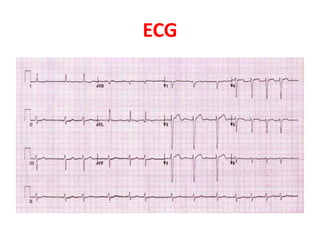
Atrial fibrillation is an irregular heart rhythm caused by multiple electrical impulses bombarding the atrioventricular node too quickly to process. It is often associated with underlying heart diseases and can cause symptoms like fatigue, dizziness, and an irregular pulse. On ECG, there are no discernible P waves due to the chaotic electrical activity in the atria, and the ventricular rate is usually between 160-180 beats per minute. While often well-tolerated, atrial fibrillation reduces cardiac output and can further compromise the heart if the ventricular rate is not controlled. Treatment depends on stability, with immediate cardioversion for unstable patients and medications or procedures to restore normal rhythm for stable patients.