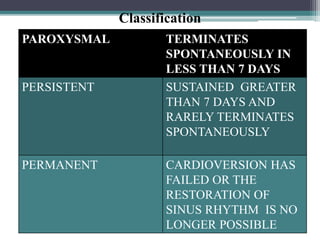
This document discusses atrial fibrillation (AF), a common heart condition where the upper chambers of the heart beat irregularly and too fast. AF can be caused by conditions like heart disease, hypertension, or hyperthyroidism. It occurs when chaotic electrical signals in the atria beat irregularly instead of in a coordinated pattern. Left untreated, AF can lead to heart failure or stroke by reducing cardiac output and allowing blood clots to form. The document classifies AF by duration and discusses its characteristic ECG findings and potential clinical symptoms like fatigue, dizziness, and palpitations.