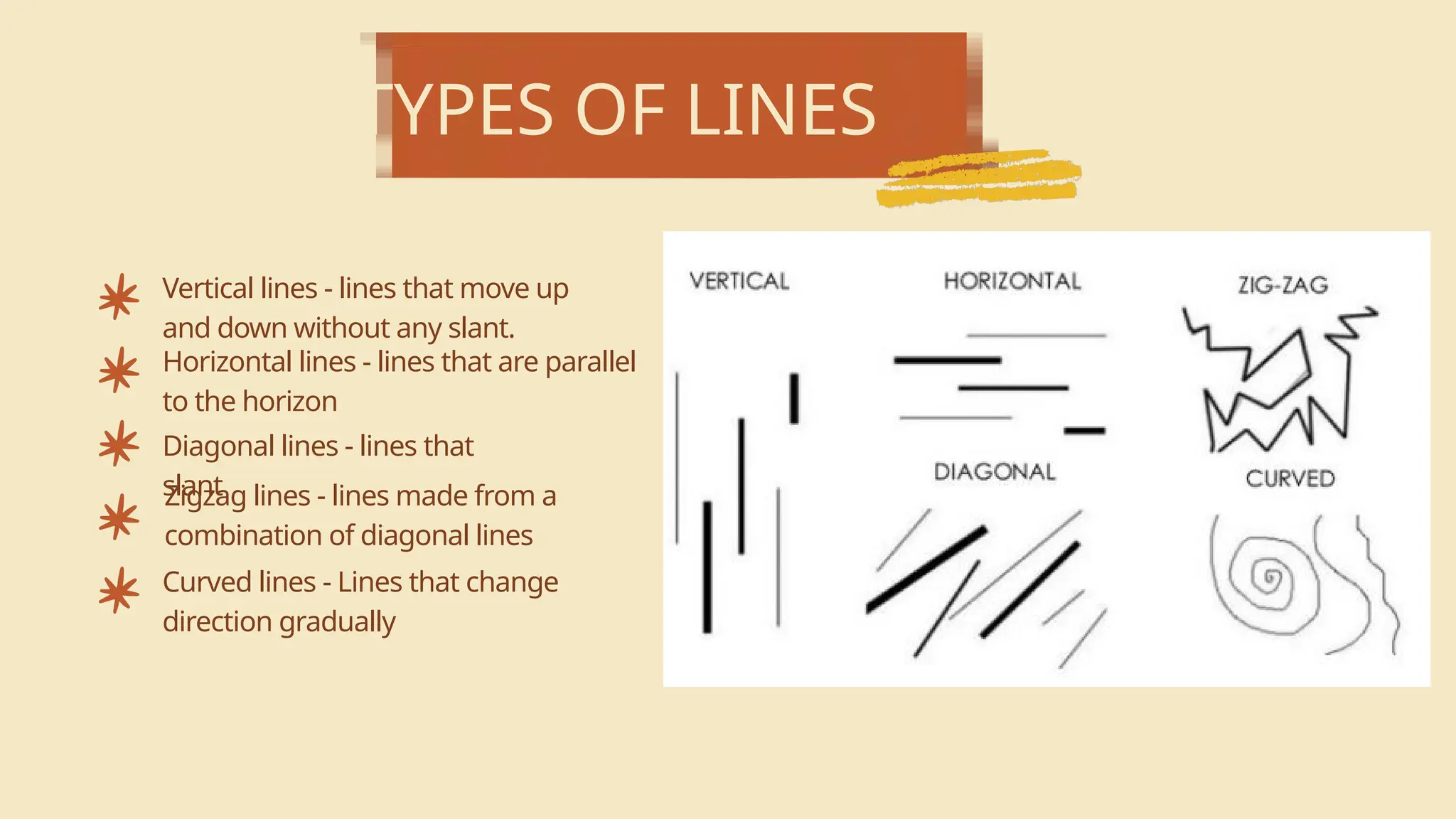
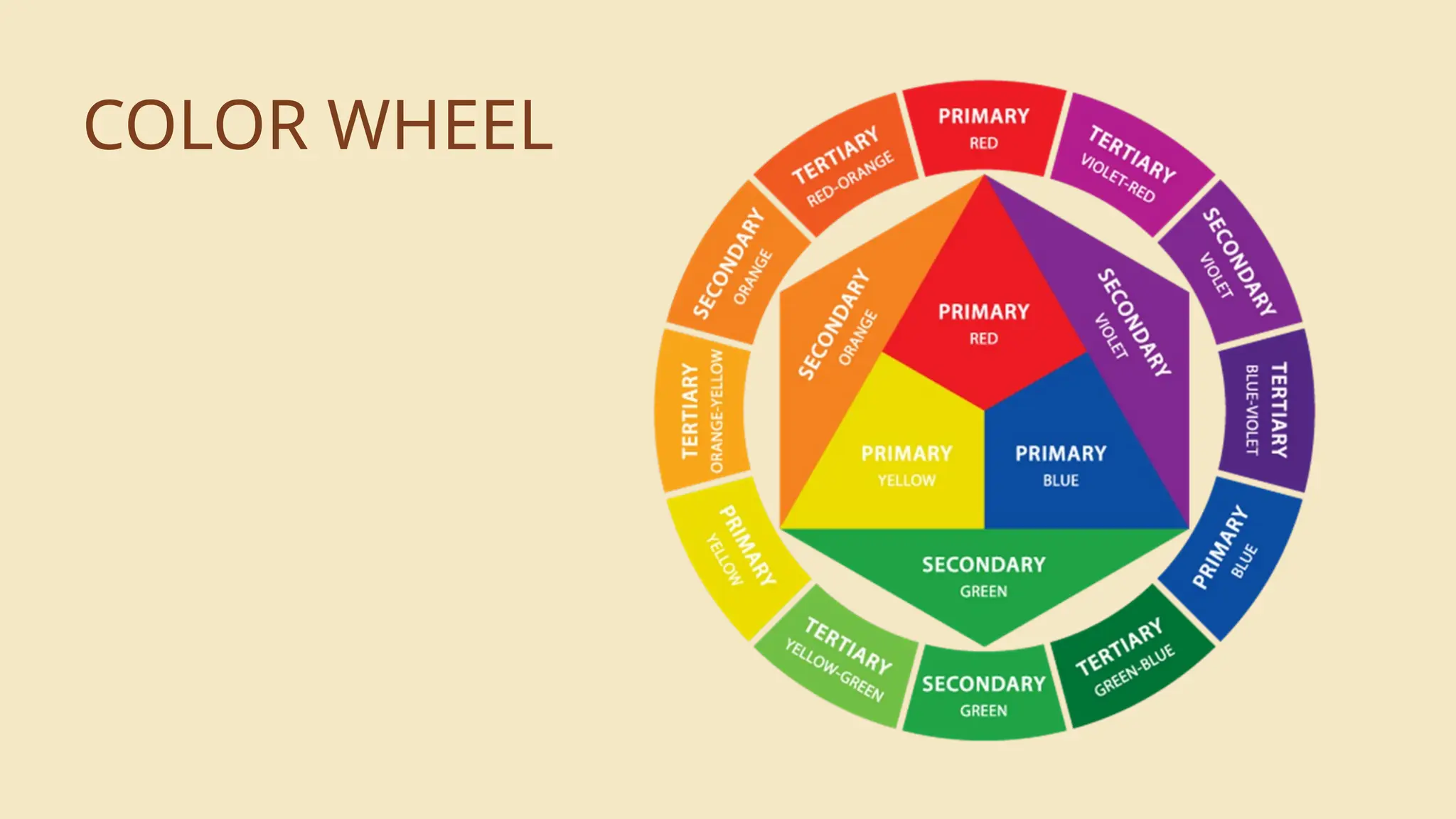
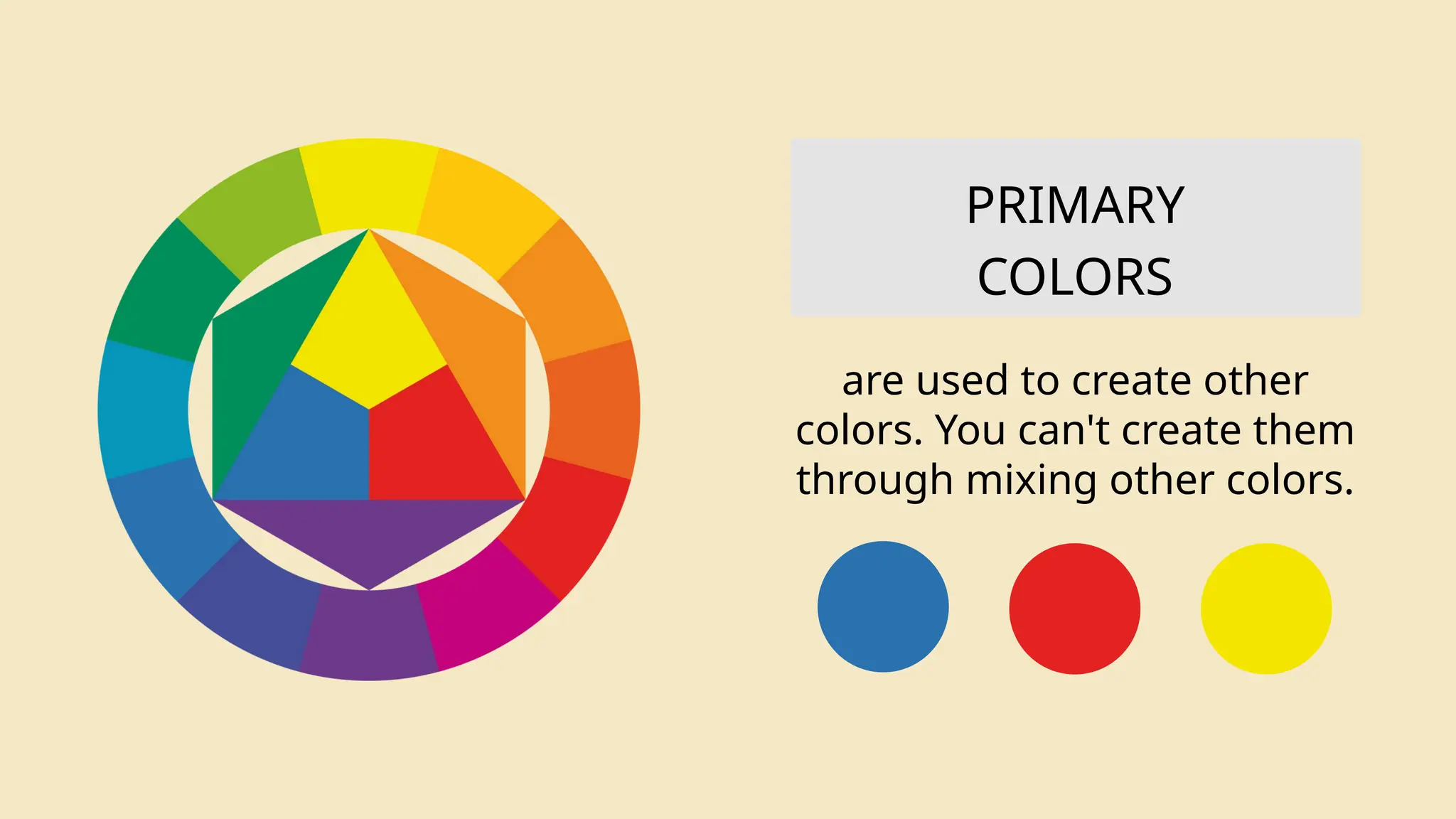
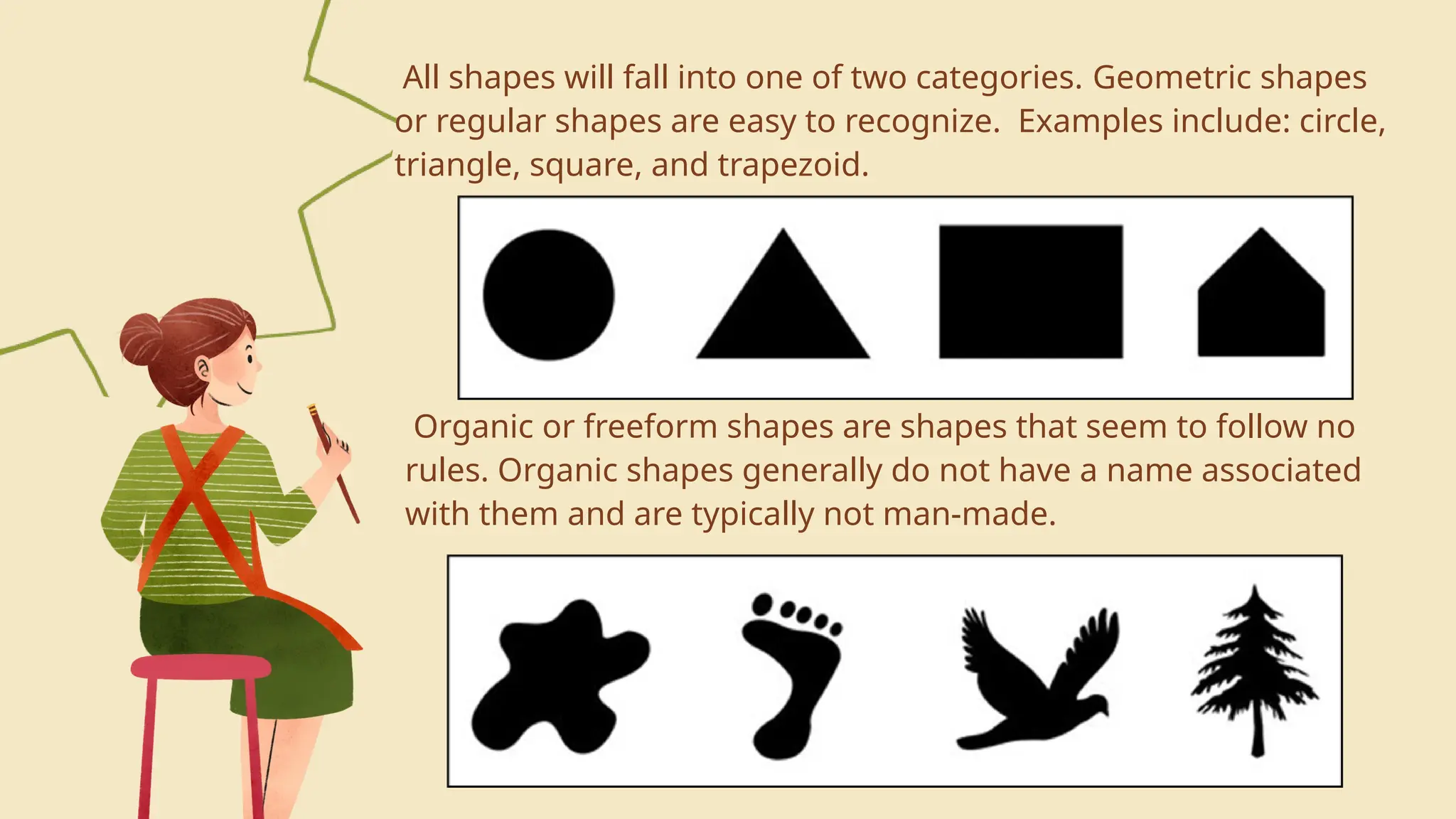
The document is an educational lesson on visual arts, outlining objectives such as identifying various forms and elements of art, defining visual art, and appreciating its production. It emphasizes the significance of art as a form of communication and details the seven elements of visual art: line, color, shape, texture, form, value, and space. The lesson aims to provide students with an understanding of both the technical aspects and the emotional expression involved in creating visual artwork.