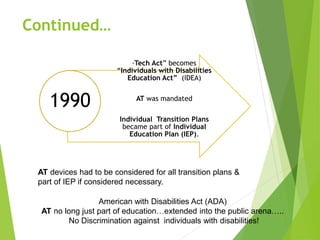
This document discusses assistive technology (AT), including its definition, history, funding sources, and appropriate uses. It defines AT as any item or equipment that helps individuals with disabilities increase their functional abilities. The document outlines how AT has evolved since the 1970s to become formally defined and mandated within education and disability laws. It also describes the AT continuum of low-tech, light-tech, and high-tech devices and provides examples of each. Funding sources for AT include school districts, Medicaid/Medicare, private insurers, and various organizations. Ethics and incorporating AT appropriately within IEPs are also addressed.