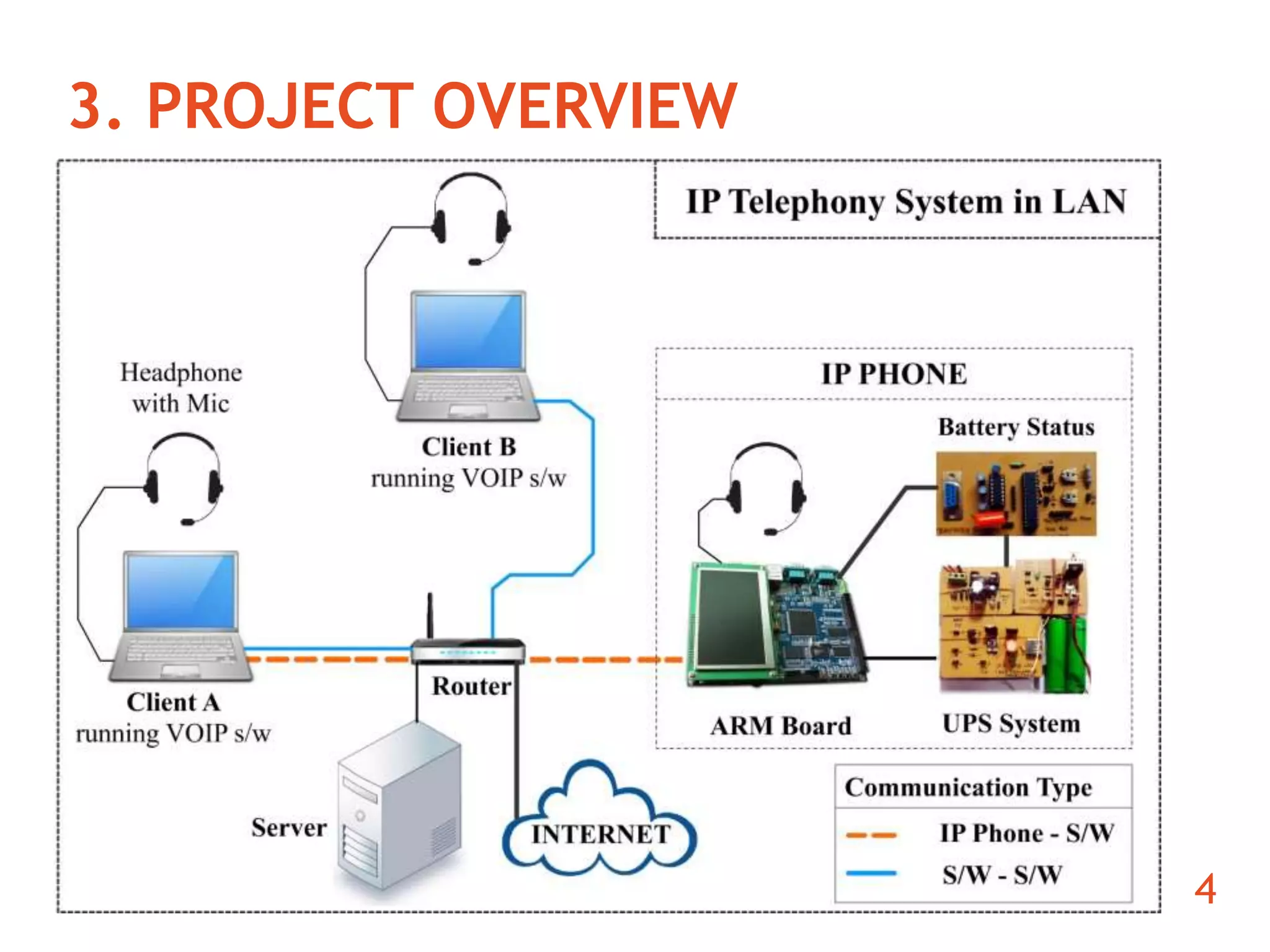
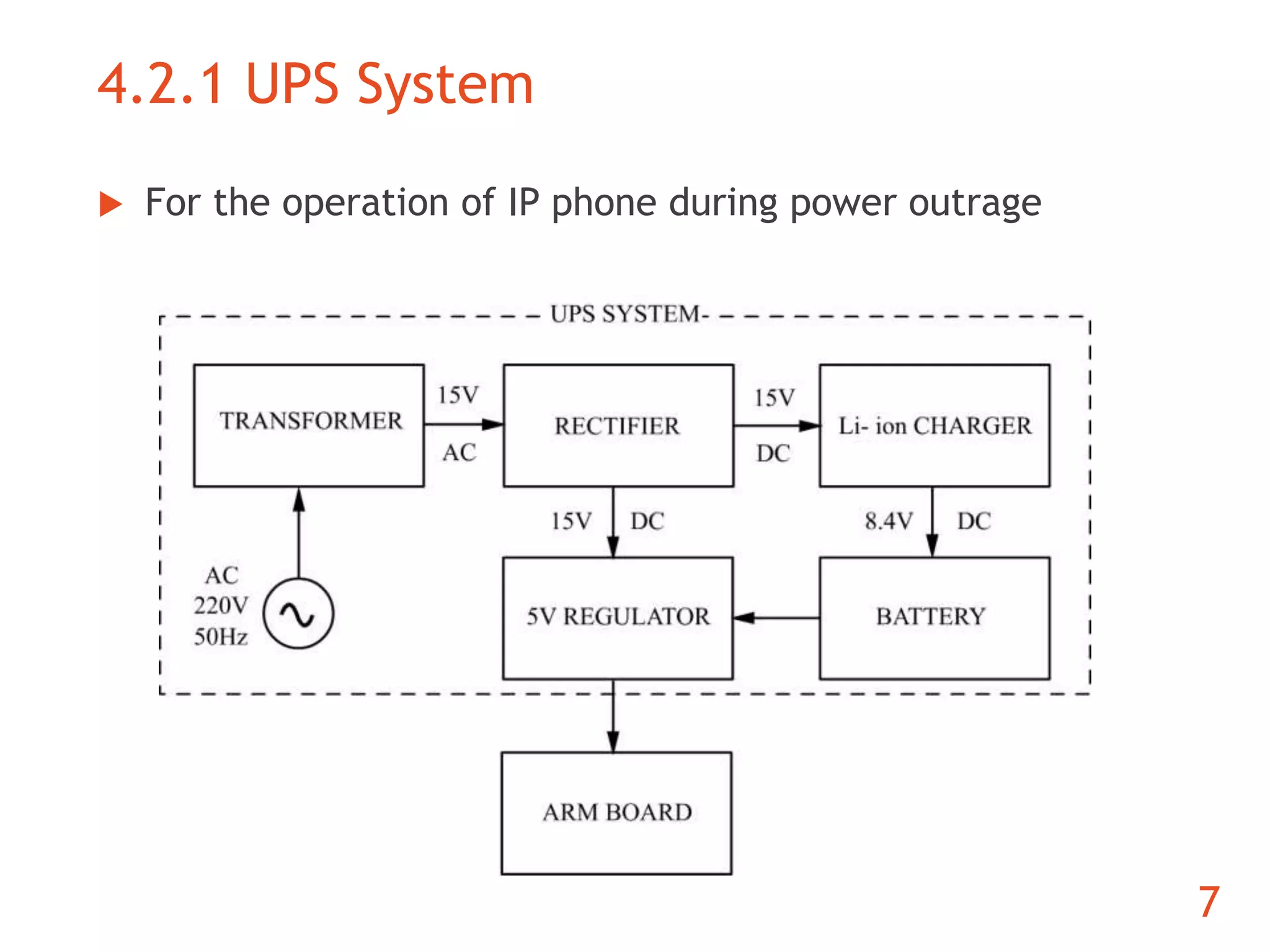
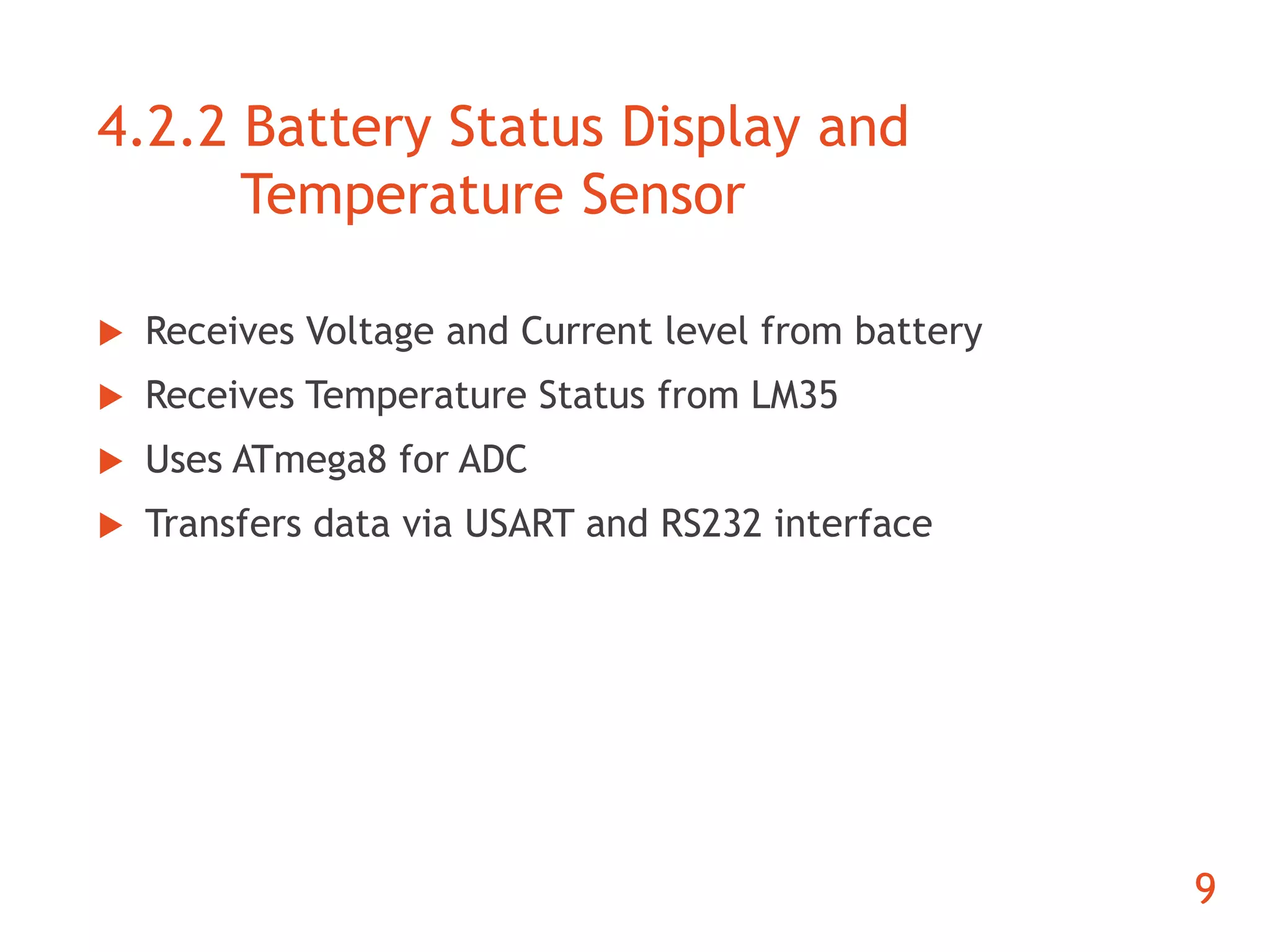
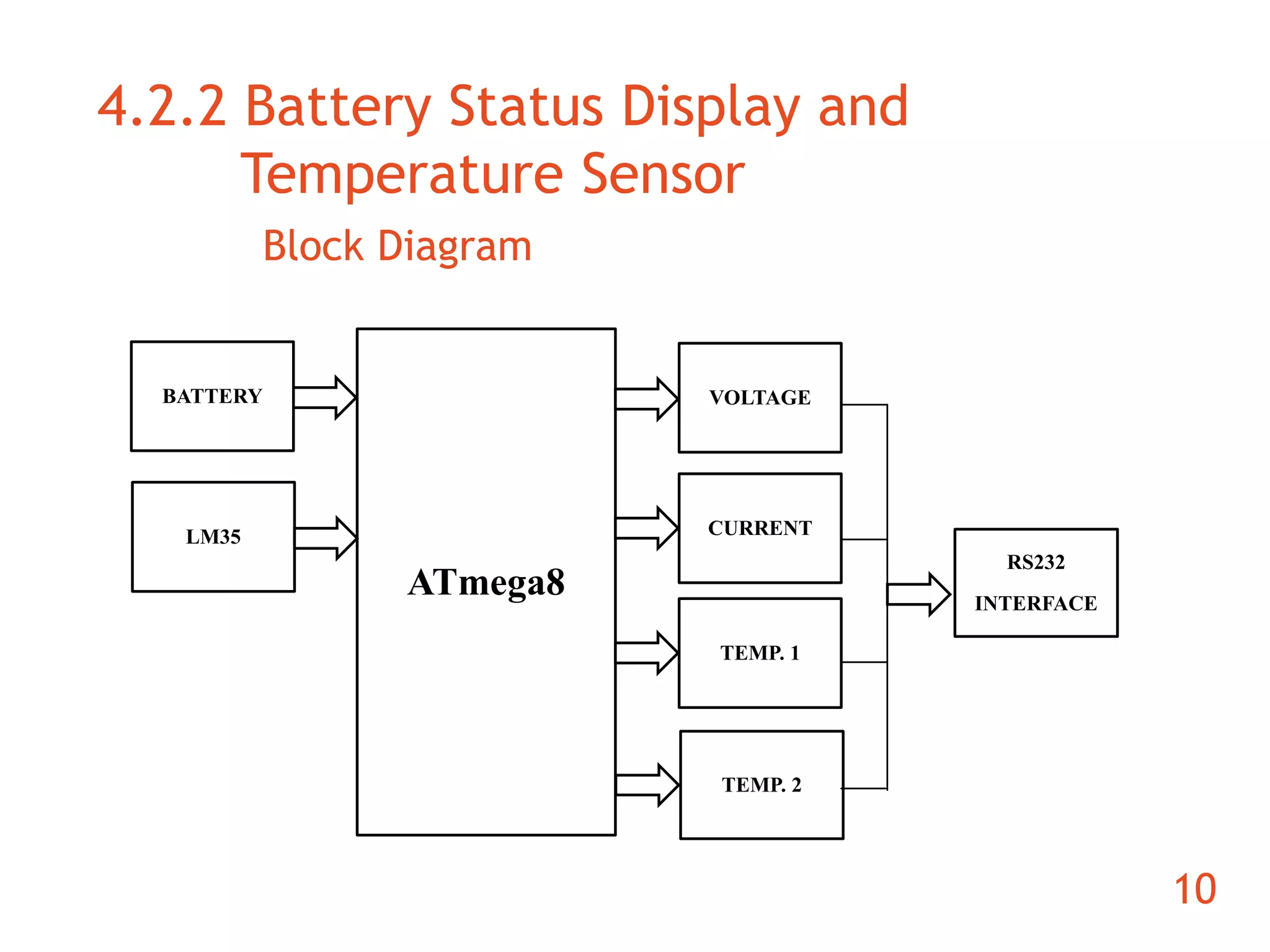
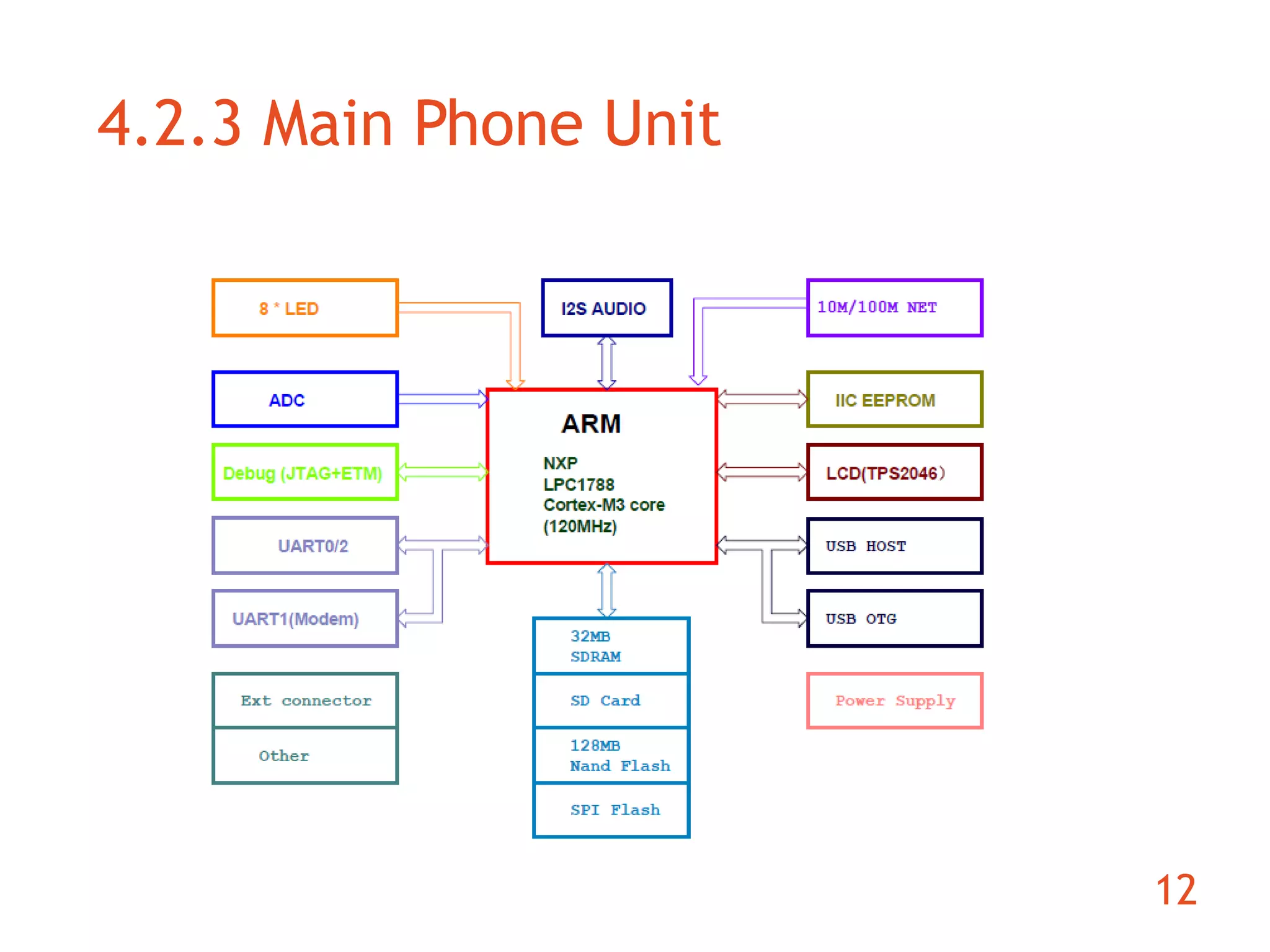
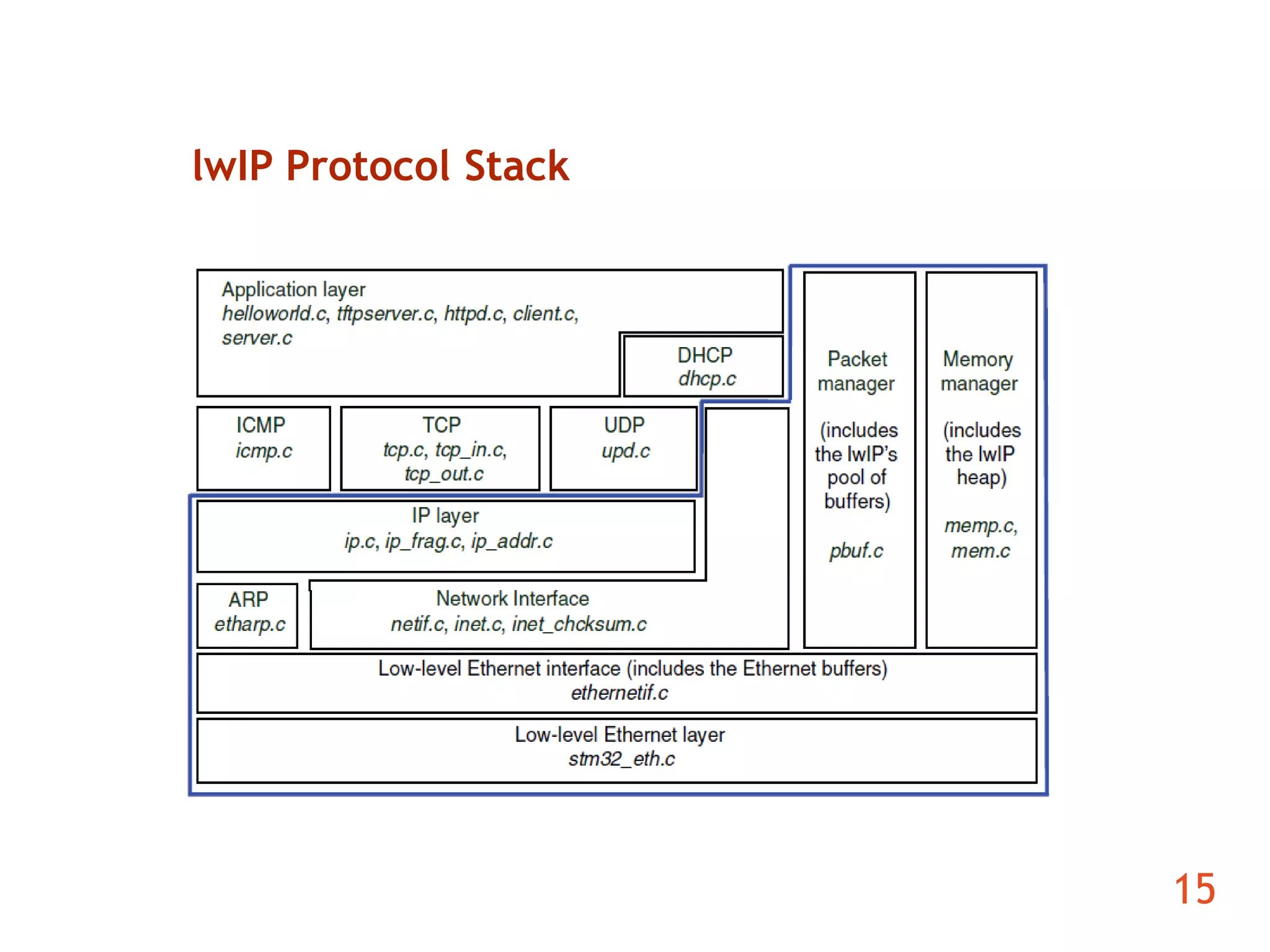
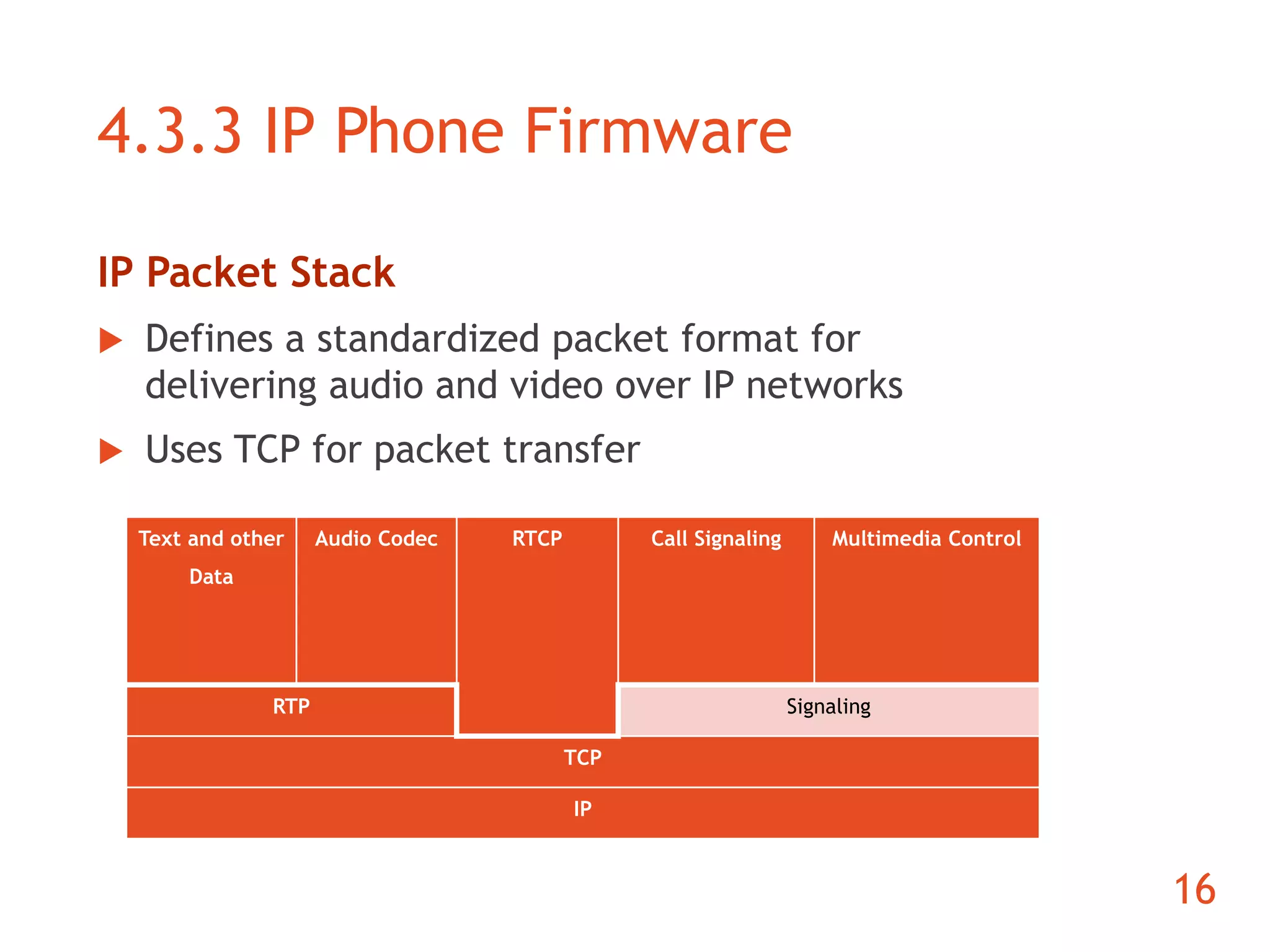
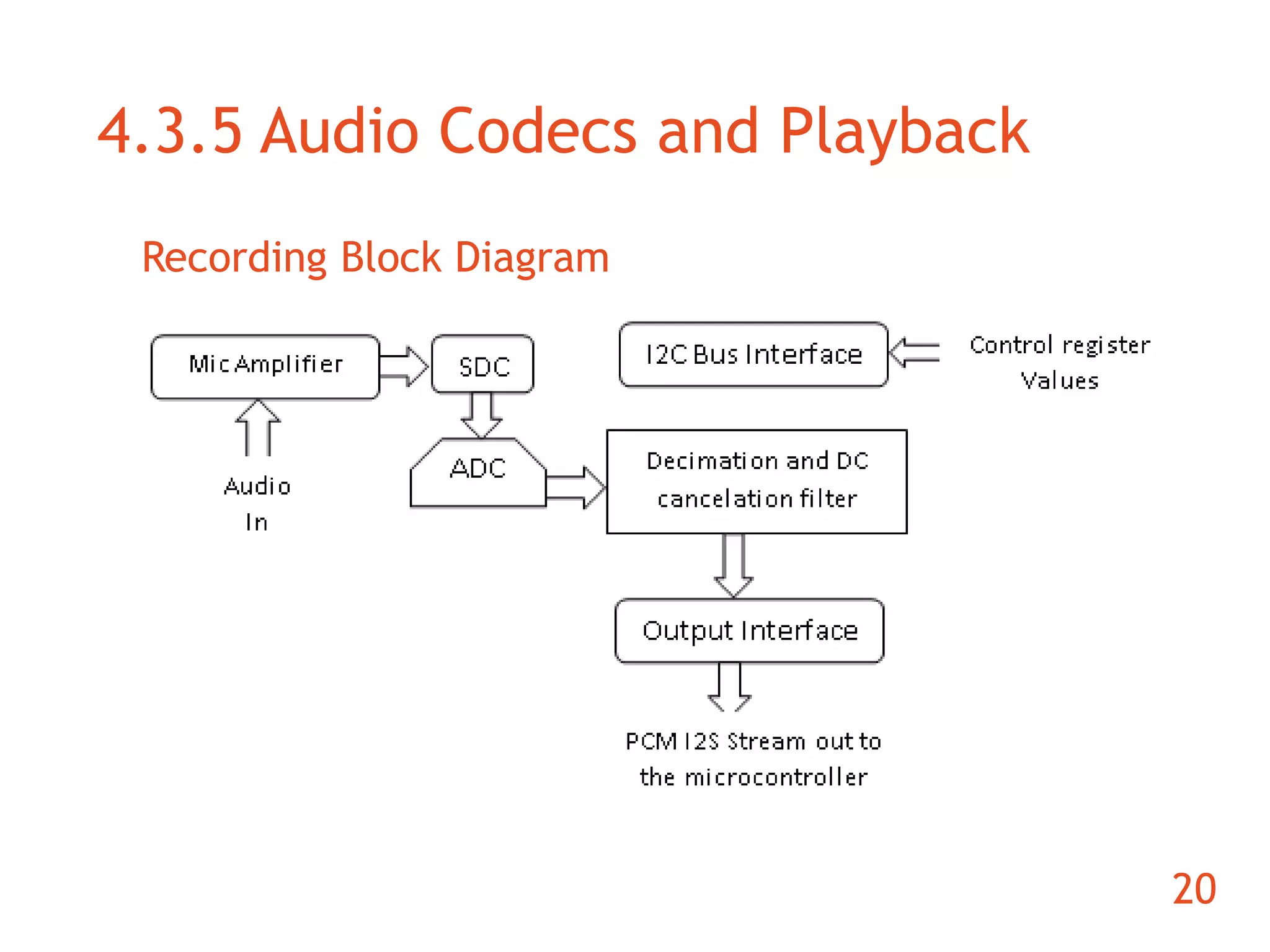
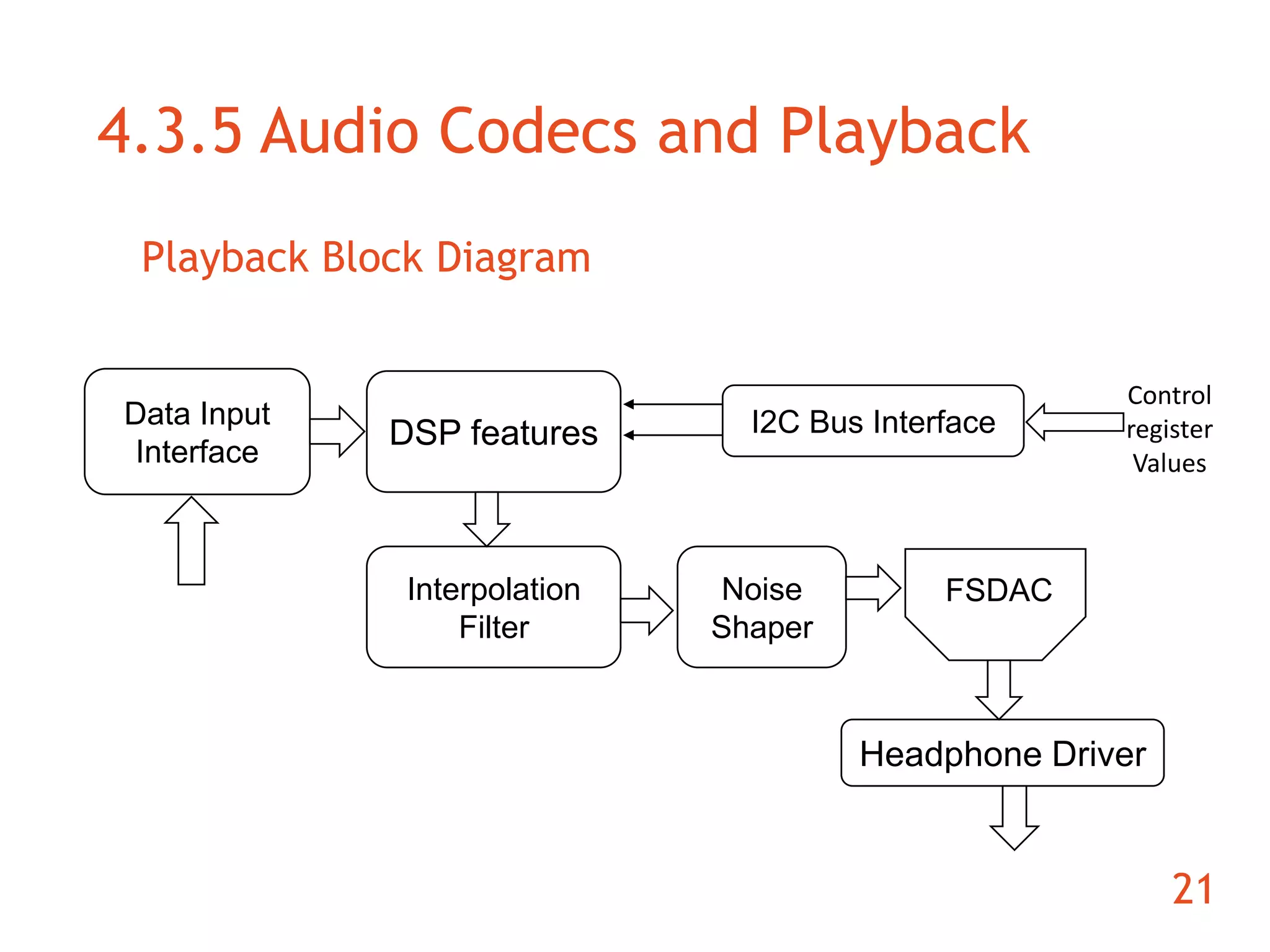
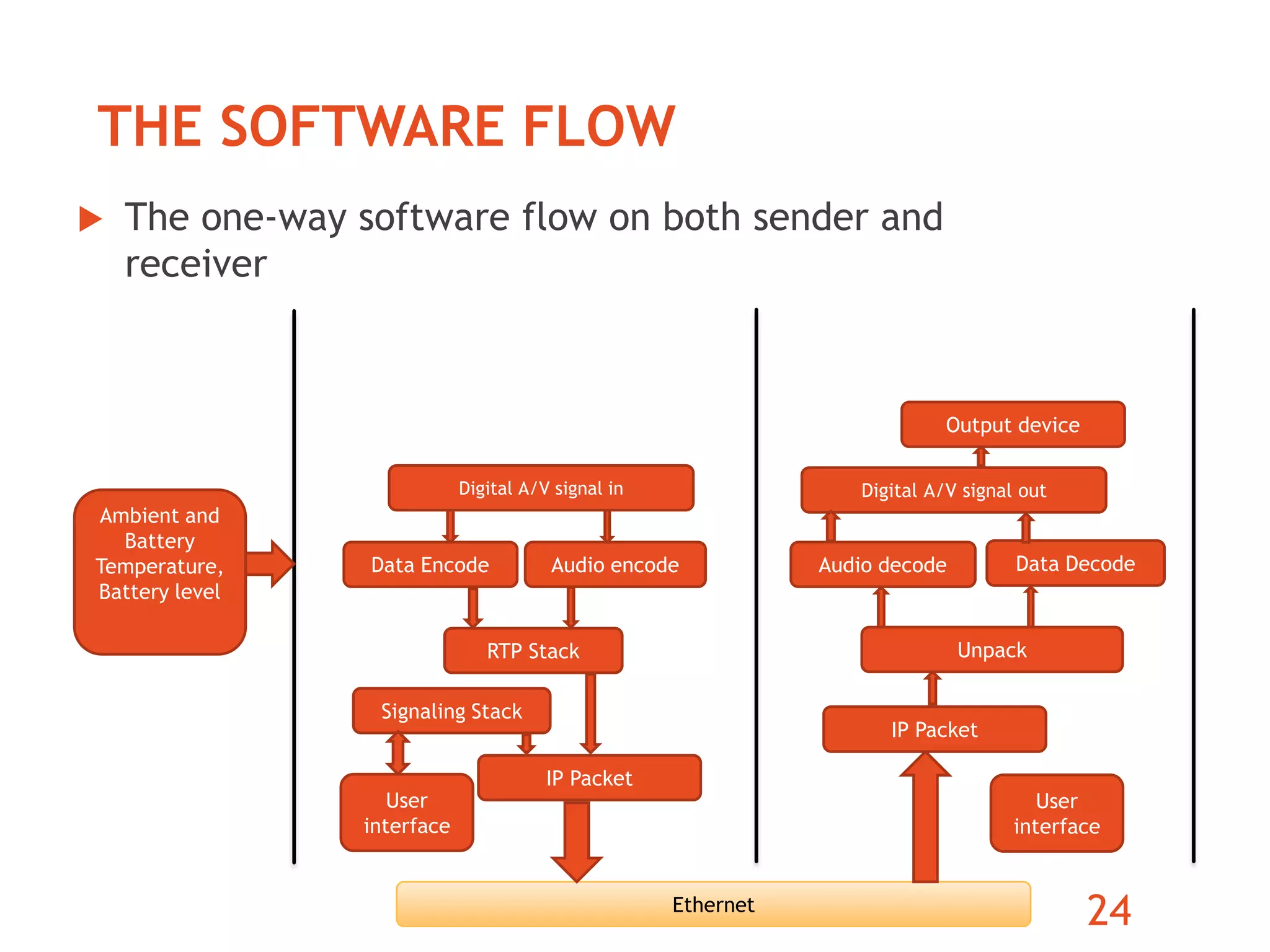
The document discusses the development of an ARM-based multimedia IP telephone designed to implement VoIP technology for LAN communication. It outlines the project objectives, hardware components, firmware specifications, and the functionalities of the device such as networking protocols and user interface. Limitations include challenges in video communication and scheduling due to the absence of a separate operating system.