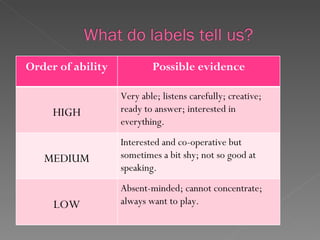
This document discusses strategies for teaching mixed-ability classes, including differentiating instruction, peer tutoring, grouping students, and having high expectations. It emphasizes treating students as individuals, teaching core content to all while providing reinforcement or extension work as needed. Partnering stronger and weaker students is presented as an option if the roles and goals of helping are made clear.