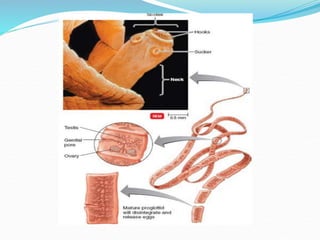
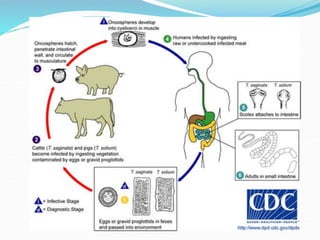
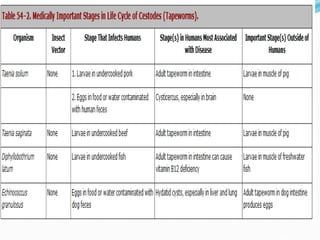
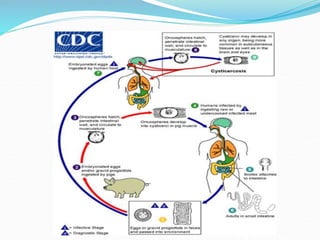
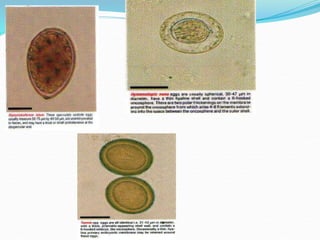
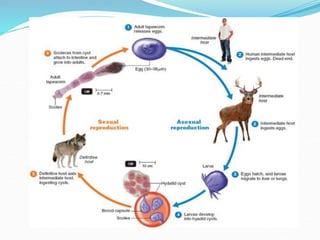
1. Taeniarichosis refers to tapeworm infections. The document discusses several tapeworm species that can infect humans including Taenia saginata, Taenia solium, Diphyllobotherium latum, Echinococcus granulosis, and Hymenolepis nana.
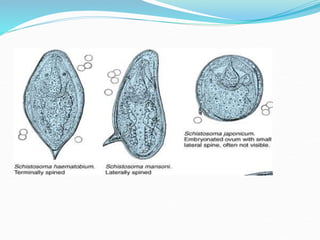
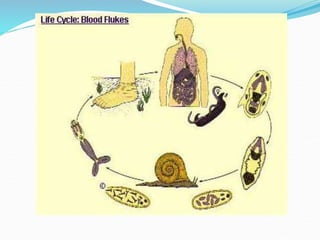
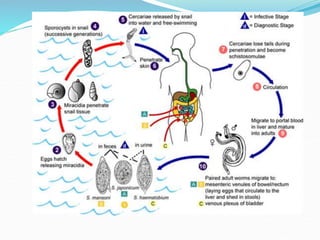
2. It also covers trematode (fluke) infections caused by parasites such as Schistosoma haematobium, Schistosoma mansoni, Schistosoma japonicum, Fasciolopsis buski, and Fasciola hepatica.
3. The life cycles of the parasites are described including the intermediate hosts involved and how humans become infected by ingesting eggs or larvae from