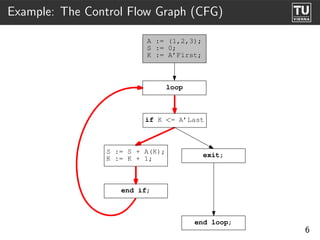
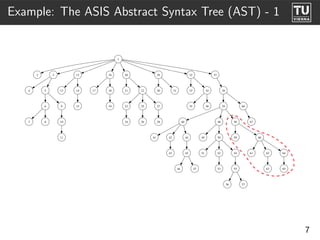
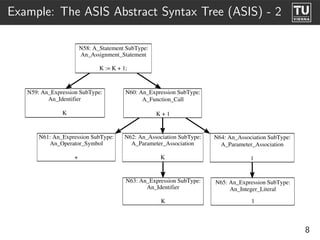
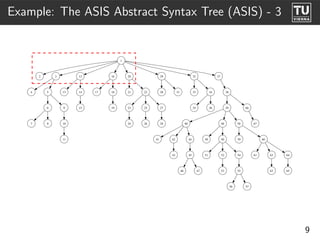
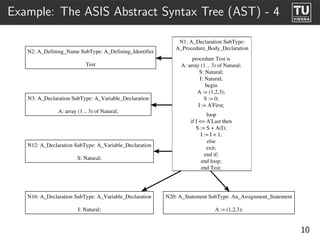
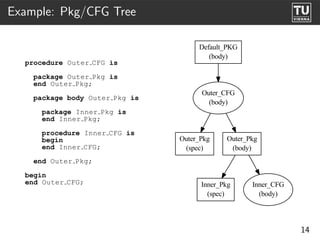
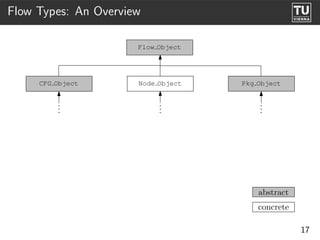
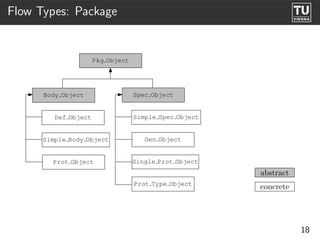
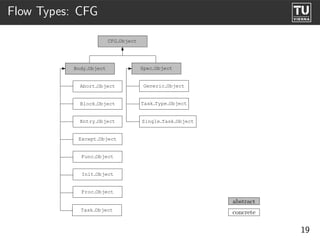
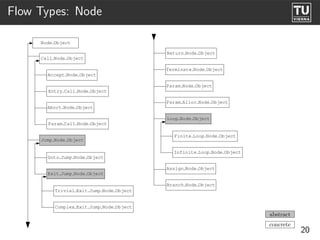
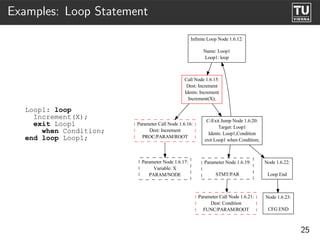
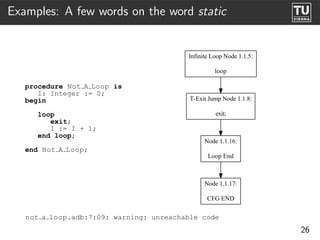
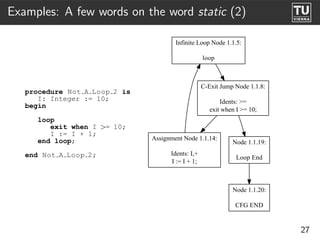
The document presents 'ast2cfg', a framework for control flow graph (CFG) analysis and visualization of Ada programs. It details how CFGs are constructed from Ada's abstract syntax tree (AST) and discusses software components like ast2cfg and cfg2dot, which facilitate this process. The framework aims to enhance Ada program analysis and optimization, supported by examples and a live demonstration.








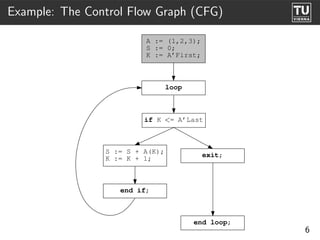






![Examples: Tasks
Node 1.3.1:
select/acc
Node 1.4.4:
−− Caller Object Node 1.3.4:
Task Object.Entry1; Idents: Condition
select
Entry Call Node1.6.7: or
−− Called Object Dest: Task_Object.Entry1
select Idents: Task_Object.Entry1
accept Entry1 do Task_Object.Entry1;
null; Accept Node1.3.8: Accept Node1.4.8:
end Entry1; Dest: CFG[1.4.0] Dest: CFG[1.5.0]
or accept Entry1 do accept Entry2 do
when Condition => Node 1.6.9:
accept Entry2 do
null; CFG END
end Entry2; Node 1.3.3:
end select;
end select
Node 1.5.4:
CFG END
28](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/08-adacfg-090707170557-phpapp01/85/Ast2Cfg-A-Framework-for-CFG-Based-Analysis-and-Visualisation-of-Ada-Programs-36-320.jpg)
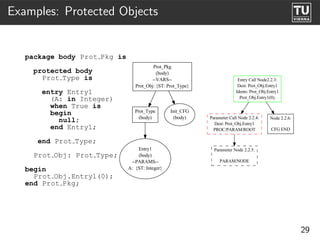
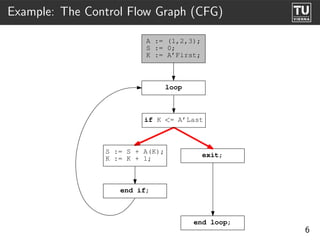
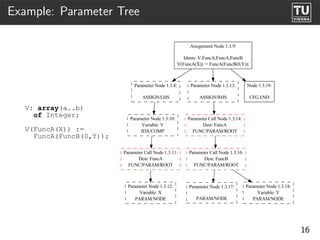
![Examples: Types
Types
(spec)
--TYPES--
Rec_Type_0
[COMPONENTS]
F: {CT: Float}
B: {CT: Boolean}
package Types is Rec_Type_1 {ST: Rec_Type_0}
type Rec Type 0 is
tagged F
record INIT
F: Float := abs(3.14);
B: Boolean;
end record;
Parameter Node 1.0.2:
type Rec Type 1 is INIT/NODE
new Rec Type 0
with null record;
Parameter Call Node 1.0.4:
end Types; Dest: abs
FUNC/PARAM/ROOT
Parameter Node 1.0.5:
PARAM/NODE
30](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/08-adacfg-090707170557-phpapp01/85/Ast2Cfg-A-Framework-for-CFG-Based-Analysis-and-Visualisation-of-Ada-Programs-38-320.jpg)