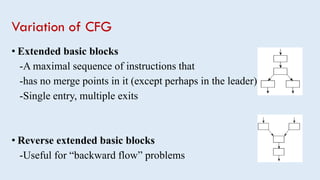
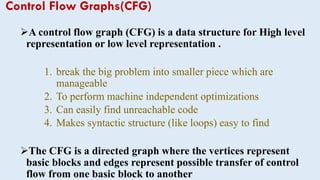
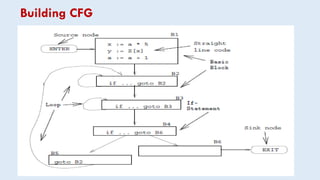
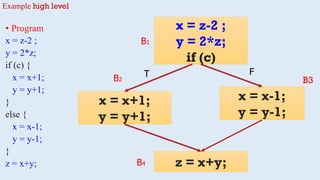
Intermediate representations are used in compilers to represent programs between the source and target languages. Control flow graphs (CFG) are a common intermediate representation that represent a program as a directed graph with basic blocks as nodes and edges showing possible control transfers. CFGs help optimize programs by breaking them into manageable blocks and making structures like loops and branches explicit. Building a CFG involves identifying basic blocks, which are straight line code sequences without internal jumps, and representing the control flow between them.




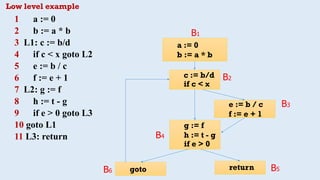
![---------Source Code-----------------------
X := 20; WHILE X < 10 DO
X := X-1; A[X] := 10;
IF X = 4 THEN X := X - 2; ENDIF;
ENDDO; Y := X + 5;
---------Intermediate Code---------------
(1) X := 20
(2) if X>=10 goto (8)
(3) X := X-1
(4) A[X] := 10
(5) if X<>4 goto (7)
(6) X := X-2
(7) goto (2)
(8) Y := X+5
X := 20
Y := X+5
goto B2
X := X-2
X := X-1
(4) A[X] := 10
(5) if X<>4 goto B6
if X>=10 goto B4
B1
B2
B4B3
B5
B6](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cfg-160511191710/85/Control-Flow-Graphs-10-320.jpg)

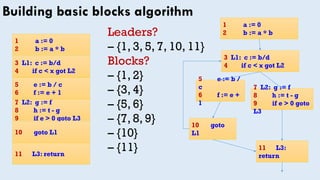
![Building basic blocks algorithm
• Input: List of n instructions (instr[i] =𝑖 𝑡ℎ instruction),
A sequence of intermediate code statements
Output: Set of leaders & list of basic blocks
(block[x] is block with leader x)
leaders = {1} // First instruction is a leader
for i = 1 to n // Find all leaders
if instr[i] is a branch
leaders = leaders ∪ set of potential targets of instr[i]
foreach x ∈ leaders //each leader is leader of it self
block[x] = { x }
i = x+1 // Fill out x’s basic block
while i ≤ n and i ∉ leaders
block[x] = block[x] ∪ { i }
i = i + 1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cfg-160511191710/85/Control-Flow-Graphs-12-320.jpg)


![Building CFG
• Input: A list of m basic blocks (block)
Output: A CFG where each node is a basic block
for i = 1 to m
x = last instruction of block[i]
if instr x is a branch
for each target (to block j) of instr x
create an edge from block i to block j
if instr x is not an unconditional branch
create an edge from block i to block i+1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cfg-160511191710/85/Control-Flow-Graphs-15-320.jpg)