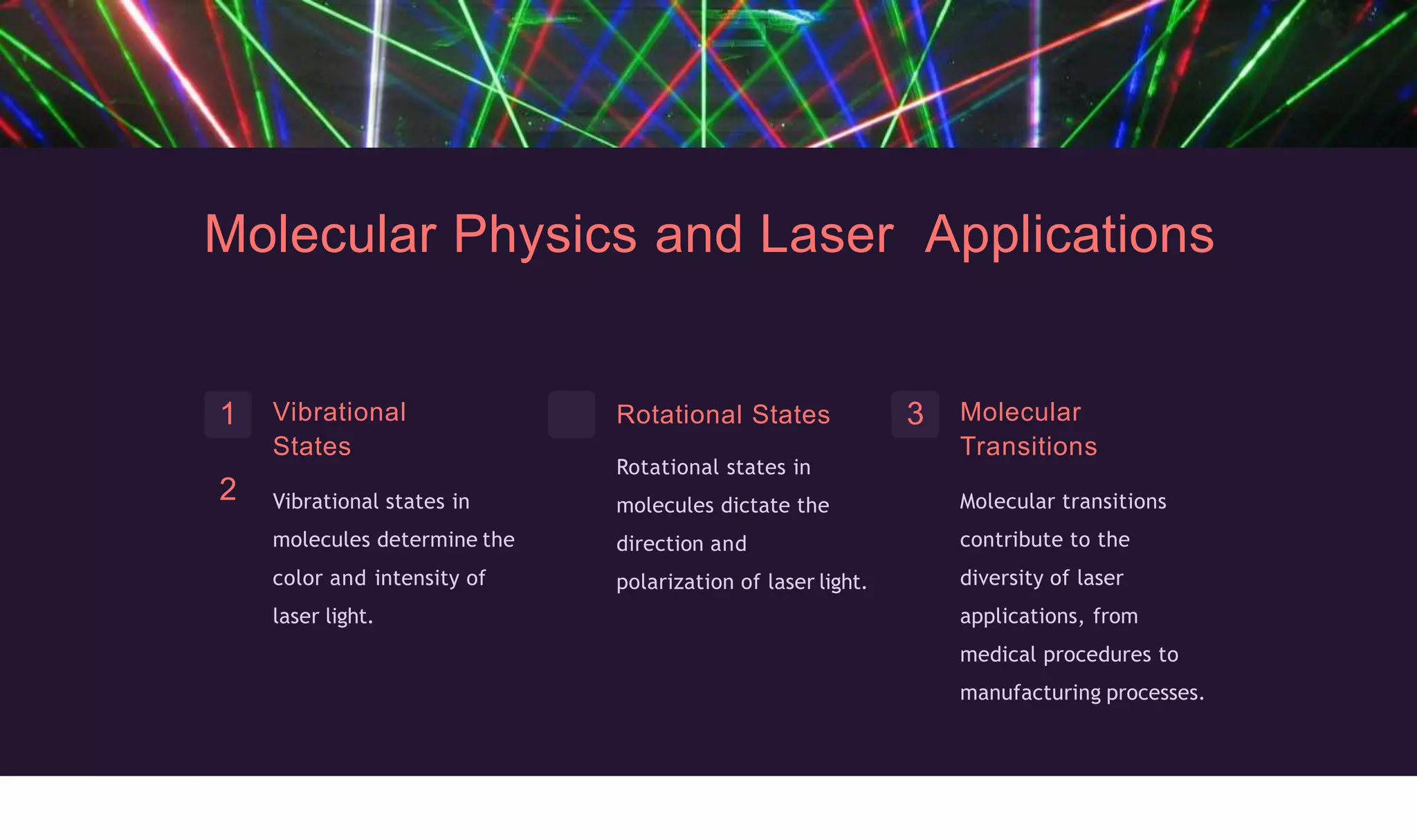
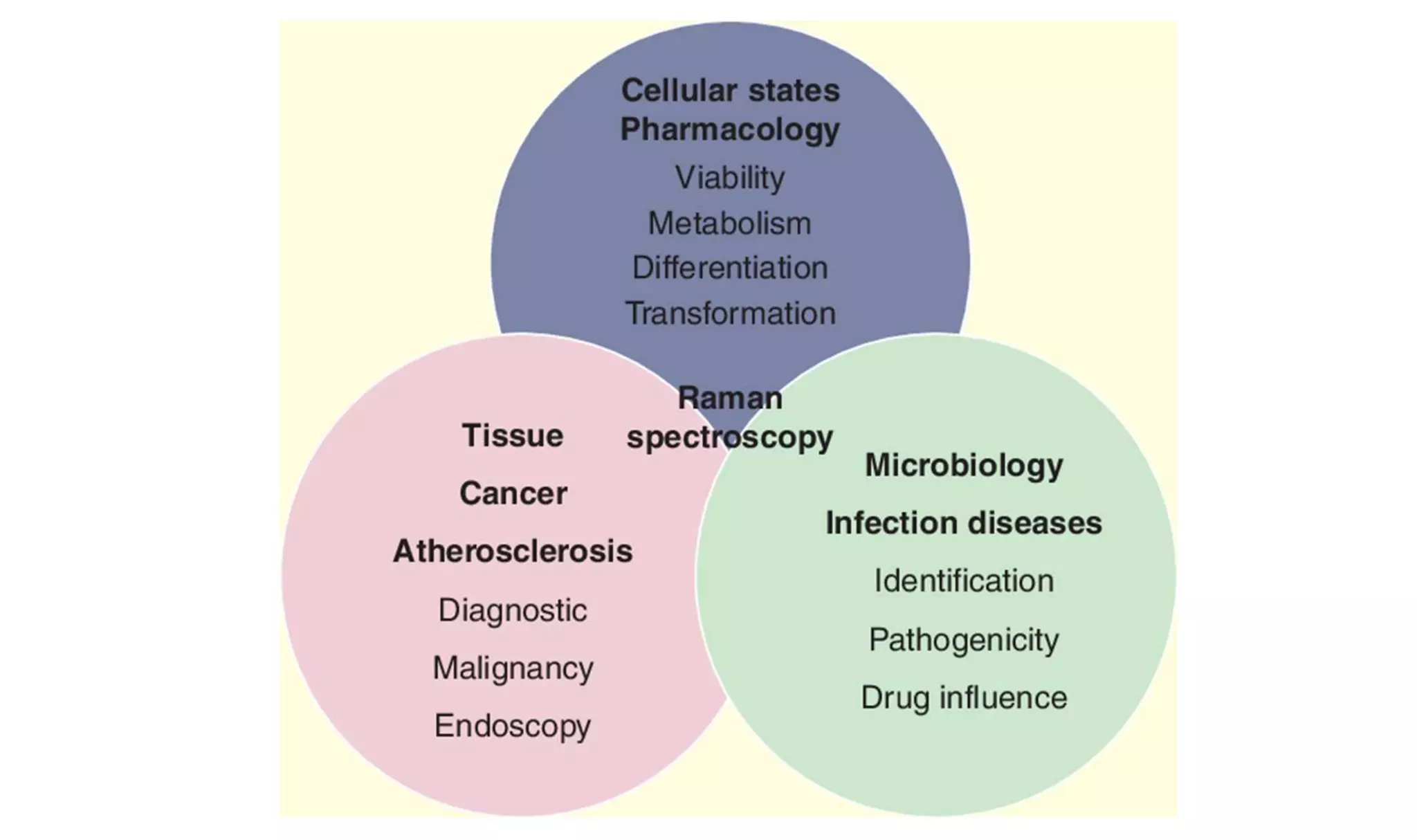
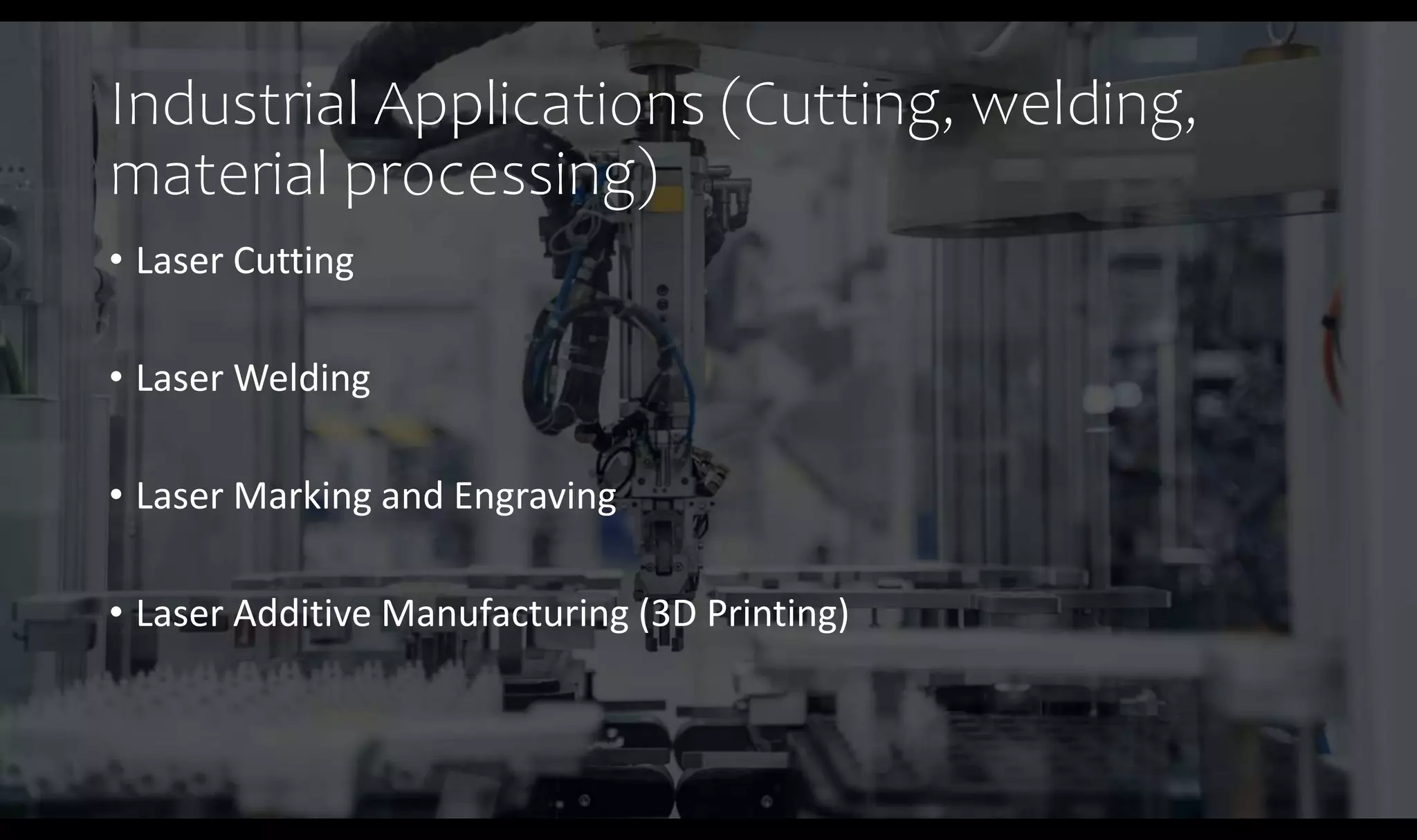
The document discusses the foundational role of atomic and molecular physics in the development of laser technology, highlighting key concepts such as energy levels, transitions, and stimulated emission. It outlines various applications of laser technology across medical, industrial, and scientific fields, emphasizing precision, efficiency, and diversity. Additionally, it explores future innovations in atomic and molecular physics, including advancements in quantum computing and high-power lasers.