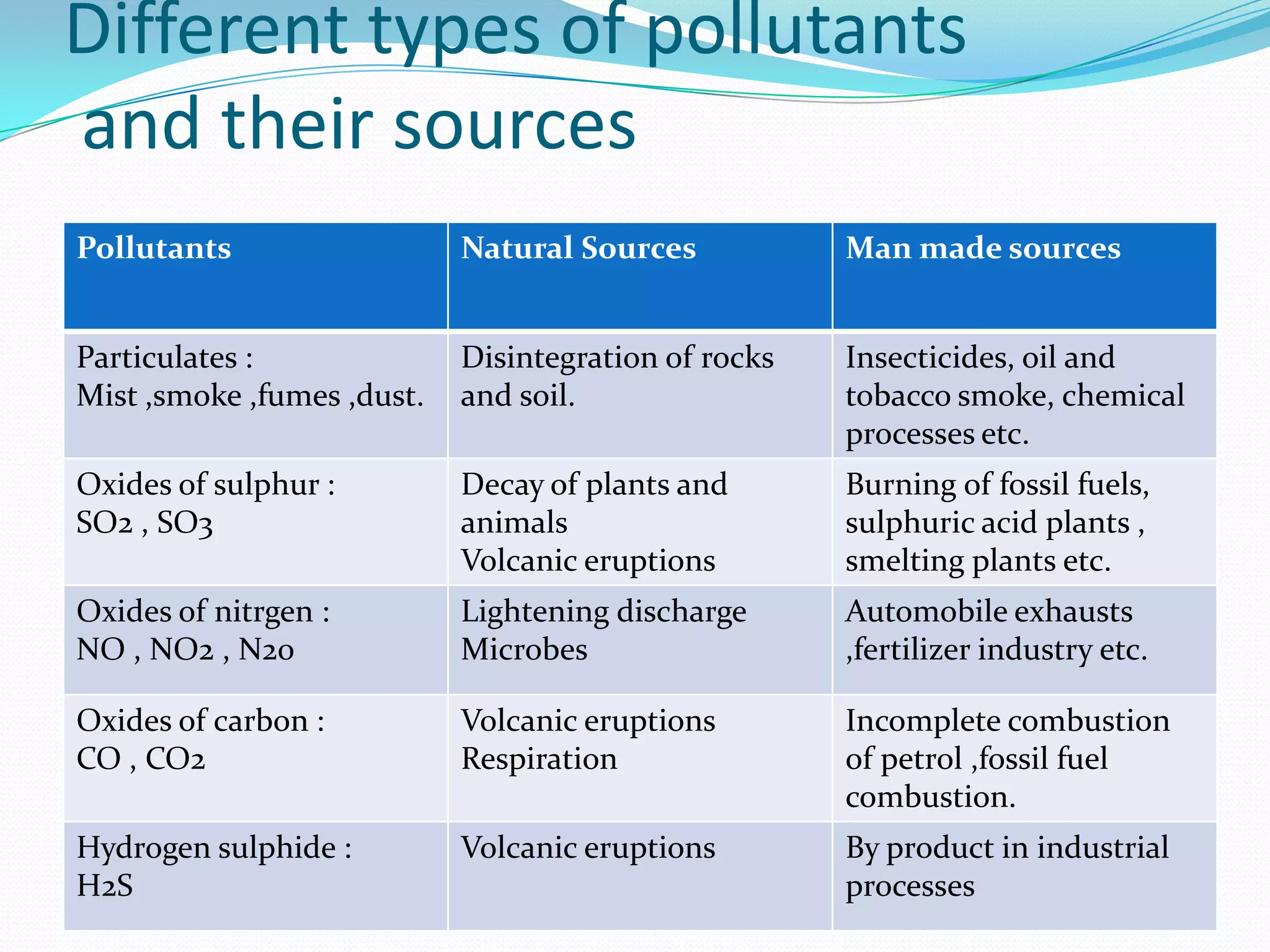
Pollution is the introduction of contaminants into the natural environment that cause adverse changes. Air pollution occurs when harmful substances affect the atmosphere, potentially causing health issues and environmental damage. Air pollutants come from natural sources like wildfires and volcanoes, or human sources such as vehicle emissions, industrial operations, and waste disposal. Air pollution has wide-ranging negative health effects and contributes to issues like acid rain, global warming, and ozone depletion. Efforts to reduce air pollution include emissions controls, land use planning, and environmental impact assessments.

![Pollution
The word pollution was derived from the latin word
‘pollutus’ meaning ‘to make unclean ‘.
Pollution is the introduction of contaminants into
the natural environment that cause adverse
change.[1] Pollution can take the form of chemical
substances or energy, such as noise, heat or
light. Pollutants, the components of pollution, can be
either foreign substances/energies or naturally
occurring contaminants. Pollution is often classed
as point source or nonpoint source pollution.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/atmosphericpollution-140209093409-phpapp01/75/Atmospheric-pollution-2-2048.jpg)







![How do we Prevent it ?
There are various air pollution control technologies
and land use planning strategies available to reduce air
pollution.[53][54] At its most basic level land use planning is
likely to involve zoning and transport infrastructure
planning. In most developed countries, land use planning
is an important part of social policy, ensuring that land is
used efficiently for the benefit of the wider economy and
population as well as to protect the environment.
Like :Control devices
Reduction of emissions and the environmental impact
assessment.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/atmosphericpollution-140209093409-phpapp01/75/Atmospheric-pollution-11-2048.jpg)
