Embed presentation
Downloaded 13 times
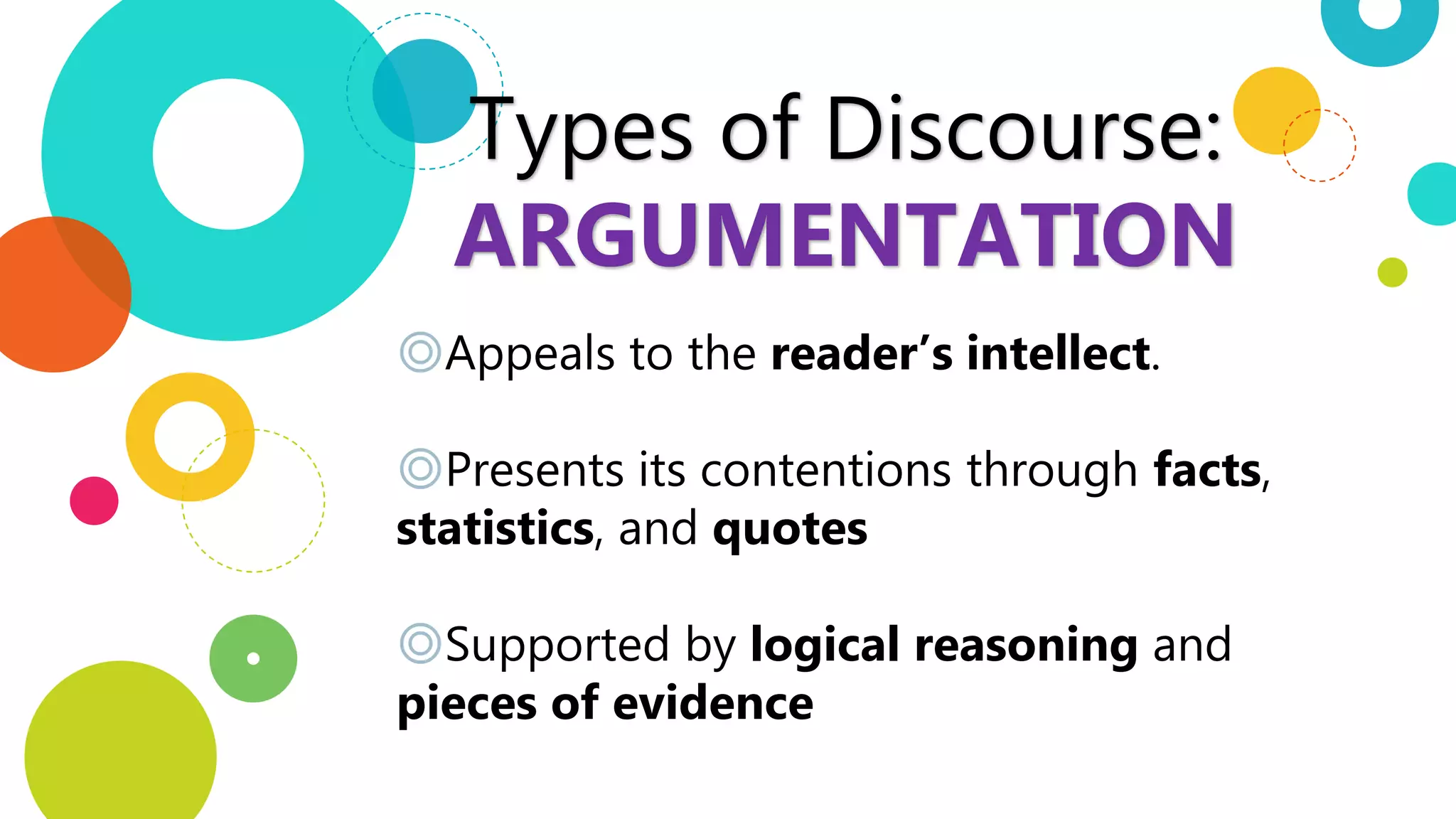
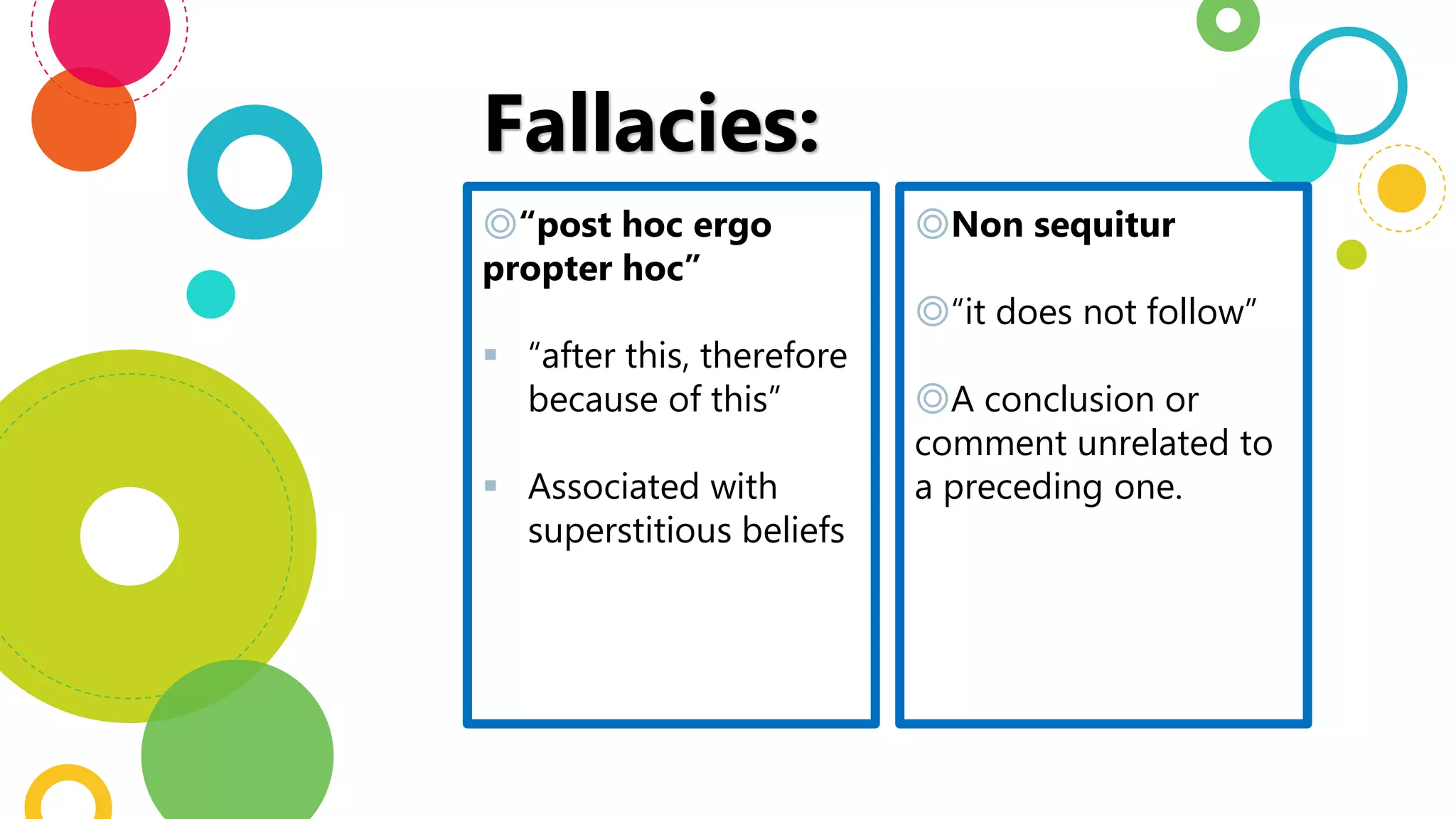


This document discusses argumentation as a type of discourse that appeals to the reader's intellect through facts, statistics, quotes, and logical reasoning to support its contentions. It also outlines several common fallacies to avoid in argumentation, including post hoc ergo propter hoc, which assumes causation without evidence; non sequitur, where a conclusion does not follow from what came before; overgeneralization, making broad claims without sufficient data; and ad hominem arguments, which attack the person rather than the issue being discussed.


