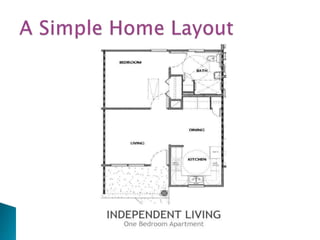
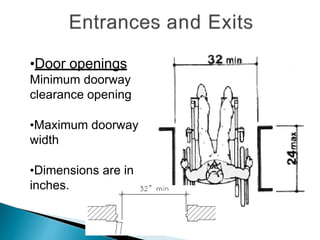
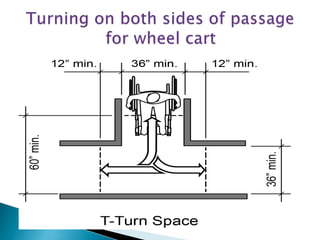
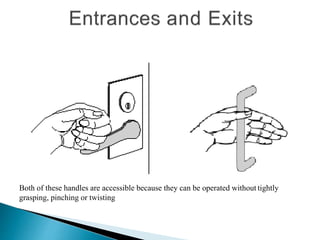
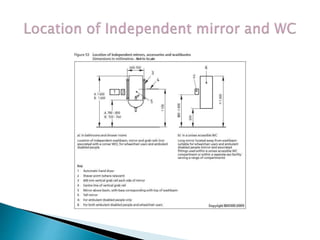
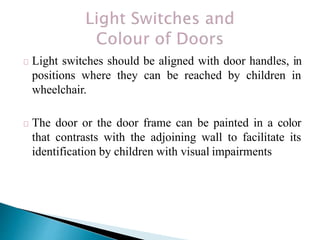
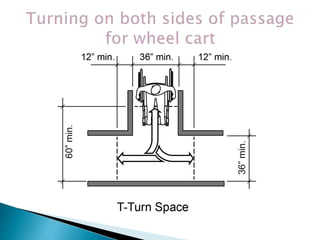
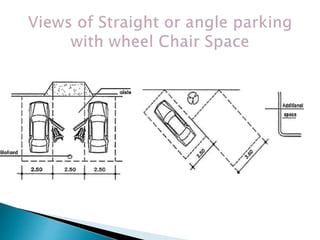
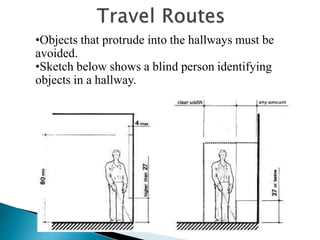
Over a billion people with disabilities encounter barriers that hinder their equal participation in society, impacting access to education, employment, and healthcare. Design solutions must consider the unique needs of disabled individuals, advocating for accessible architecture and environments, including adaptive features in homes and public spaces. Effective design not only enhances mobility and safety but also empowers disabled children, promoting their independence and dignity.