The document discusses streamlining and automating virtual network control. It presents several options for deploying and managing VXLAN including:
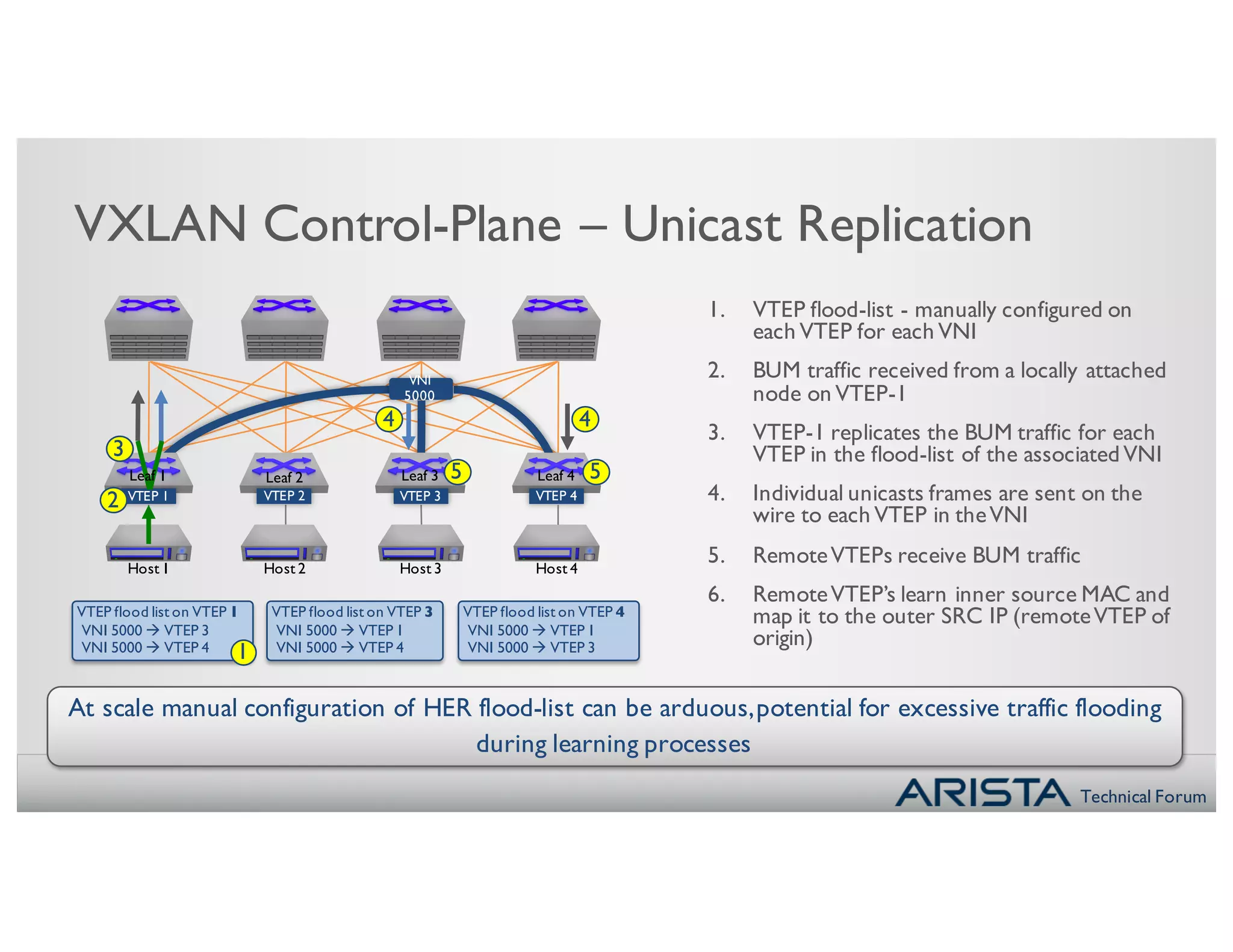
- Manually configuring VTEP flood lists, which is suitable for small scale solutions but difficult to manage at scale.
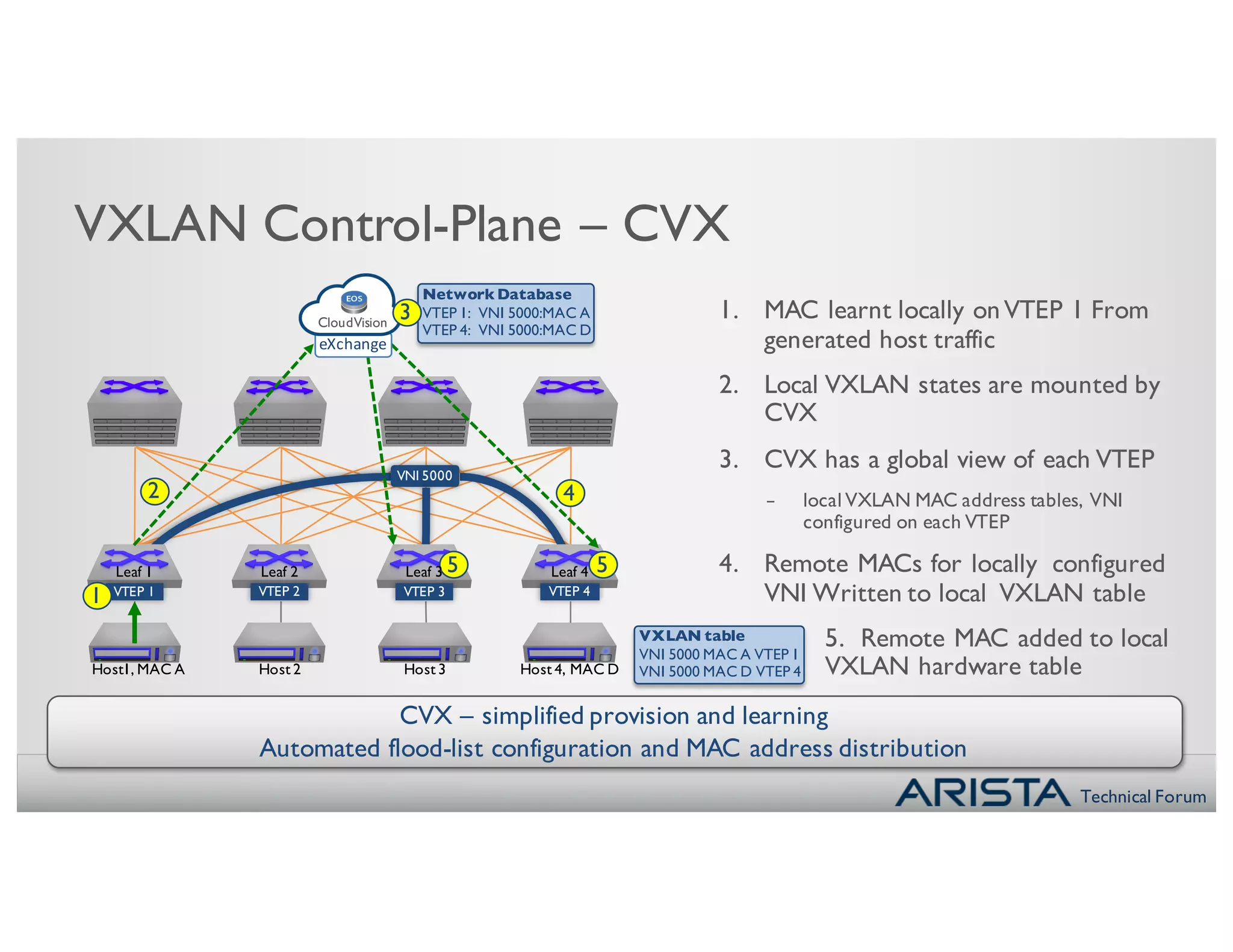
- Using CloudVision (CVX) alone to provide a centralized database and automate flood list population, allowing for more scalable intra-DC solutions.
- Integrating CVX with third-party controllers like NSX and OpenStack to distribute MAC learning between software and hardware VTEPs in large data centers.
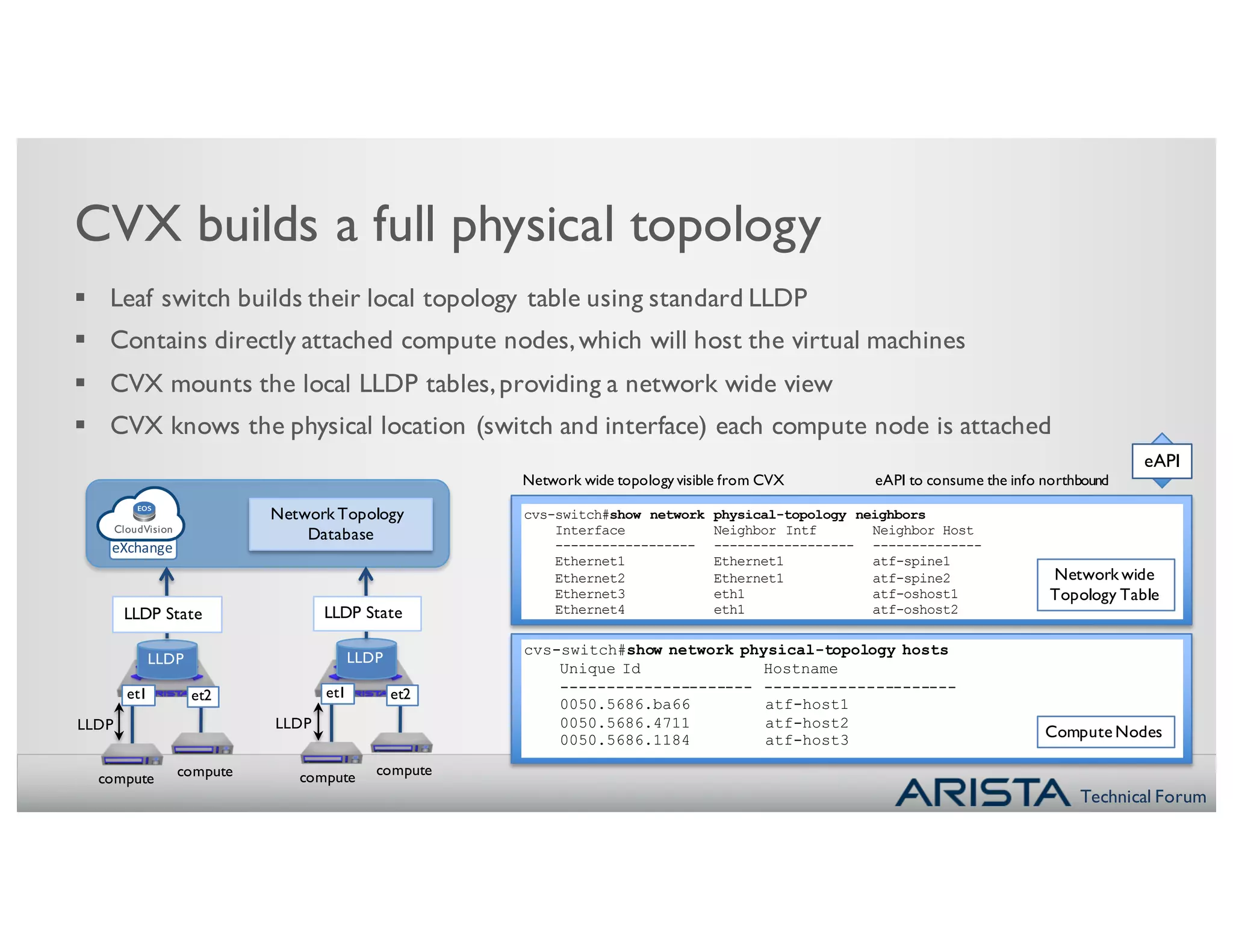
The document demonstrates how CVX builds a physical topology view from individual switch LLDP data and how it can automate the V

![Technical Forum
CloudVision, VXLAN
What’s Next ?
Next ?
Optimisation of
the
resource pool
40%
VM
Decrease &
automate
Deployment time
VM VM
Remove islands of
service connectivity
VM
Operational
Efficiency
P P P P
• Undefined SDN strategy ?
• Team interactions,Skills,Planning,
Strategy, Processes not ready ?
What Orchestration
platform choices ?
‘BYOC’
What corporate
Challenges ?
…But you are ready
C
6C
L
FG O ]
?
6](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/atf-3q15-5-streamliningandautomatingvirtualnetworkcontrol-160308055833/75/Atf-3-q15-5-streamlining-and-automating-virtual-network-control-2-2048.jpg)