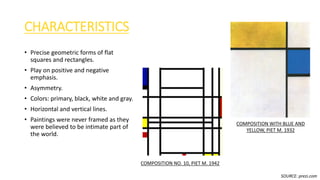
De Stijl, meaning 'the style' in Dutch, is an art movement founded in the Netherlands between 1917 and 1931 that emphasizes geometric forms, primary colors, and asymmetry to achieve harmony and order. Key figures include Theo van Doesburg, Piet Mondrian, and Gerrit Rietveld, who sought to create a utopian society through their art and design. Notable characteristics include precise geometric forms, use of primary colors, flat roofs, and a strong focus on the relationship between solid forms and negative space.