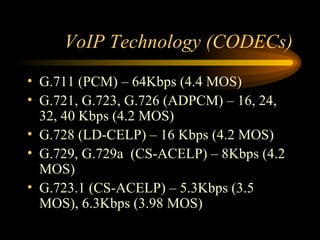
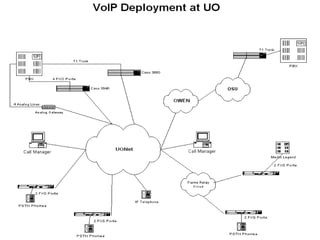
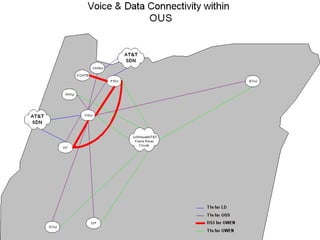
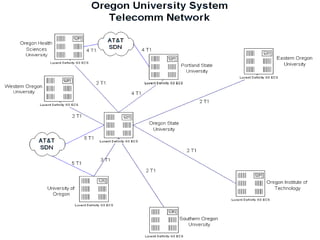
The document discusses VoIP technology developments. It describes several uses for VoIP including voice trunk replacement and end-user appliances. It also outlines common VoIP elements like switching devices, end-user devices, and access gateways. Additionally, it covers VoIP technologies including codecs, delays, call setup standards, quality of service methods, and concerns to be addressed regarding VoIP services.
![VoIP Technology Developments [email_address] Co-leaders: José A. Domínguez (University of Oregon) [email_address] http://ns.uoregon.edu/~jad/Net@EDU/](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/voip-technology-developments-netedu4405/75/VoIP-Technology-Developments-Net-EDU-1-2048.jpg)









![Tracking Technology Changes Mailing Lists IETF’s IP Telephony WG ( [email_address] ) IETF’s PSTN & Internet Internetworking WG ( [email_address] ) IETF’s Media Gateway Control WG ( [email_address] ) Session Initiation Protocol WG ( [email_address] ) Other IETF WGs (SPIRITS, ENUM, RSVP, DIFFSERV, AVT, INTSERV) Computer Telephony Newsletter ( [email_address] )](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/voip-technology-developments-netedu4405/85/VoIP-Technology-Developments-Net-EDU-15-320.jpg)


