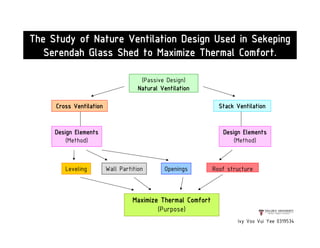
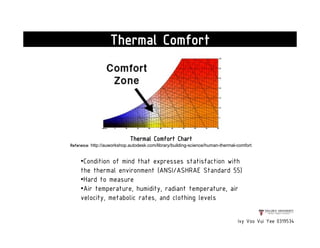
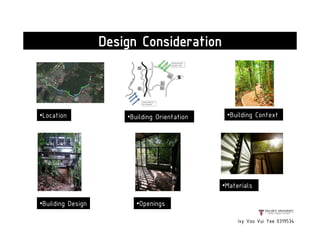
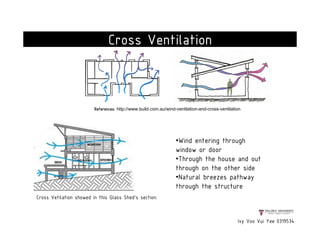
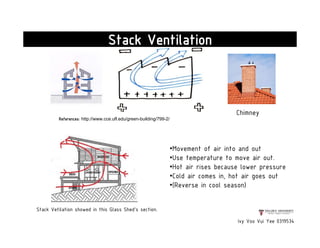
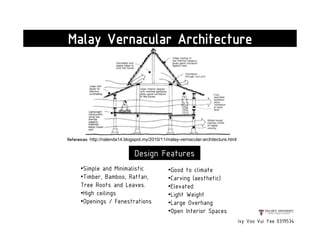
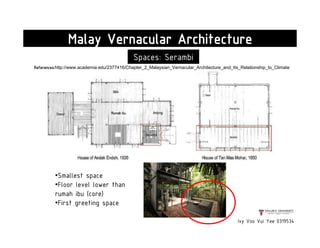
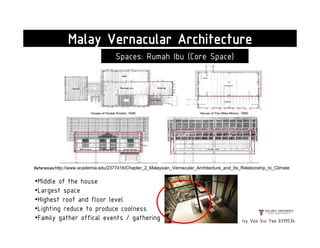
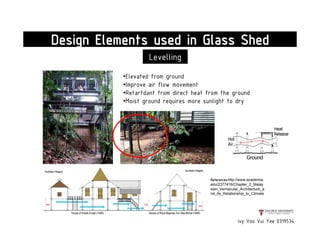
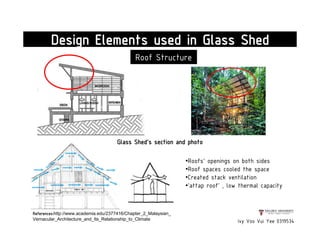
This document presents a case study on the Sekeping Serendah Glass Shed in Selangor, Malaysia. It discusses the passive design elements used to maximize thermal comfort, including natural ventilation techniques like cross ventilation and stack ventilation. Some key design elements that enhance ventilation are the building's elevated level, open wall partitions and openings, and the roof structure. Materials like steel, glass, and brick are used to allow air flow while providing shading and insulation. The design draws from principles of traditional Malay vernacular architecture and effectively combines natural ventilation with modern materials to create a thermally comfortable space.