This document discusses network virtualization and the Arista CloudVision eXchange (CVX) platform. It provides 3 key points:
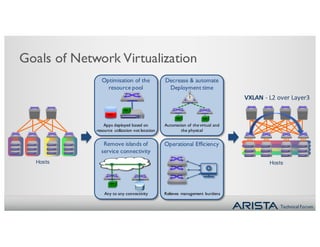
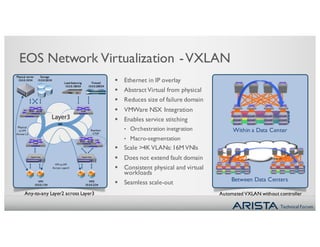
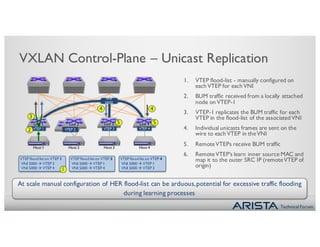
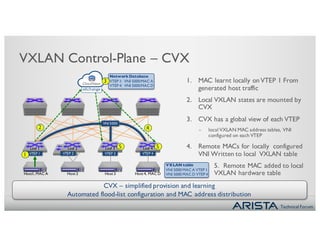
1. Network virtualization using VXLAN allows for any-to-any Layer 2 connectivity across Layer 3 subnets, enabling VM mobility. The CVX platform provides automation of VXLAN deployment without a controller.
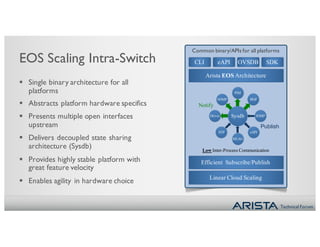
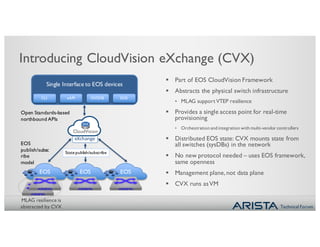
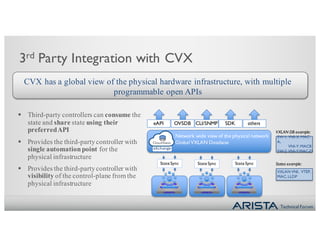
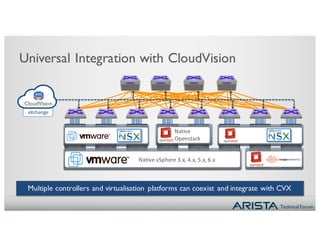
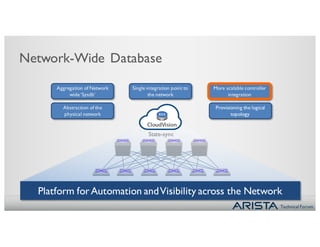
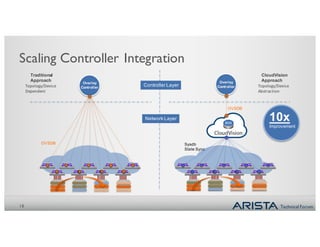
2. CVX acts as a single point of integration and provisioning for the physical network. It aggregates network state from EOS switches and presents it to controllers through open APIs. This provides visibility, simplifies provisioning, and improves scalability of controller integration.
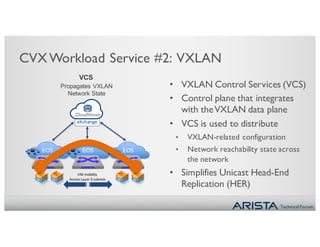
3. CVX services include providing the physical topology database, distributing VXLAN configuration