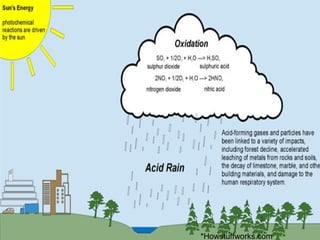
Pollution is the introduction of substances or energy into the environment that cause harm. More sophisticated lifestyles, growing population needs, and increased economic activity have led to greater pollution over time. Air pollution occurs when noxious gases and small particles contaminate the air. Major causes of air pollution include emissions from vehicles, industry, power plants, and other sources which can harm human health and the environment through respiratory diseases, acid rain, ozone depletion, and global warming. Laws and initiatives aim to control air pollution through emissions standards, cleaner fuels, and new technologies.