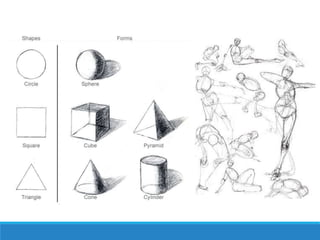
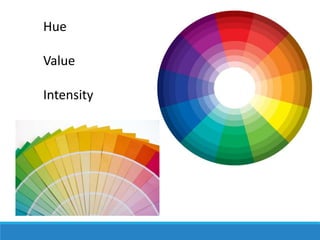
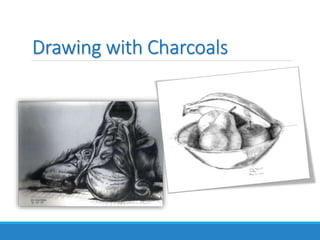
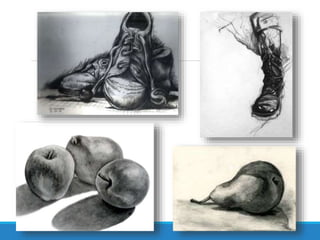
The Art Merit Badge document outlines the requirements to earn the badge, which includes defining different types of art, discussing elements of art like line and color, exploring art careers, and completing art projects in mediums such as charcoal and oil pastels. Candidates must also discuss what art means to them and how it makes them feel.