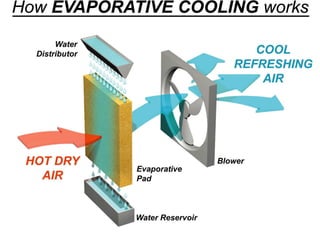
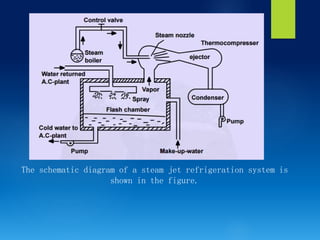
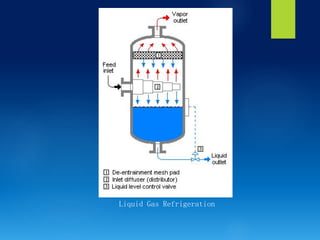
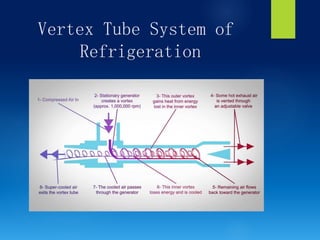
The document presents various artificial methods of refrigeration including dry ice refrigeration, evaporative refrigeration, thermo-electric refrigeration, steam jet refrigeration, liquid gas refrigeration, and vortex tube refrigeration. It describes the principles and applications of each method, highlighting key characteristics such as the sublimation of dry ice and the cooling effects of evaporation. The information is derived from a course on refrigeration and air-conditioning.