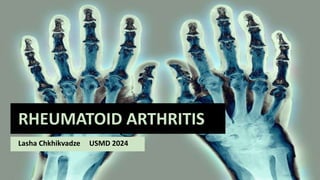
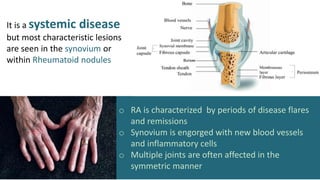
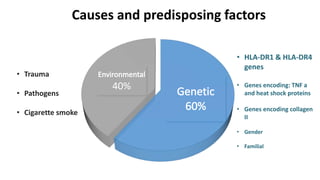
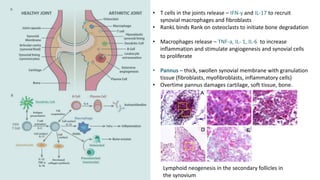
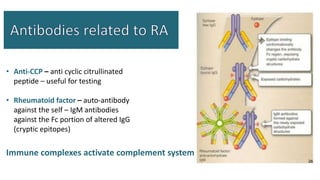
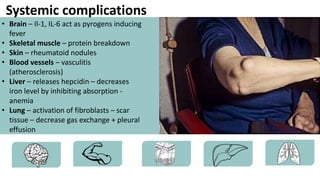
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disease characterized by joint inflammation and systemic symptoms. It affects around 1-3% of the population, occurring more frequently in women between ages 30-50. RA causes periods of disease flares and remissions. The synovium becomes engorged with new blood vessels and inflammatory cells. Genetic and environmental factors may contribute to disease development. Diagnosis involves assessing symptoms of joint pain and stiffness as well as blood tests for rheumatoid factor and anti-CCP antibodies. Treatment includes NSAIDs, corticosteroids, disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs), and biologic medications to reduce inflammation and prevent further joint damage.