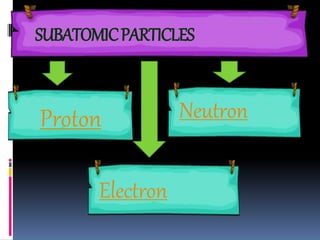
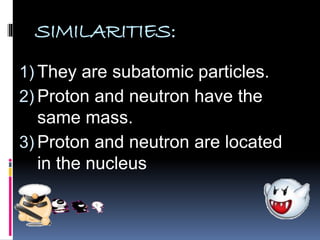
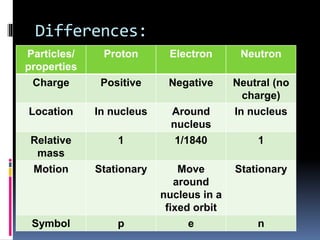
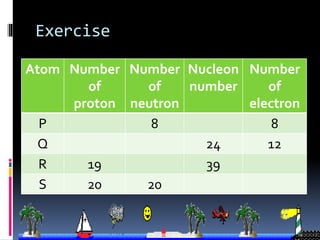
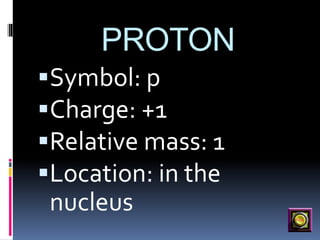
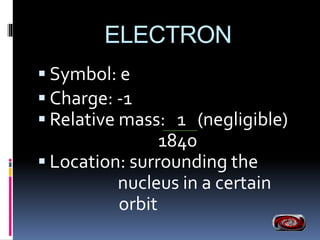
The document discusses the structure of atoms. It describes the historical understanding of atoms from Dalton's theory that atoms cannot be created or destroyed to Rutherford's discovery of the nucleus and Bohr's model of the atom. The structure of the atom is explained including subatomic particles like protons, neutrons, and electrons. Protons are located in the nucleus and have a positive charge while neutrons are in the nucleus and have no charge. Electrons surround the nucleus and have a negative charge. The proton number and nucleon number are defined and examples of calculating these numbers are provided.