The document discusses several types of artificial neural network architectures:
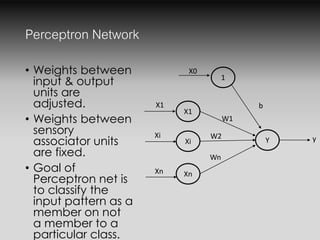
- The Perceptron network classifies inputs into categories by adjusting weights between input and output units.
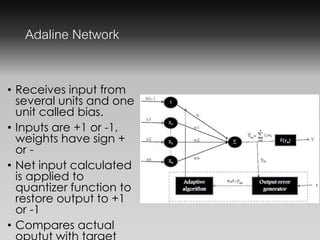
- The Adaline network receives multiple inputs and one bias input, with weights that are positive or negative. It compares actual and predicted outputs.
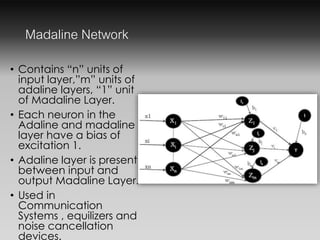
- The Madaline network contains input, Adaline, and output layers. It is used in communication systems for equalization and noise cancellation.
- The Backpropagation network is a multilayer feedforward network that calculates outputs from inputs and uses backward signals in learning.
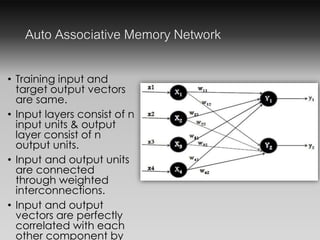
- The Autoassociative memory network trains inputs and outputs to be the same, connecting input and output layers with weights.
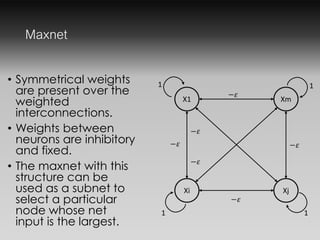
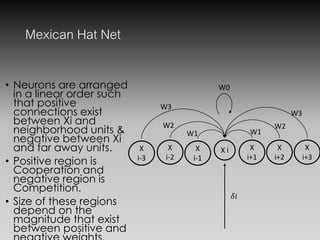
- Maxnet and