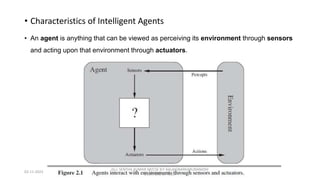
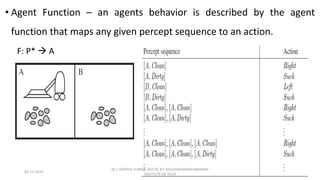
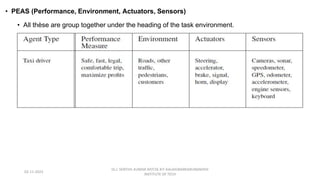
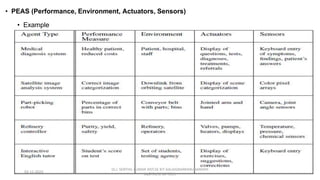
The document provides an overview of artificial intelligence (AI), discussing its definition, goals, and types of intelligent agents. It covers various approaches to understanding AI, including the Turing Test, cognitive modeling, and the rational agent approach, alongside characteristics of intelligent agents such as autonomy and adaptivity. Additionally, it outlines the future possibilities for AI technology, including applications in transportation and smart cities.