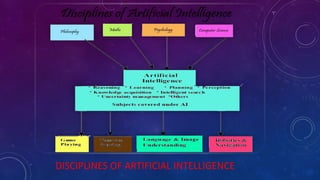
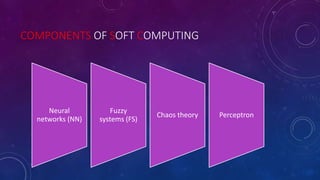
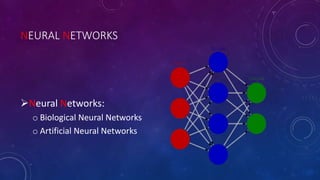
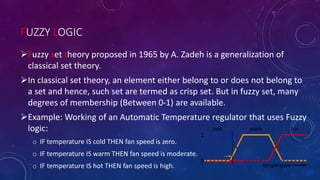
The document discusses artificial intelligence (AI) and soft computing, covering their definitions, differences from natural intelligence, history, applications, and objectives. It highlights AI's evolution since the 1940s, its interdisciplinary nature, programming languages used, and the components of soft computing, including neural networks and fuzzy logic. The conclusion raises concerns about the reliance on AI and the need for control over its growing influence in society.